Background
Overview:
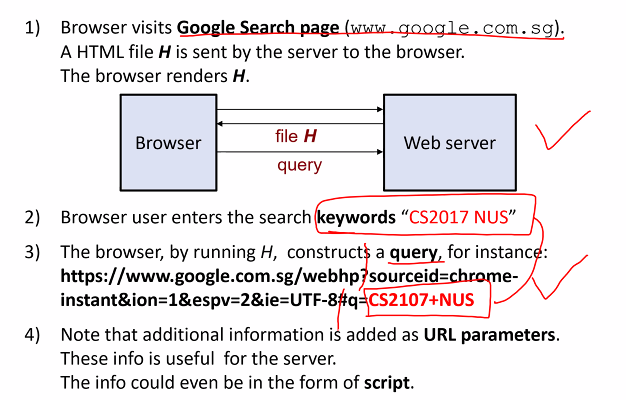
- User click on url link
- Http request is sent to server
- Server construct and include a html file inside its HTTP response to the browser (Possibly with set cookie headers)
- Browser renders the html files, which describe the layout to be rendered and presented to the user and any cookies are stored in the browser
Sub-resource of a webpage
- Contain subresoources (Images, multimedia files, css, scripts) including from external party
- Browser will contact the respective server for the resources
- Seperate http request for every singe file on a page
Request and Response format
Web client and server components
- Client:
- HTML: Webpage content
- CCS: Webpage presentation
- JS: Webpage behavior, making pages responsive and interactive
- Server:
- Web server: Scripting language is typically use as well
- Database server: Interaction between webserver and database server via sql
What javascipt can do
- Write text into page
- Read and change html elements
- React to events, such as when a page has finished loading or when user clicks on an HTML element
- Validate user data
- Access cookies
- Interact with the server
Security issues and threat models
Complications
Browser Operation:
- Browser run with same prev as user: Browser can access user files
- Multiple server could provide the content: Access isolation among sites is requried
- Browser support rich command set and controls for content providers to render the content
- For enhance funcitionality many browser support plugins, add-ons extensiion by third party
Browser usage:
- User info and secrets
- User could update content in the server:
- Forum social media sites where names are to be displayed
- More and more iusers sensitive data is stored in the web cloud
- For PC, the browser is becoming the main/super applicaation, in some sense the browser is the OS
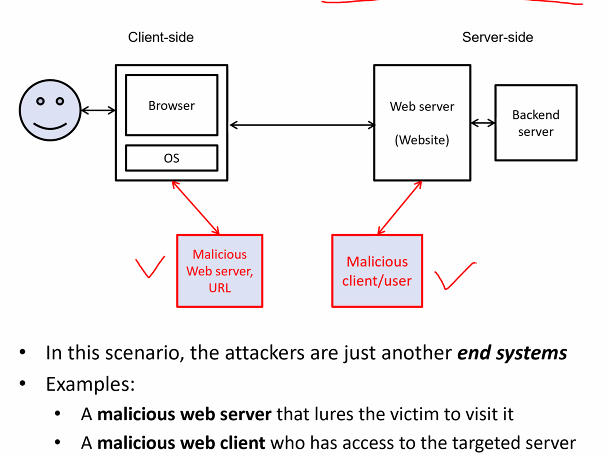
Attackers on another end system
- 1A forum poster
- Weakest
- User of existing app
- Does not register domain
- 1B Web attacker
- Oqwns valid domain and server with ssl cert
- can entice victim to visit site
- Can not intercept/read traffic for other sites
- most commonly assumed attacker type
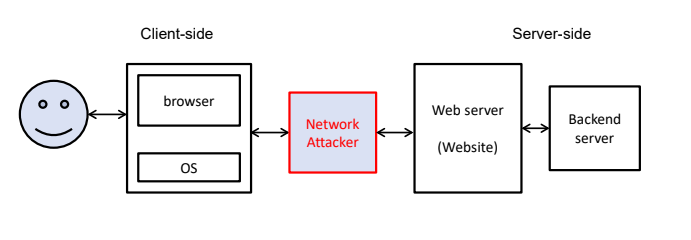
Attacker as network attackers
- 2A: Passive network attacker:
- Eve who can passively eavesdrop on network traffic, but cannot manipulate or spoof traffic
- Can additionally act as a web attacker
- 2B: Active network attacker:
- Mallory who can launch active attacks on a network, e.g. MiTM
- Can additionally act as a web attacker
- The most powerful threat model
- Yet, it is not generally considered to be capable of presenting valid certificates for HTTPS sites that are not under his control: Why not?
Attacks on the secure communcation channel
Two pre-conditions of a MiTM attack:
- The attacker is a MiTM in between the browser and web server
- The attacker is able to sniff & spoof packets at the TCP/IP layers
If connection is HTTPS, MitM is unable to compromise both confidentiality and autenticity unless:
- Web user accept forged certificate or rouge ca
Misleading web user (UI)
URL
Componments:
- Scheme
- Authority
- Path
- Query
- Fragment
THe attacker will aim authority and path
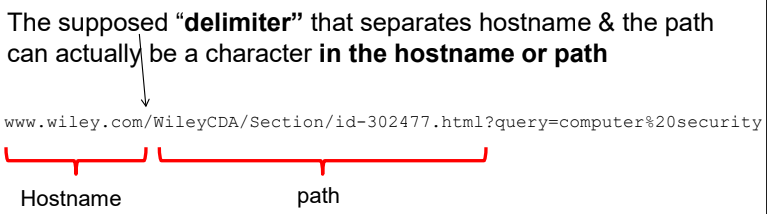
Misleading delimiter
- There is no clear visual distinction between host name and path of URL
- The supposed delimiter that seperates hostname and the path can be a chara in the host name or path
- The displayed different intensities could help user spot the attack
Address bar spoofing
- webpage can render objects or popups in an arb location
- malicious page to overlay a spoofed address bar on top of the actual address bar
- Attack trick the user to visit bad url
Cookies and same origin policy
Cookies
- Set by webserver
- Send in response using header
- Consist of name value pair
- Usually use for user preference, shopping cart content or session identifier
- Stored by user browser
- Browser auto send in inscope cookies to the server in its HTTP Request
Usage
- Session cookie: Deleted after session ends
- Persistent: at specific date or after a specific length of time
- Secure cookie: Can only be sent on HTTPS
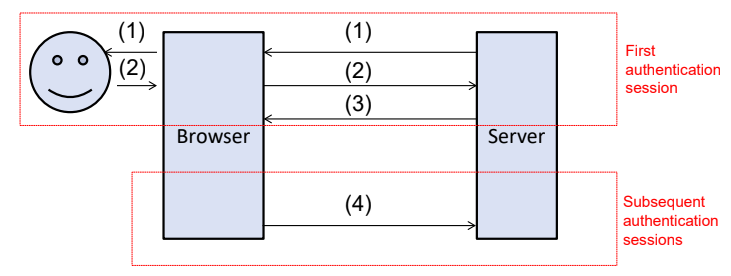
Token base authentication
- Auth: Ask username and password
- Valid, server send token t
- Browser keeps token t
- For every other (Subsequent) request to server, browser will attach t to the request
- Token is use to identify session
- Also called SID (Session ID)
- Stored in cookie often
- Using cookie is better approach than attching the SID as a url encoded parameter
Choice of token and storage requirement
- t needs to be random and long
- if t is a random chosen number, then server has to keep a table to store all tokens issued
- To avoid storing the table,
- (Insecure) Cookie is some meaningful infomation concat with predictable seq number - Insecure because attacker can forge it
- (Secure) Cookie is two parts, random chosen value or meaningful infomation (Expire data) AND concat with the message authentication code (MAC) computed with server secret key - relies on MAC’s security
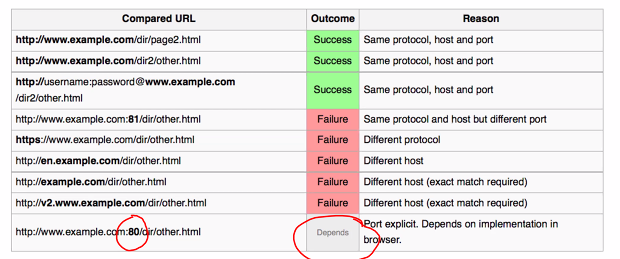
Scripts and same origin policy (SOP)
- Browser employs same origin policy access control
- Scripts in webpage A can access the cookies stored by webpage B iff both A and B have same origin
- Origin is combi of
- Protocol
- hostname
- port number
Complications:
- There are exception
Cross site scripting (XSS) attacks
Background
- Client can enter string s in the browser which is to sent to the server
- Server response with html that also contain s
- BUT WHAT IF, s is a script
e.g http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/<script>alert("hehehehe");</script>
Note that the attack wint work if the server performs html encoding which replace the character
<with<
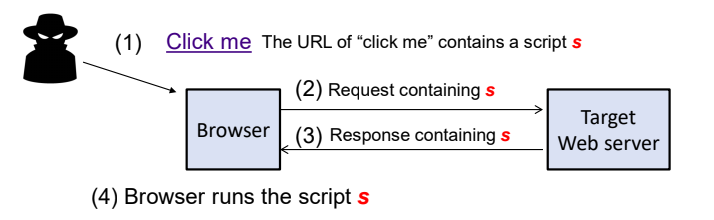
The attack
- Tricks user to click on url which contains the target website and malicious scriot s
- Request sent to server
- Server construct a response html but does not check the request carefully
- Browser renders the html page and runs the script s
- Attacker can know the session id of the user
- Can deface the original webpage
- Steal cookies
- Example of priviledge escalation: A malicious script coming from attacker has privilege of the web server and read the latter’s cookie
- The attack above the expoits the client trust of the server: The browser believes that the injected script is from the server
Stored (Persistent) XXS
- The script s is stored in target web server
- More dangerous than reflected xss
- The malicous script is rendered automatically
- The victim to script ratio is many to 1
XXS: “A type of injection attack on web apps, whereby a forum poster or web attacker attacks another web user by causing the latter run a (malicious) script from the former in the execution context of a page from an involved web server, thus subverting the Same Origin Policy”
Summary
- Reflected: web server that returns a page reflecting the injected script
- Persistent: web server that stores a page containing injected script
Defences
- Relies on server side
- Server filters then removes any malicious script in http request
- Filters and removes any malicious script in a user post before it is saved into forum database
Examples:
- Script filtering
- Noscript region: do not allow javascript to appear in certain region of a webpage
- This is not a fullproof method
- Additionally detect reflected XSS attack, some browsers employ a client side detection mechanism: XSS Auditor
Cross site request forgery attacks
- Session riding
Example
- Click on url
- Alice is already authenticated by the website, S accepts the authentication token cookie
- All request from Alice, the cookie will be attached to this request
- Web server can then define which is Alice
- Bob trick alice to click on url of S whcih request for the service using the alice’s cookie to transfer money
- No click link
- Requirement: Bob must have a web server
- Alice is auth by website and S accepts the authenthenticaation cookie
- Alice visit the attacker’s site whose page contains
<IMG src = "www.bank.com/transfer?account=Alice&amount=1000&to=Bob" WIDTH = "1" HEIGHT = "1" BORDER = "0"> - This is a subresource
- Alice browser would automatically try to get this request without Alice knowing it
- To the server, it seems as if Alice is just making a request although it is through Bob’s website
The image size is small so it wont be notice by Alice
CSRF
- An authorisation attack on web application
- Web sttacker attacks a web user by issuing a forged request to a vulnerable webserver on “behalf” of the victim
- Distrubs the integrity
- It exploits the server’s trust of the client
Defences
- Relative easier to prevent compared to XSS
- SID sent by the browser is insufficient, server must issue and require extra dynamic info -> Anti CSRF Token
Example:
- Server includes a anti crfs token in the money transfer request page
- The request will get the token attached where the token is dynamic
- Bob cant prepare a working link for alice to click since the token is randomly generated
- Alt, the token can be done for a hidden form field, it get transfer together with the post request and Bank.com will know if the request is real
- HTTP request header field
Terminologies
- Drive by download
- Web Bug
- Click jacking
- Click fraud