Question slides
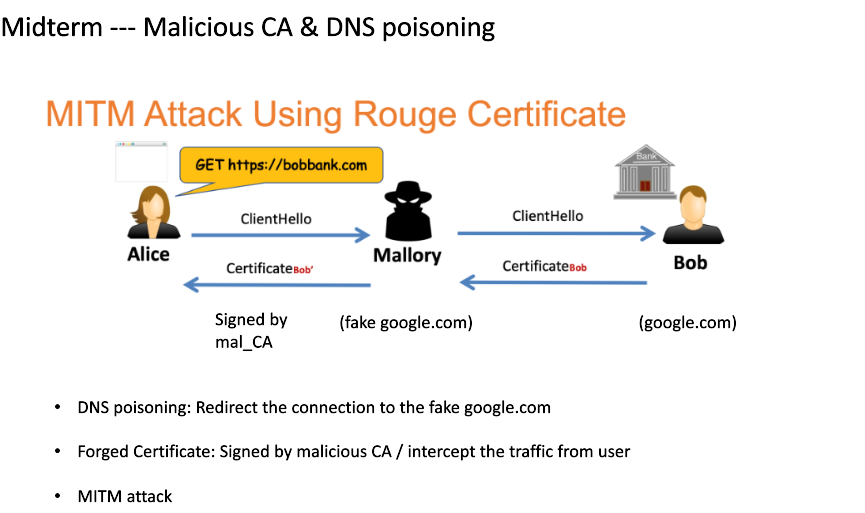
Malicious CA and DNS poisoning
Standard MITM Attack. The attacker should redirect the connection to desired website to attacker fake website. TO impersonate a fake website. The forge certificate, since the malicious cert has been trusted, it has been signed by the malicious. The attacker can see the traffic between the user. It can also establish another secure channel to transfer the infomation to the real google and get the response.
Third party Cookie
(Answering how it works) For each time the certain resource has been requested, the A.com would generate cookies. There are other explaination that is accepted as long as its reasonable. Attacks such as CSRF to inject cookies is not a reason.
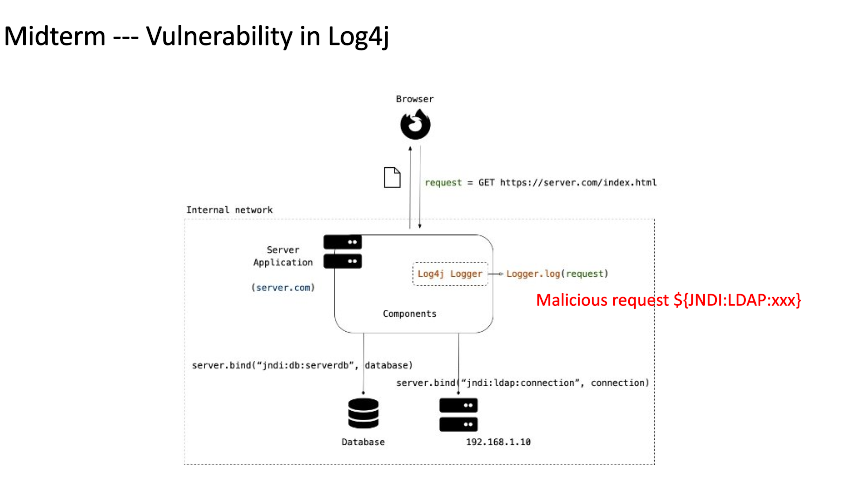
Log4J
Since the assumption is that the log4j can parse the request, it can look up certain resource. Based on the idea of remote file inclusion, our attacker can include malcious string such as JNDI that would be parse and executed. It could look up certain resources using the privlege of the server.
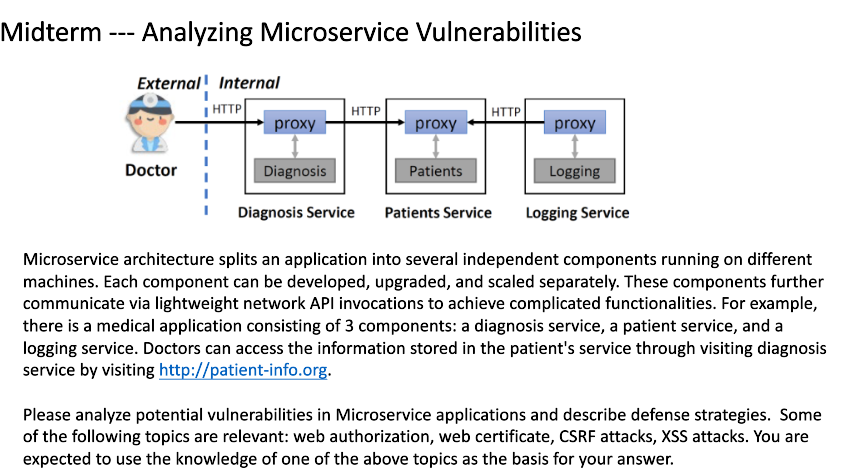
Microservice Vulnerability
Given the microservice, find some vulnerabilities
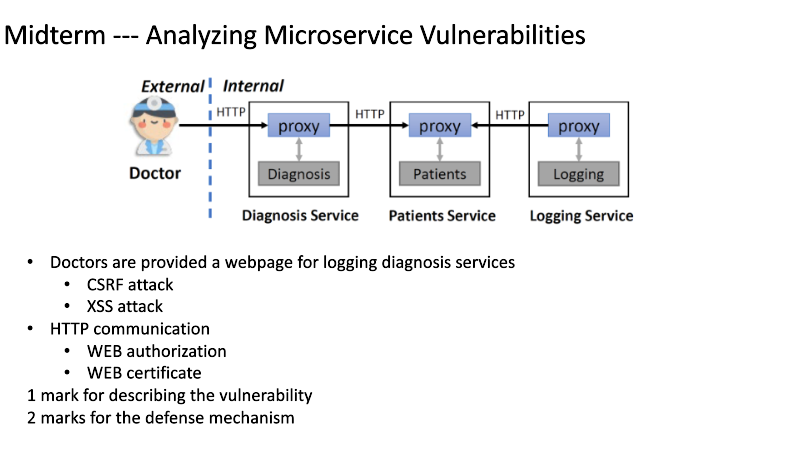
If the doctor wants to access a patient service, it would go through the diagnosis service.
- Web authentication: Attacker can do some attack to find information when the service communcation
- Defence: Https instead of http
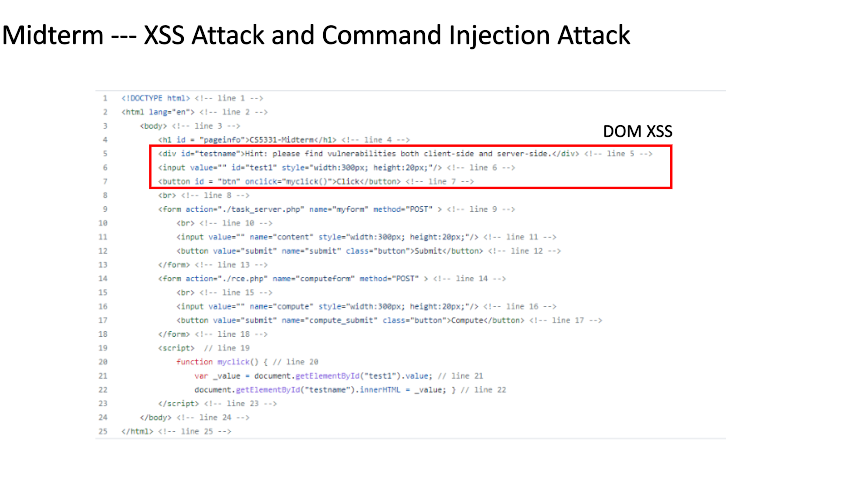
XSS attack and Command injection attack.
Given the code, identify the vulnerability
Dom base XSS
If the user click the buytton, it would call the js function. It would read the text1 box. If you replace the content in the text1, the attacker can input anything they want and it would not be filtered in line 22.
(Server side) Reflected XSS and Command Injection attack
There is some filter done that remove some strings. But then the it only filters words such as script. Which is still vuln For command injection, it just read the post parameter and put it under the eval. The attacker can use this to retrieve files from the server.
Some possible payload includes:
- Using
imgtag - Using
bodytag