Threat Model
- Desired Security property/ Goal
- Attacker capabilities
- Assumption about the setup
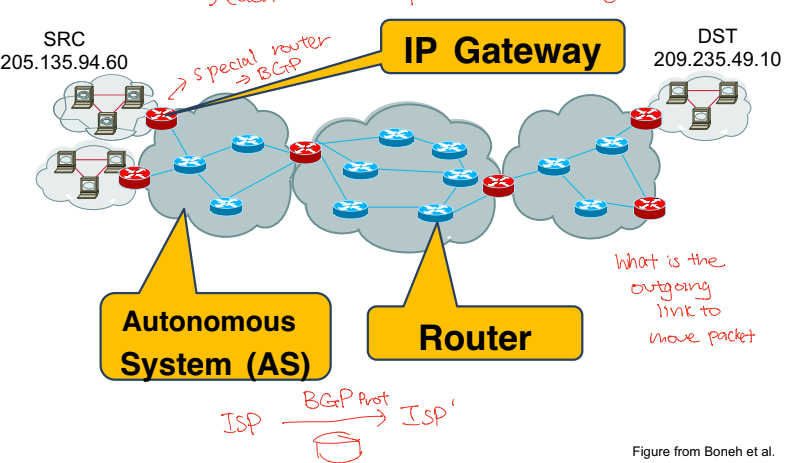
How the internet works
- Collection of subnetworks
- Each sits on ISP (Autonoumous system)
ISP
- Special router
- Runs on BGP
What is the outgoing link to move packet
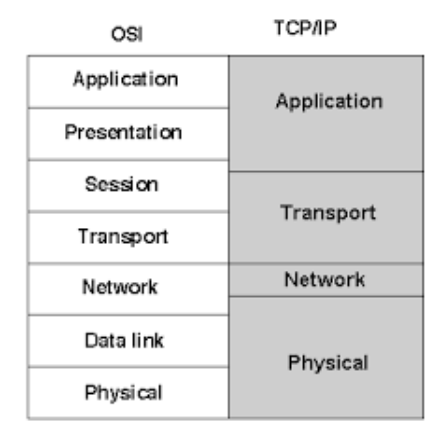
BGP (TCP/IP: Physical layer)
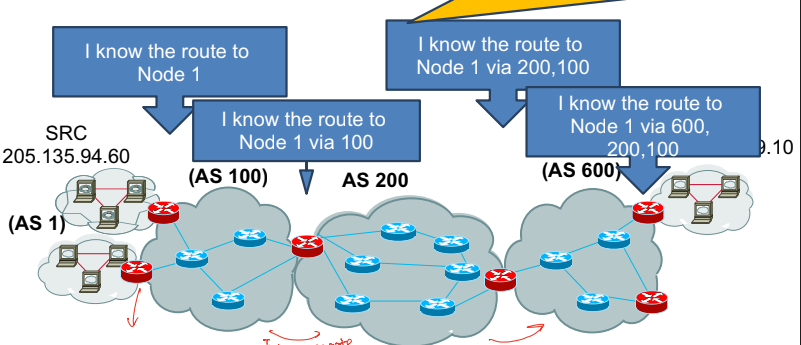
- NLRI Update: Network Layer reachability infoamtion
Announce to the world that it knows the gateway info. The info will then propagate from AS to AS
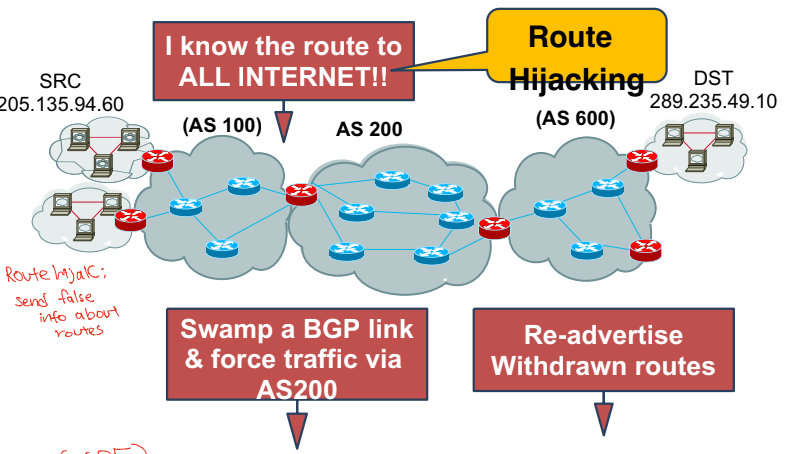
Route Hijacking
- Send false info about routes
- Swamp the BGP link & force traffic
- Readvertise withdrawn routes
IP (Physical: Network layer)
- UDP: Unreliable
- TCP: Reliable - Ensures that the packet reaches
Attacks
- Confidentiality: Location
- Packet Sniffing
- Integrity: Modifying
- IP Data Pollution
- Source IP forgery e.g Slammer worm
Smurf attack
- Amplify DDOS
- Working:
- Attacker ICMP packet with the victim IP as its DST
- Broadcast to all the network
- VIctim would then recieve a flood of echo results from other computers
- DDOS
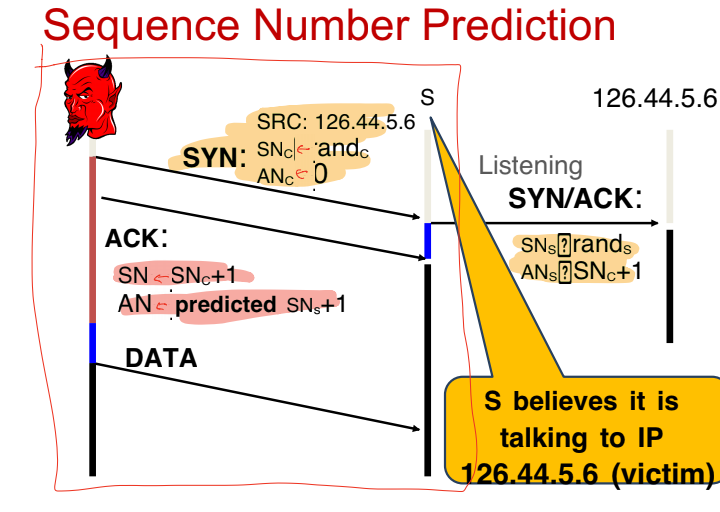
A classic attack on TCP
- BUG: Random Value is not random, thus it is predicable by anyone
- The attack works by : The network thought they are talking to A but infact is not A but imposter
- Authencity
- A sends SYN/ACK to B
- C hears this and replies with a predicted ACK
- A assumes C is B and connect to it
- This is due to IP authentication (WEAK)
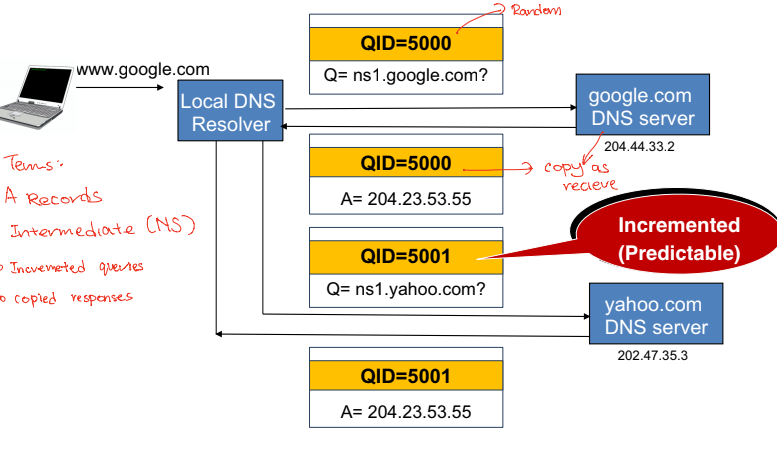
DNS Attacks
DNS is a sequence of queries to resolve
Remember recursive DNS: One local DNS resolver will search up answers by querying servers starting from root
Attack
Terms:
- A records (Authoritative)
- Intermediate records (NS)
- Incremeted queries
- Copied responses
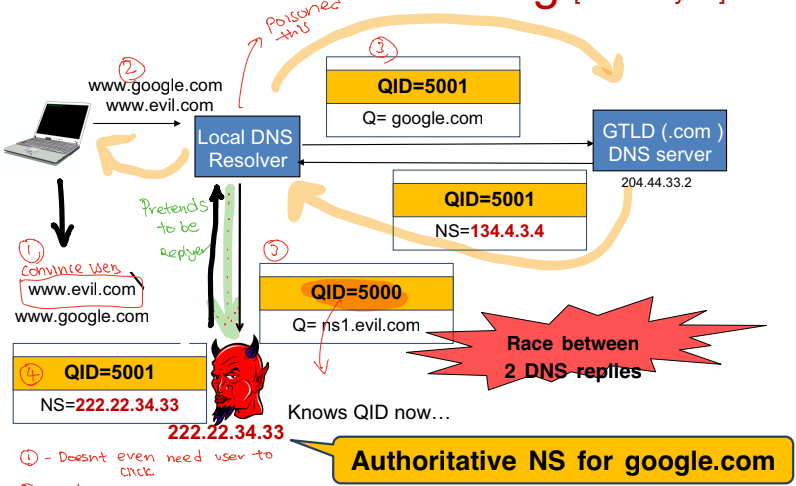
The attack can carry out because the queries number which the DNS resolver relied on to identify the query session can be easily predictable (Incremented)
- Victim DNS query to resolver for google and some evil website A
- The victim doesnt need to click on the evil website
- DNS tries to resolve
- Evil website gets query request and predicted that google’s dns reply is an incremement/decrememnt and respond to the resolver with the fake query id
- DNS thought that evil website dns server is google and set it as such
- End result: Race between 2 DNS replies, evil server become authoritative NS for google.com
This is also known as cache poisoning
Firewalls
- Control the flow of traffic
- Look at services, address, data etc
- Packet can be allowed or dropped based on policy
- Operate at TCP.IP Level
Design pricipal: Default fail-close policy - Deny on default
Stateless are fast but are limited in filtering because they do not store memory of the past packets, thus they are unable to look at a sequence of packets coming in (TCP) and decide base on them.
Thus there are stateful packet filters which maintain the memory.
Threat model (Weak)
- Weak adversary
- Reactive
- Defender needs to know specific attack patterns
- Easy to violate the assumptions
- Attacker can change attack details to make it harder to keep track (Evade)
- Violate assumption
- Bring your own device > malicious software in device > pass in virus into uninfected network
- Filtering base on content might be hard due to encryption (HTTPS/TLS)
- Hard to simulate the end device since there are multiple types of end devices in market