Overview
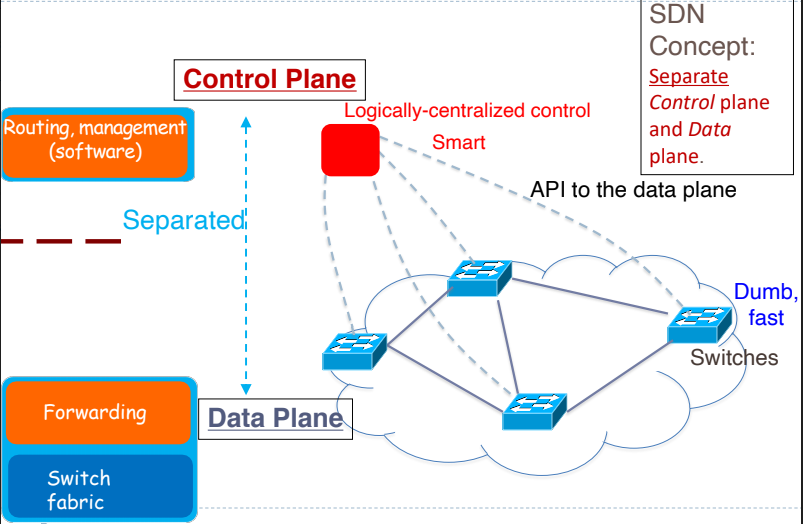
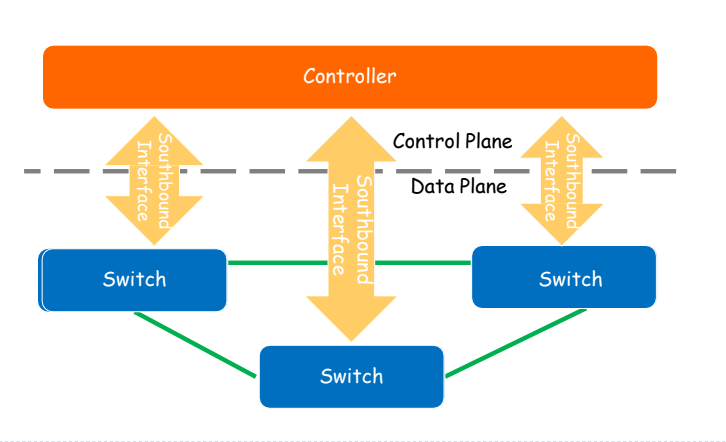
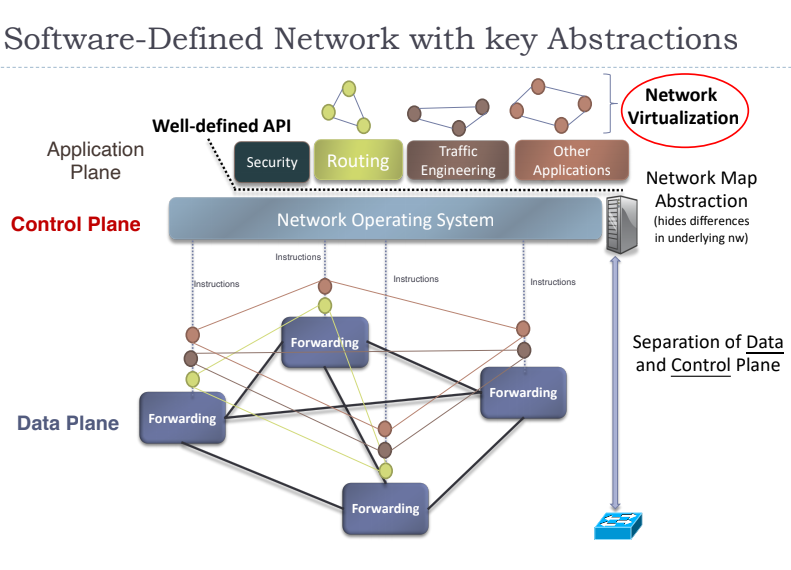
SDN - Seperate control plane and data plane entities
- Network intelligence and state are logically centralise
- The underlying network infrastructure is abstracted from the applications
Openflow is communication interface/protocol between the control and data plane of an SDN architecture
- Network Virtualisation: Making a physical network appear as multiple logical ones (Network slicing)
Why is it good
- Best effor packet delivery service
- Key functionalitu are programmable at the end hosts
- Ease of adding host and link tech
- Ease of adding sercvices
- Change is only easy at the edge
There is nothing new at the core of the network
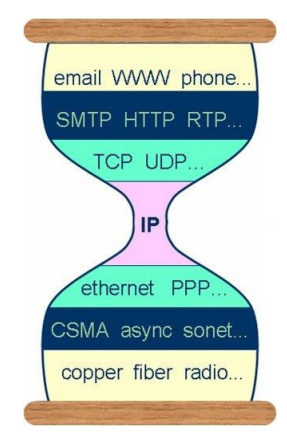
- Hourglass IP model
- Layered service abstraction
- Decomposse delievery into fundamental components
- Independent, compatible (Innovation at each layer)
- Only for network edges
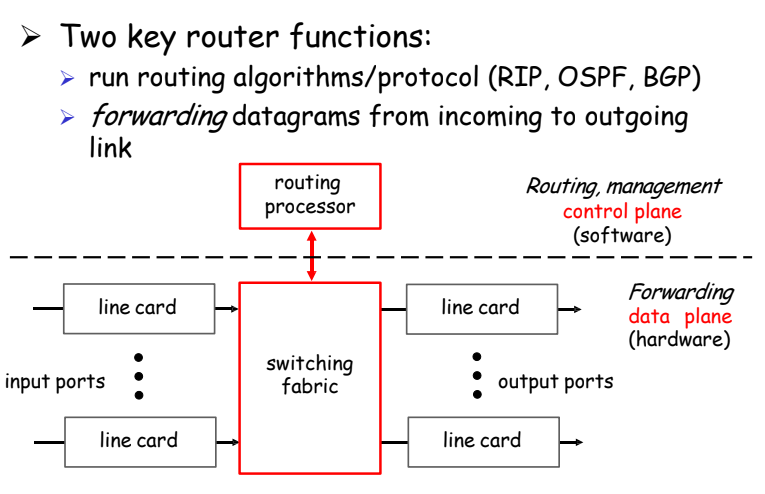
Current Internet: Complicate router at the core
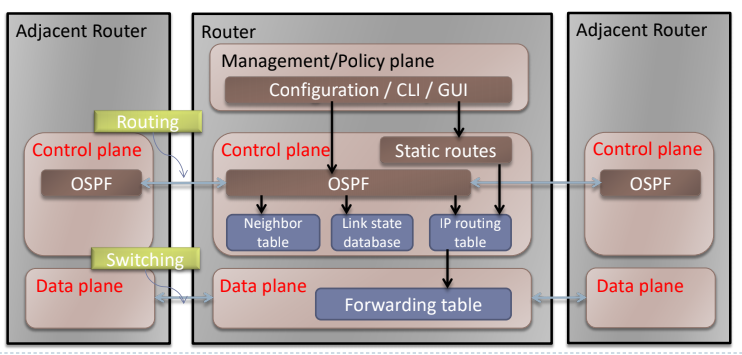
- Router can be partition into control and data plane
- Management plane: Configuration
- Control plane: Decisions: Run routing algo/protocols (RIP, OSPF, BGP)
- Dataplane: Forwarding- forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link
Dataplane
- Processing and delivery of packets
- Based on state in routers and endpoint
- E,g IP, TCP, Ethernet etc
- Fast timescles per packet
Control plane
- Estanlishing the state in rrouters
- Determines how and where the packets are forwarded
- Routing, traffic engineering, firewall state
- Slow time scales(Per control event)
What is wrong with the current internet
- Control by manufactors
Application are like
- Routing
- Management
- Mobility management
- Access control
-
VPN
- An industry with a mainframe mentaility
- Consequence: Buggy software in the equipment
- Cascading failures, vulnerabilities, etc
Operating a network is expensive
- More than half the cost of a network
- Yet operator error causes most outages
Demand and complexity are increasing
- Major ISPs: Upgrade their internal network infrastructure (router and switches) every 18 months to keep up with the current demands for network
Other problems
- Close equipment
- Software bundle with hardware
- Vendor-specific interfaces
- Over specified
- Slow protocol standardization
- Few people can innovate
- Equipment vendor write the code
- Long delay to introduce new features
Even if you standardised something, every vendor must agree to it. This would take some time because most vendors would not change it as they need to retest everything. Once something is deploy, it is very hard to change the software
Networking as a discipline
- Other fields in the system: OS, DB, DS
- Teach basic principles
- Are easily managed
- Continue to evolve
- Networking
- Teach big bag of protocol
- Notoriously difficult to manage
- Evolves very slowly
A failure from an academic point of view
Why does networking lag behind
- Use to simple: Ethernet, IP, TCP
- New control requirements led to great complexity
- Isolation: Vlan, acls
- Traffic engineering: MPLs
- Packet processing: Firewall, NATs
- Payload analysos: Deep packet inspection
- Mechanisms designed and deployed independently
- Complicated control plane design, primitive functionality
- Stark contrast to the elegantly modular “data plane”
- Ability to master complexity
- Extracting simplicity is needed to build a discipline
- Getting system to work
- Focus on mastering complexity
- Making system easy to use and understand
- Focus on extracting simplicity
- Networking still focused on mastering complexity
Extracting simplicity builds intellectual foundations which is Necessary for creating a discipline, this is what networking lags behind
Example: Programming
- Machine languages: No abstraction
- Mastering complexity is needed
- Higher level languages: OS and other abstractions
- File system
- Virtual memory
- Abstract data types
- Modern languages: Even more abstraction
- Object orientation
- Garbage collection
Abstraction key to extracting simplicity
The power of abstraction
- Layer only deal with data plane
- Processing the delivery of packet
- Based on state in router and endpoints
- IP, TCP, Ethernet
- There are no control plane abstraction
- Establish state in router
- Determines how and where packets are forwardwed
- Routting, traffic engineering, firewall state
Network control problem
- Compute the configuration of each physical devices Operate without communciation guarantees
- Operate within given network level protocol
- RIP, OSPF
Traditional Network Router in Summary
Imagine if network is:
- We just need to change the centralised control instead of changing every single one
Benefits of seperation
- Independent evolution and development
- The software control of the network can evolve independently of the hardware
- Control from high level software program
- COntrol behavior using higher order programs
- Debug/check behavior more easily
Benefits of centralisation
- Decision are easier to make
- OSPF
- Distributed system part
- Routing algo
- Logicial vs physically centrallised
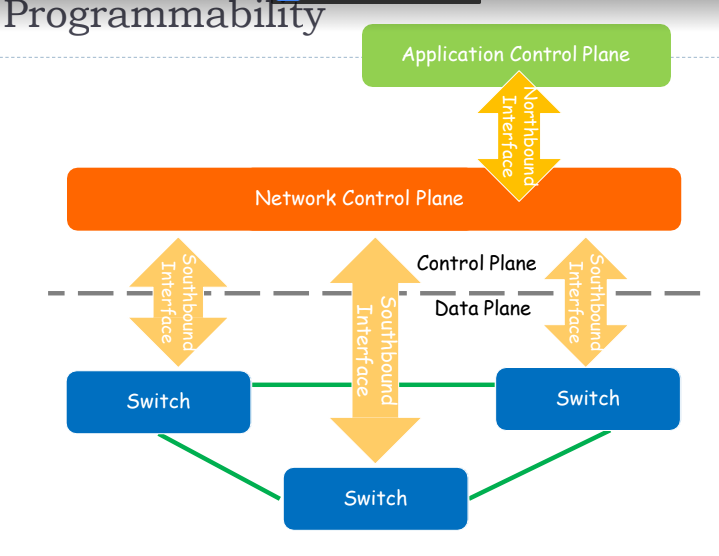
Open interfaces and programilities
Open interfaces:
Programmabilitiy:
- Enable competitive tech
- Independent development
- Rapid innovation and fast evolution
- Cheap and better networks
- Makes network management much easier
- Management goals are express as policies
- New control services for network providers
- Detailed configuration are done by controller
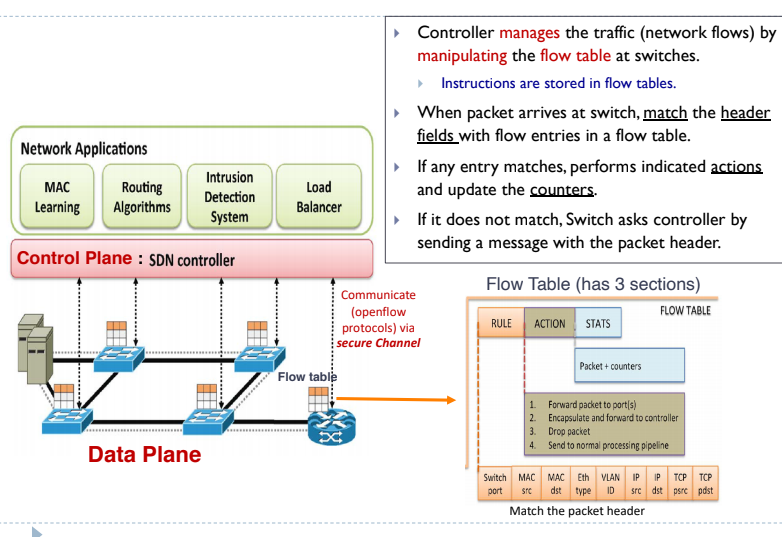
Open flow
- Allow seperation of control and data planes
- Centralisation of control
- FLow based control
- Takes adv routing tables in ethernet switchs and routers (l2/l3)
SDN Is not openflow
- SDN is a concept of the physical seperation of the network control plane from the forwarding plane and where a control plane controls several devices
- OpenFlow is communication interfaces btween the control and dataplane of an SDN architecture
- Allows direct access to and manipulation of the forwarding plane of the network devices such as switches and routers: Both physiucal and virtual
- It is liike a protocol use in switching devices and controllers interfaces
How does it work
The actual flow table looks like
Basic Action
- All: To all interfces except incoming interface
- Controller: Encapsulkate and send to controller
- Local: Send toits local networking stack
- Tabel: perfoming action in the next flow table
- In_port: Send back to input port
- Normal: Forward using traditional ethernet
- Flood: Send along min spanning trr exceopt incomng interface
With packet
- For eachpacket
- Header and geader fikled
- Ouoekube fuekds
- Action
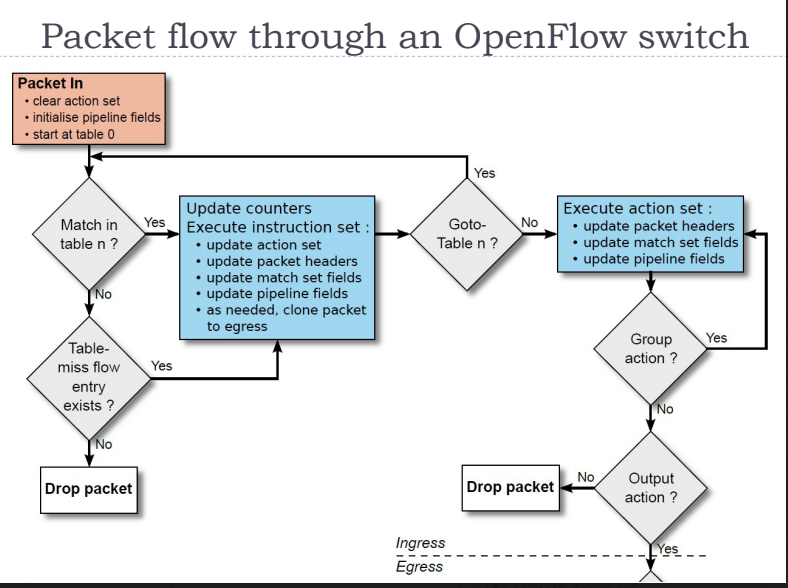
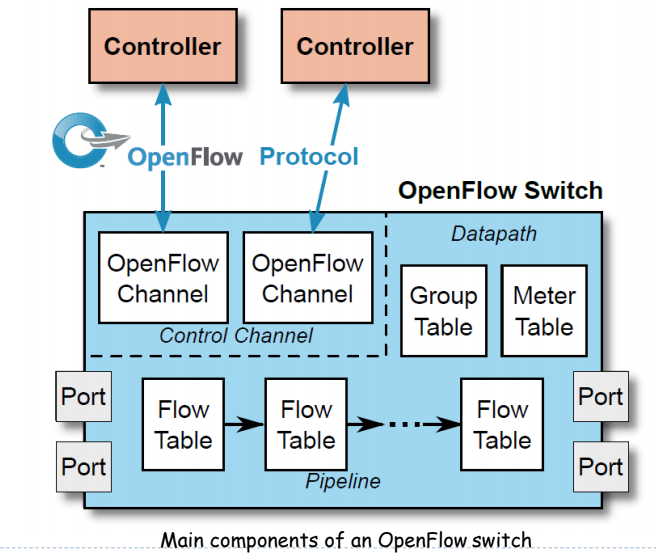
Openflow is a communication interface between the control and data plane of an SDN acrhitecture
- Openflow switch componenets: Flow table
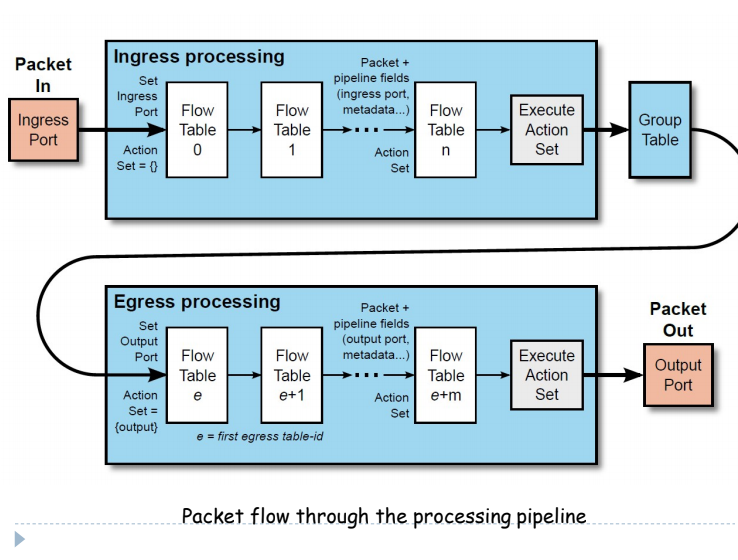
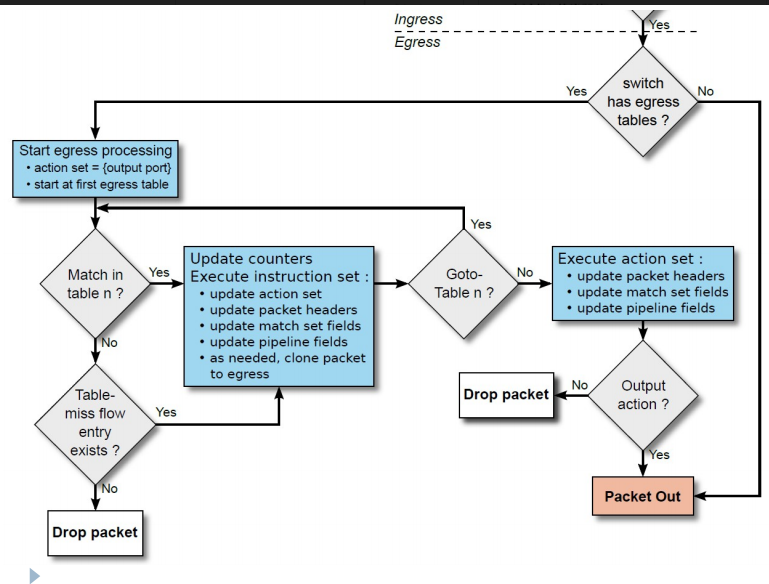
- A packet through open flow switch
Network Virtualisation
- Application of SDN
- Virtualisation
- Abstraction between physical resource and logical representation
- Can be implemented in various layers of computer system or network
- Storage
- Server
- Network
Server virtualisation
- Partitioning of the resource of a single physical machine into multiple execution environment each of which can host a different server
Network Virtualisation
- ALlows heterogenous virtual networks that are isolated indepednently managed to coexist over shared physical network infrastructure
- Making a physical network appear as a multiple logical ones (Network slicing)