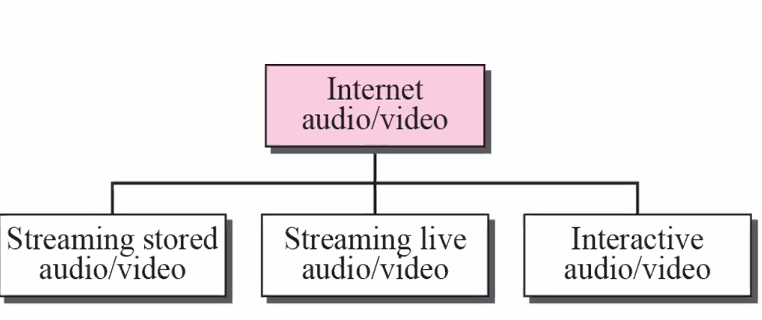
Streaming audio/video
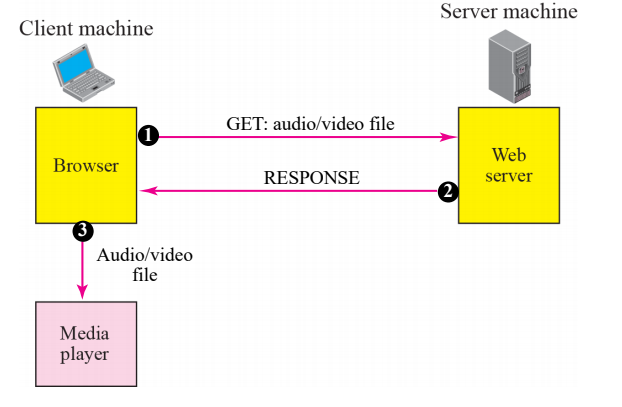
Streaming using a web server
- Browser makes a request for file
- Response has the file
- File is send to the media player
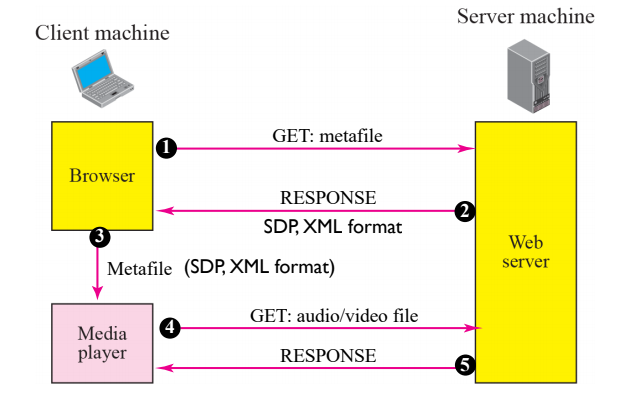
Streaming using webserver with metafile
- Client request webserver
- Webserver sends more more details about the audio
- metafile is sent to the media player
- media player makes a seperate connection
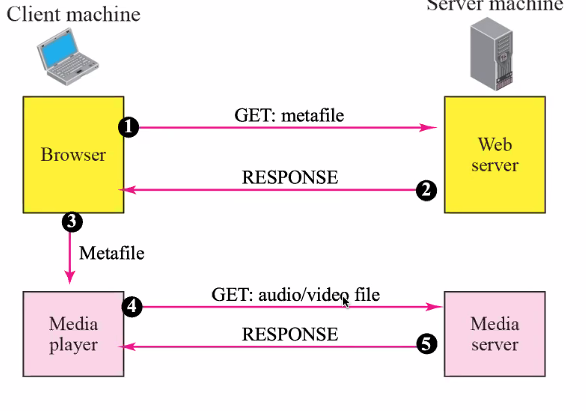
Streaming using a media server
- Similiar
- Media server just focus on serving the media player
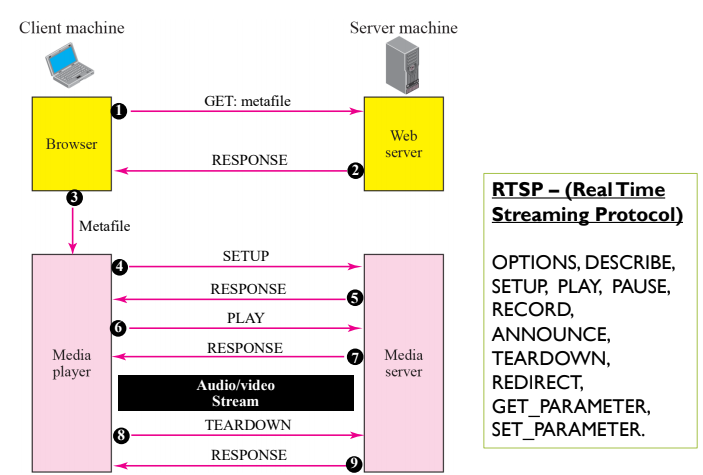
Streaming using media server and rtsp
In the past: Can only stream data but cannot rewind forward etc etc.
- RTSP : Real time stream protocol, provides the different calls such as record, option, play pause
Streaming live vs Stored audio/video
- Stream live audio and video
- Broadcasting of audio and video by radio and tv stations
- There are several similarities between streaming stored audio/video and streaming live audio/video
- Sensitive to delay
- Neither can accept retransmission
- There is a difference wherer in the first applicaiton, the communication is unicast and on demand. In the second the communication is multicast and live
Streaming real time interactive audio and video
- In real time, interactive audio/video, people communicate with one another in real time
- the internet phone or voice over IP is an example of this type of application
- Video conferencing is another example that allows people to communciate visually and orally
- Cloud games
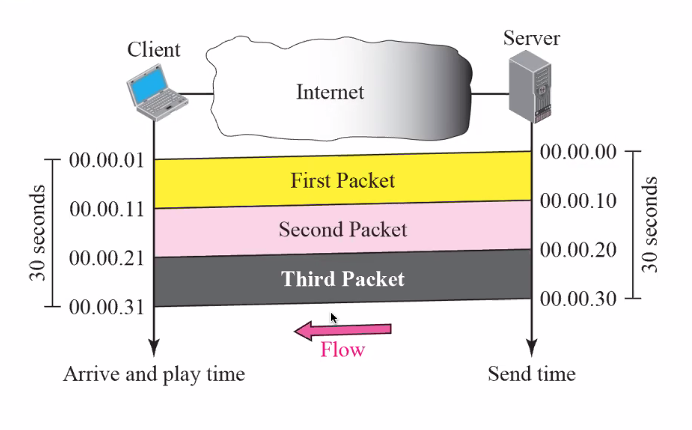
Streaming: Arrive time = playtime
- Play as soon as packet comes
- This looks perfect
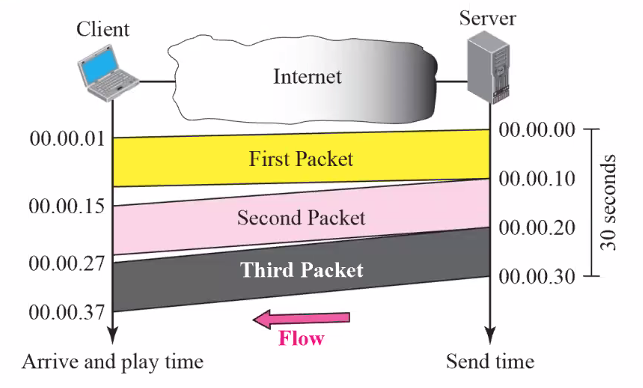
Streaming: Arrive time = playtime and jitter
- THis is the accurate way
- Jitter is introduce in real time data by the delay between packets
The jitter cause the playback to not be constant, the play time cannot be the same as arrive time
Jitter: variation in delay
Streaming: Handling jitter with playback buffer in client
To hide and prevent jitter:
- Timestamp the packets and separate the arrival time from the playback time
- Use client side playback buffer
- Add sequence number to packets
Question: How long to buffer? How to decide
- Delay
- Jitter
- distance from server
- packet loss
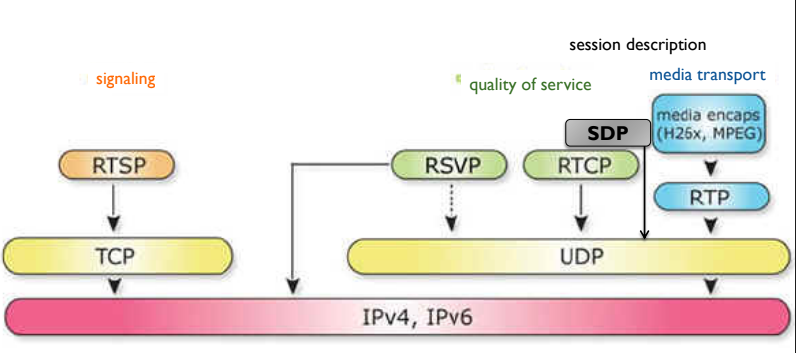
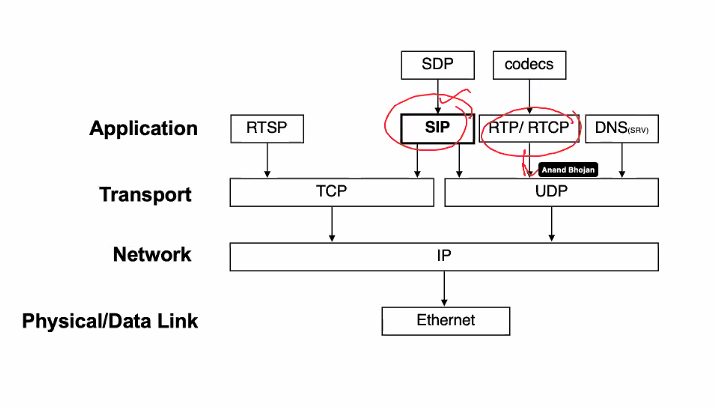
UDP and RTP
UDP:
- More suitable than TCP for interactive traffic
- RTP is used another transport layer protocol to make up for deficiencies of UDP
RTP:
- Designed to handle real time traffic on the internet
- RTP does not have delivery mechanism (Multicasting, port numbers etc)
- Must be use with UDP
- The main contribution of RTP are time stamping,seqeuncesing and mixing facilities
- RTP uses a temp even number UDP port
RTP also uses a companion protocol RTCP which enables the sender to monitor hte netowrk condition and react
SIP
Application layer control protocol for creating modifying and terminating session with one or more participants
- Voice
- Video
- Instant message
Follows http
VOip with SIP
- Session initiation protcol: APplication layer signalling protocl for creating mdofiying and terminating session with one or more participants.
- Can be use for voice video and isntant messaging, gaming
- Follows on HTTP
- Text base messaging
- URI
SIP Components:
- Client: Make request
- Servers: Accepts request
Server types:
- Redirect server
- Proxy server
- Registrar server
- Location server
- Session border controller
Peer to peer
- Which is the audio video code
- What is the codac
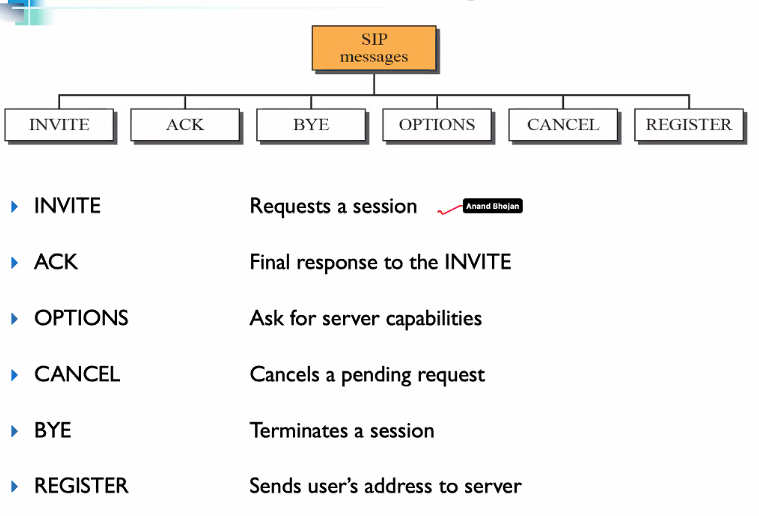
Method messages
Responses
- 302: Redirection
- 5xx: Server issues
- 6xx: Global failure
Address format
- the registra will register all these under your account
- People can call you using the email address, phone number etc
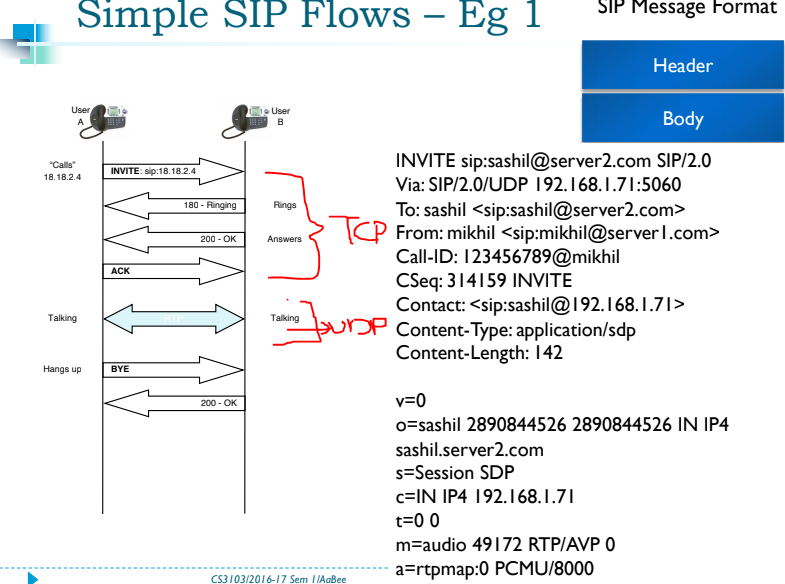
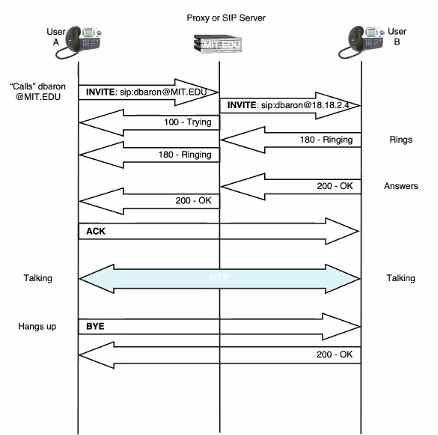
Simple flows
- SDP infomation is present in the initial invite
- RTP session can be establish using this
Normally the SIP may or not have content
SIP flows Via proxy
- When a client sends invitiation
- If we know ip, we can send directly, but most we dont know the ip address of the other side
- Prob email id
- Number
- Packet cannot be transmitted directly
- Takes the email if the user is login, send a registra command to register the ip address
- Establish the connection to the other side (Server)
- Ring will foward to the user A
- User a ack and just call directly
NOtice in 7, the communication is direct.. the sip server only using for directing
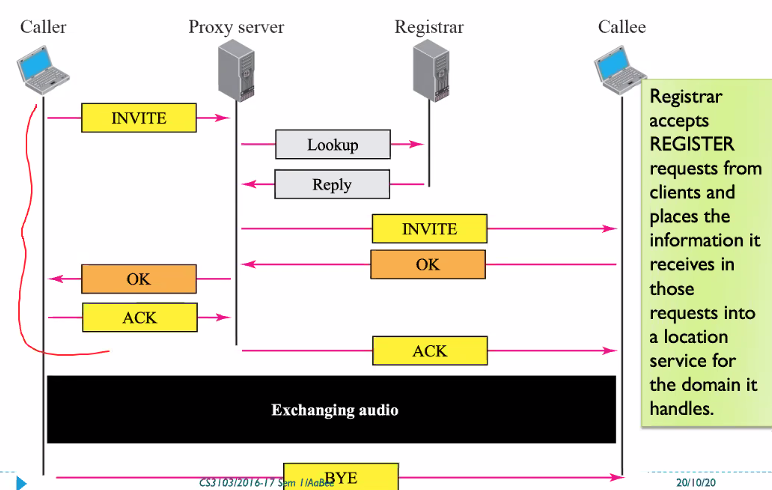
REGISTER WITH THE SERVER
-
SIP clients always connect to a sip server which in turn connects to destination by converting SIP address to IP address
-
All clients should register with SIP server with its current IP address when they login.
- SIP server should have REGISTRAR compoennt
Log in to two devices
- If someone calls me, server knows that you are log in
- Which device does the server forward to
- Answer: All
SIP flows via proxy: Tracking the callee
As client base increases, we want to divide the functionalities, the proxy server will be the one that does the lookup to the registra isntead of caller direclty to the register
There is also security we have to worry about
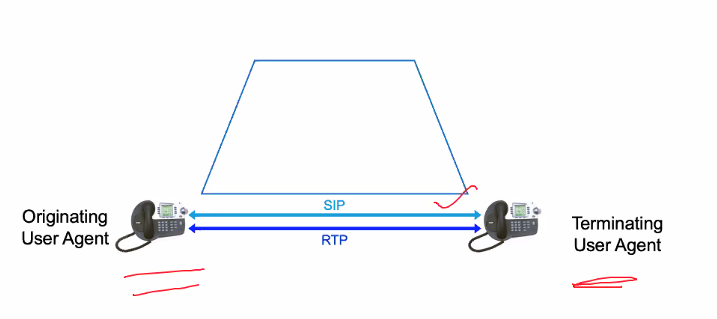
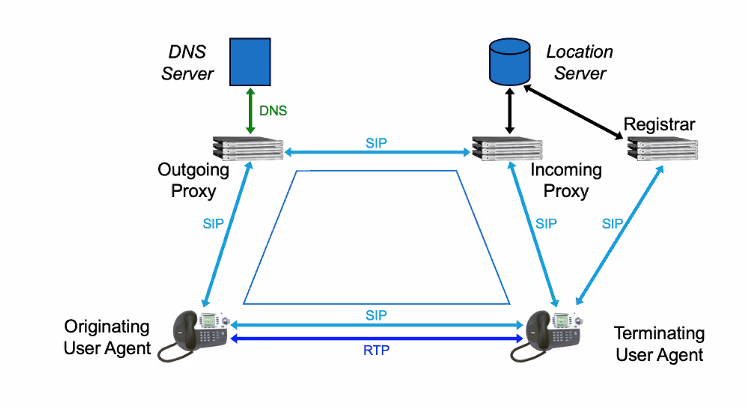
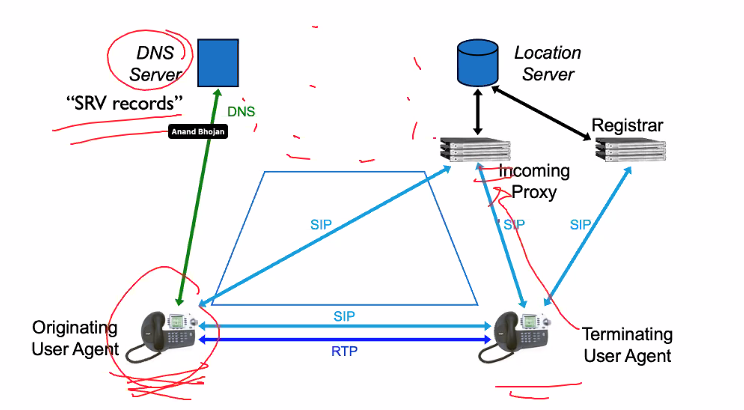
SIP Trapezoid
- To which the proxy server us ocnnect
- find from dns (potentional proxy search)
- send to porxy
Registra is a service that tells the infomatin of the user using the database
Registra is a process and the data is stored int he location server
SIP triangle
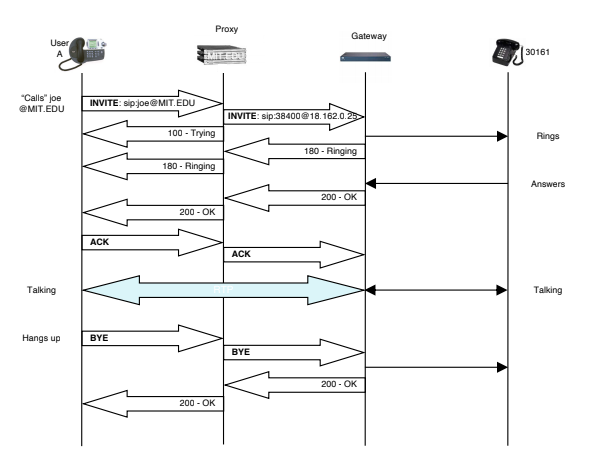
SIP flows: Gateway
- message goes through a gateway before reaching the other side
This is for crossing to another protocol, but the router needs to have this installed already
SDP: Session description protocol
- Intended for describing multimedia session for the purpose of session announcement session ivnitation and other forms of multimedia session initiation
Includes:
- Types of media
- Transport protocol
- Format of the media
- Infomation to recieve those media (Address ports formats and so on)
CODEC
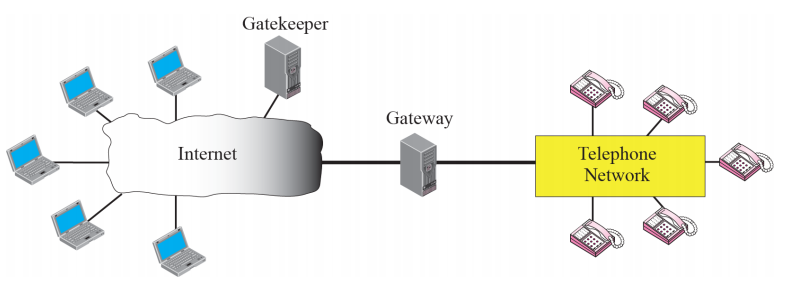
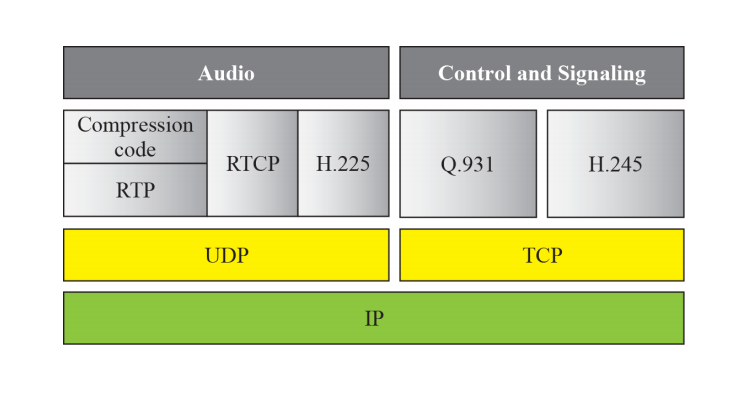
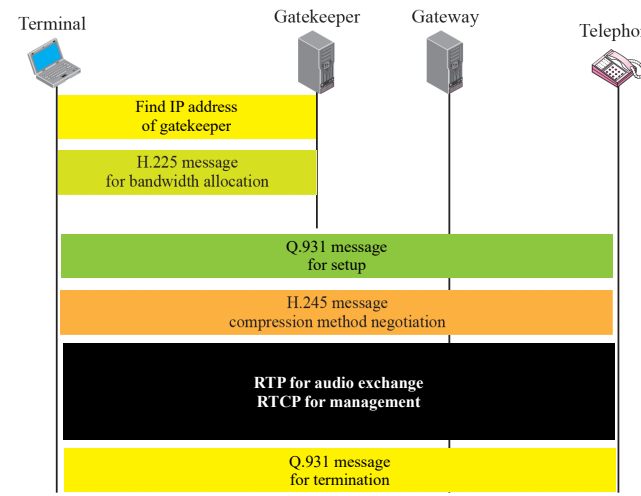
H323
- Telco companies use this and not SIP
- Recommendation covers the technical requriements for multimedia communciation system in a packet based network
- Defined for video conferencing
- Terminals: Endpoints that enable real time voice or video communcation
- MCU/MC/MPs: Multipoints controller units which includes multipoint controller and one or severalk multipoints processors that enable managed multipoint conferences
- Gateways: Intercommuncation between ip networks and legacy switch circuit networks such as ISDN and PSTN
- Gatekeepers: Perform the roles of central managersw of voIP services to the aend points, Mandatory functionalities includes address resolution, authentiation, service authentication
Architecture
- Gatekeeper: Register that keep track which ip address is to which device
Protocol
Flows - Via gateway
SIP and H323 communcication
- Needs another gateway from SIP user agent to H323 terminal Choose who?
- SIP is newer than H323
- SIP provides a similiar set of services to h323 but provides far lower complexity, rich extensibility and better scalabilitiy
- Use of SIP is rapidly increased in Telco networks with IP multimedia ssubsystem (IMS). IMS uses many existing IETF protocols