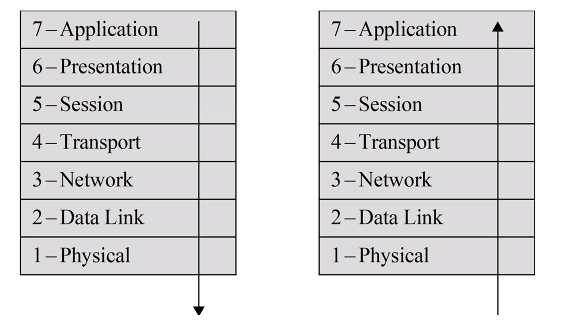
Network layers
- Partions a complex communcation system into several abstraction layers
- The peer entities at the same layer N communcate with each other by executing a protocol at that layer
Why
- Layer N protocol is built on top of virtual connection at layer N-1 below
- Example of protocol at layer 5 (Authentication protocol):
- A -> B “Hello”
- A <- B: certificate of B
- The peer entities at the same layer N “Conceptually” communicate with each other by executing a protocol at that layer
-
The virtual connection at layer 4 sends the message “hello” from A to B in step 1 and sends B certificate in step2
- At layer N:
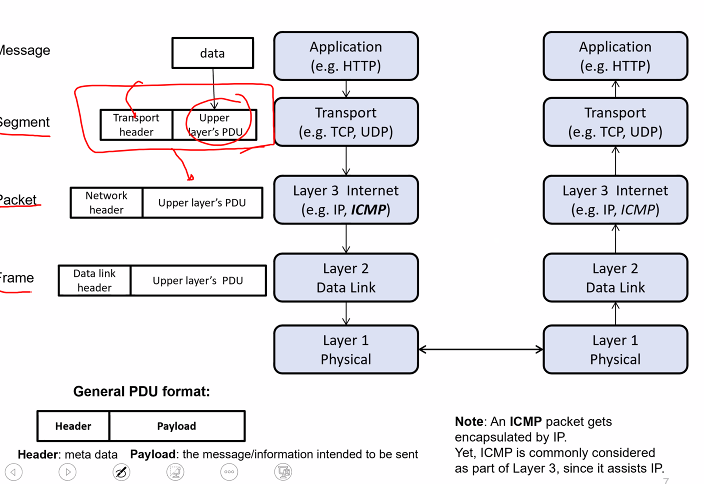
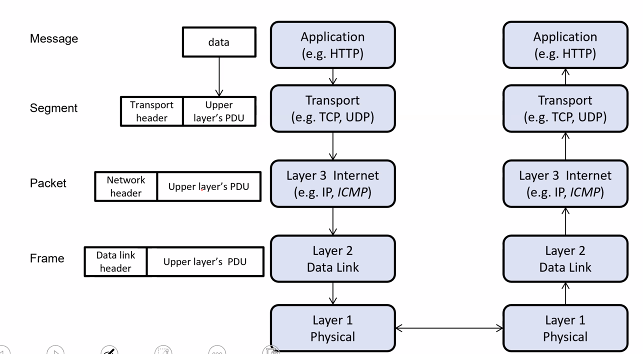
- A message to be send is called layer N protocol data unit (PDU)
- Encapsulation of upper layer PDU
Devices used in each layer are…
- Physical layer or below : Hubs, Repeaters, Cables, Fibers, Wireless..
- Data-link layer: Bridges, Modems, Network cards, 2-layer switches.
- Network layer: Routers, Brouters, 3-layer switches.
- Transport layer: Gateways, Firewalls.
- Session layer: Gateways, Firewalls, PC’s.
- Presentation layer : Gateways, Firewalls, PC’s.
- Application layer: Gateways,Firewalls, all end devices like PC’s, Phones, Servers..
Security weakness
- Original network design does not account for intentional attacks
- Possible threats:
- Interception: unauthorised viewing
- Modification: Unauthorise change
- Fabrication: Unauthorised creation
- Interruption: Preventing authorized access
- An attacker at any layer can modify the data and the header:
- Consider the source IP address in the IP header
- Wihtout protoection, the attack can send a packet with spoof source ip address
Name resolution and attacks
- Each peer entity has a name
- on a single node at different layer, the name can be different
Naming schemes and resolution
- Peer entity use virtual connection in layer below to find the corresponding name mapping
- E.g ip address of domain name
- Protocols that perform name mappings are resolution protocols
- Many resolution protocol didnt take into account of security, attackers can manipulate the outcome
Resolution protocols
- DNS (Domain name system)
- Maps domain name to IP address
- Hierarchical decentralised naming system
- Attacker can target the association of domain name with IP address
- ARP (Address resolution protocol)
- Associates or Maps ip address (Logical) with Mac address (physical)
- Use broadvase mechanism in local
- Attacker on local can target the association
DNS
- Ipaddress found by looking up a locally stored hash table or querying a dns server
- This is called name resolution
- Entity (Client) that initiates is called resolver
- If a domain name is found, this is called resolved
Light weight authentication of DNS query
- Query comes with 16 bit number (QID): Query ID
- Response must also come with QID
- IF QID in response does not match the one in the query, the client rejects the answer
- No encryption or MAC is used
QID was originally not meant for authentication but efficient way to match multiple queries
Local DNS Attack
Alice:
- Use free wifi to surf
- wants visit a page something.com
- types domain name into browsers address bar
ALice browser:
- Makes query to DNS server to determin the IP address
- connects to IP address after obtaining it
Mallaory (attacker)
- At physical layer: Can be another person in the same wifi
- WIFI is not protoected so attacker can:
- Sniff data from communciation channel
- Spoof data from the communication channel
- AAttacker cannot remove/modify data already sent by ALice
- Attacker owns a web server with IP address that is a spoofed something.com website
Attack
- Alice ask for address
- Mallory sniff and knows abt it
- She spoof a reply with the same QID
- DNS server also sends a reply
- Since Mallory is closer to ALice
- Mallory reply is likely reach Alice first
- Alice takes first reply as answr and connect to spoof website
Additional remarks
- DNS is at application layer
- Attacker at physical layer and is just below the application layer: There exist some virtual connection that can send the message across
- DNS is important component as it resovles the domain name
- DNS can be a single point of failure for network
- DoS instead of attacking webserver could attack the DNS server instead
Denial of services attacks
The prevention of authorised access to resources or the delaying of time critical operation
Affects:
- Availability: Property of being accessible and usable upon demand by authorized entity
Types
- Local attacks: more easily tracked
- Malform attacks: Does not usually work on updated OS
- Packet flooding:
- Overwhelm victims with request or data
- Attacker amplify small traffic to obtain large traffic typically by using abailble public servers (Internet infrastructure) such as DNS, NTP, CharGen
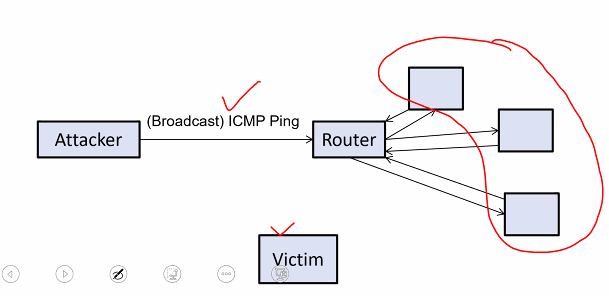
- ICMP/SMURF flood attack
- Sends ICMP ping request to router
- Instructs router to broadcast this request to all local nodes
- Request source IP is spoofed with victims IP address
- Router broadcast this echo request
- Entity that recieves the request replies to it by sending an echo reply to source which is the victim
The victim is overwhelm with echo reply from the entire network, the attacker takes advatnage of the amplification effect
ICMP/SMURF preventive
- Its not effective
- Router now configured not to broadcast the request
- Prevent: Disable the feature that is thought to be useful previously
HTTP GET Applicaation layer DOS attack
- Flood a web server with HTTP request
- Large number of attacker required
- Dos is carried ot by large number of attackers which is called DDos (Distributed Denial of service)
Bot net
- Zombie: a compromised machine
- Botnet: A large collection of connected bots communicating via covert channels
- Botnet has a command and control mechanism and thus can be controlled by individual to carry out DDOS
- Possible uses:
- Flooding
- Vulnerability scanning
- Anonymizing HTTP proxy
- Email address harvesting
- Cipher breaking
Why covert channels are use by botnets
- To stay hidden
Userful network security tools
- Wireshark
- Sniff packets
- Nmap (port scanner)
- Can scan for vulnerabilitiies
Protection: Securing the communication channel using cryptography
Achieve:
- Confidentiality (Encryption)
- Authenticity (MAC, PKI, Strong authentication)
Protocols:
- TLS/SSL
- WIFI protected acccess 2 (WPA2)
- Internet protocol security (IPsec)
Layers:
Some protection span across multiple layers or do not provide full protoction of the target layers
- Analyse a attack: Figure out what layer the attacker resides
- Complication: Some attacker span across multiple layers
Remarks
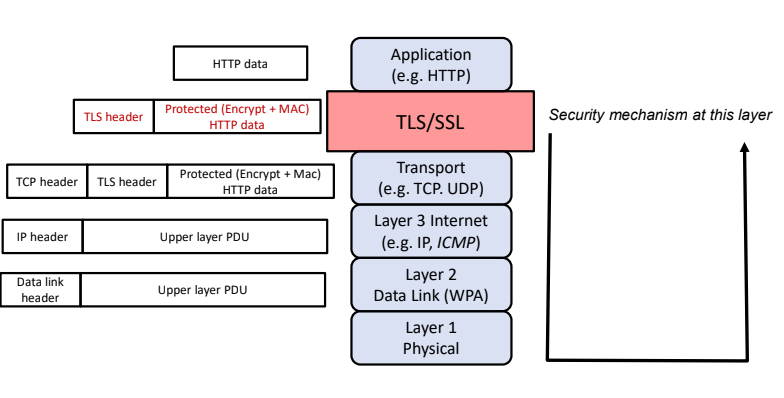
- A secuirty protocol that protects layer k would protect infomation from that layer and above against an attacker sitting at layer k-1 and below
E.g: What happens if attacker resides at layer 1 and there is a security protcol that protects layer3?
- What is protoected by security protocol: The infomation generated in the layer 3 and above
- Not protected: Infomation generated in layer 2
Protocols
SSL/TLS
- Sits on top of transport layer
- When application wants to send data to the other endpoint, it first pass the data and the destination IP address to SSL/TLS
- TLS/SSL protects the data using encryption (Confidentiality) and MAC (Authenticity) and then instructs the transport layer to send the protected data
- End to end encryption is performed
Note: HTTPS employs ssl/tls
Usage:
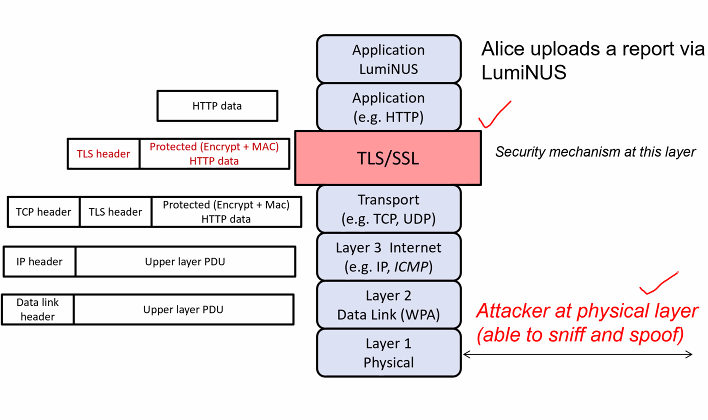
- Alice access Luminus to upload her file a.pdf
- Alice machine:
- Luminus client passes the file a.pdf to HTTPS and then to TLS
- TLS protects the data by encryption and MAC
- TLS passes the protoected data to the transport layer
- Luminus:
- The transport layer passes the protected data to TLS
- TLS decrypt the data and verify the MAC for integrity
- TLS passes the decrypted data to luminus application
Handshaking is also used here (Jus ommited)
Attacker at physical layer
- Mallory can sniff and spoof the pdf locally
- E.g Alice upload her report in cafe in open WIFI without WPA protection. Anyone in the cafe has access to the physical layer and can sniff and spoof messages in that layer
What can attacker learn?
- Cannot learnt about the report (The report is protected by TLS encryption/MAC)
- Alice is visiting Luminus website (Based on the IP)
Attacker at application
- At application layer
- E.g Malicious javascript is injected into Luminus and executed by ALice browser
What can attacker learn?
- Can learn about the report (Not protected by TLS)
- MAC (Generally No)
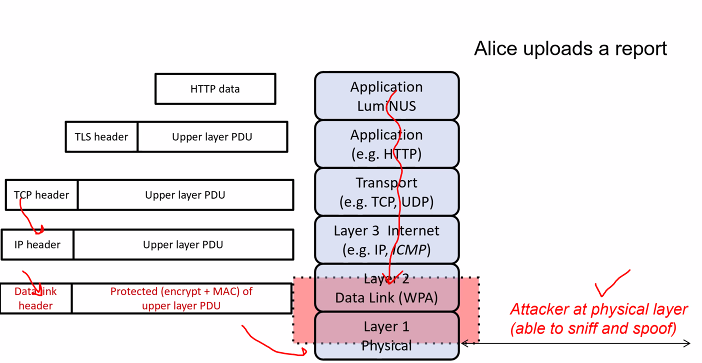
WPA2
- Wifi protected access 2:
- Employed in home wifi access point
- More secure than WEP (broken), WPA Protections:
- Layer 2 (link)
- Layer 1 (Physical)
Not all info in layer 2 is protected
If the attacker is at the physical layer:
Can the attacker learn
- Report: No
Alice visiting luminus? No
- Mac (Not clear)
IPsec
- Provides integrity and authenticity protoection of IP address but not their confidentiality
- Attacker cant spoof source IP
- Can still learn source and destination
However IPsec is not widely used..
Reason
In the past, IPsecs is a very good solution to this communication issue. If all the machine given the pkc and pki, all communication can be secure involving two nodes. But at that time, there was economic issue and then it turns out TLS and SSL is good enough
Protection: Firewall
Protocols are not sufficient to protect - Cant protect against Dos
- Need to control the flow of traffic between networks especially between untrusted public network (internet) and trusted internal network
Firewall:
- Between two networks
- Looks at addresses, services and other characteristics of traffic
- Controls what traffix is allowed to enter the network(ingress filtering) or leave the network (egress filtering)
Definition:
Firewall are devices or programs that control the flow of network traffix between networks or hosts that employ differing security postures
- DMZ (demilitarized zone)
- Small subnetwork
- Exposes org external service to untrusted internet
Design
- Enforce a set of rules
- Examples
- Block HTTP
- ALlow from internal network to Mail server: SMTP, POP3
- Front end firewall: Allow from anywhere to Mail Server: SMTP only
Types
- Traditional packet filters:
- Filters packet based on infomation in packet headers
- Stateful inspection (Packet filters)
- Maintain a state table of all active connections
- Filters packets based on active connections states
- Application proxy
- Understands application logic
- Acts as a relay of application level traffic
Protection: Network security management
Need: Continously monitor and adjust network characteristics
Terms:
- Security Operation Center (SOC)
- Centralised unit in an organisation that monitors the IT systems and deals with security ISSUes
- Security Infomation and Event Management (SIEM)
- SIM
- Provides real time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and application
- May include the following capabilities: - Data aggregation and correlation, event alerting, compliance report generation, forensic analysis