Attacks on internet
Threats:
- Disruption: From an over reliance on fragile connectivity
- Premeditated internet outrages bring trade to its knees
- Randsomware hijacks the itnernet of things
- Priviledge insiders coerced into giving up their crown jewels
- Distortion: As trust in the integrity of infomation is lost
- Automated misinfomation gains isntant credibility
- Falsifed infomation compromises performance
- Subverted blockchains shatter trust
- Deterioration: When controls are eroded by regulations and technology
- Surveillance laws expose corporate secrets
- Privacy regulation impede the monitoring of insider threats
- A headlong rush to deploy AI leads to unexpected outcomes
Original vision: A group of mutaully trusting users attached to a transparent network
- Infecting/attacking host/ users: Malware, spyware, spam emails, phishing, unauthorise access
- Denail of service: Deny access to resources
- Network of compromised devices/nodes is known as botnet
- Control by bad guys
- Use for spam email, distributed DoS
Malware
- Virus: Infection by receiving object
- Trojan Horse: Hidden parts of some otherwise useful software
- Worm: Infection by passively recieving (It gets executed itself)
- Spyware: Infection by downloading webpage with spyware
- Records keystrokes, websites visited and upload infomation into collection site
Worm and virus is self replicating: Propogates itself to other hsots and users
Ransomware: Is a type of malware/crimeware that encrypt a user’s data then demands payment in exchange for unlocking the data
Denial of service
- Attackers make resources unavailable to legitimate traffix by overwhelming resource with bogus traffic
- Select target
- Break into host around network
- Send packet towards target from compormised host (TCP SYN packets)
Intude
- Sniff, Modify, Delete your packets
- IP spoofing: Send packet with false source
- Record and playback: Sniff sensitive info and use later
Cheat:
- Phishing: Web/UR: phishing email phishing
Services by security system
- Confidentiality
- Message integrity
- Message authentciation
- Non repudiation: Sender must not be able to deny sending a message that he have
- Entity Authentication: Need to authentciate the user before any message communication starts
- Access and availablity
Access and avilability
- IP spoofing
- Ingress filtering
- Routers should not forward outgoing packets with invalidnsource address
- Great but ingress filtering acan not be mandated for all networks
- Denial of service
- Filter out flooded packets
- Traceback to source of floods (Most likely an innocent compromised machine)
Network layer security
- Network layer secrecy:
- Sending host encrypts the data in IP datagram
- TCP and UDP segments; ICMP and SNMP messgages
Network security
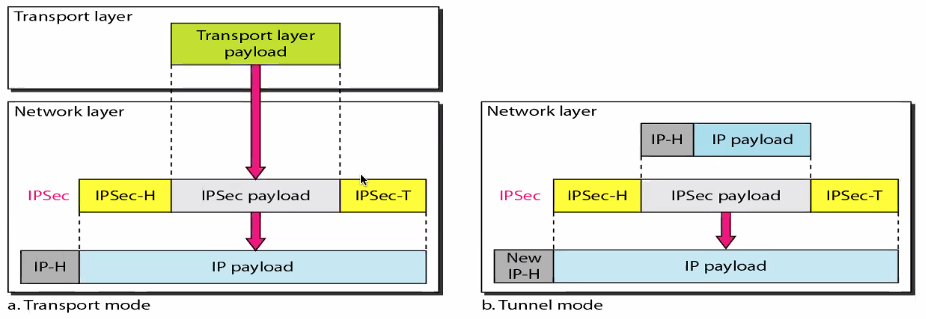
- IPsec in the transport mode does not protect the IP header, it only protects the info coming from the transport layer
- IPSec in tunnel mode protects the original IP header
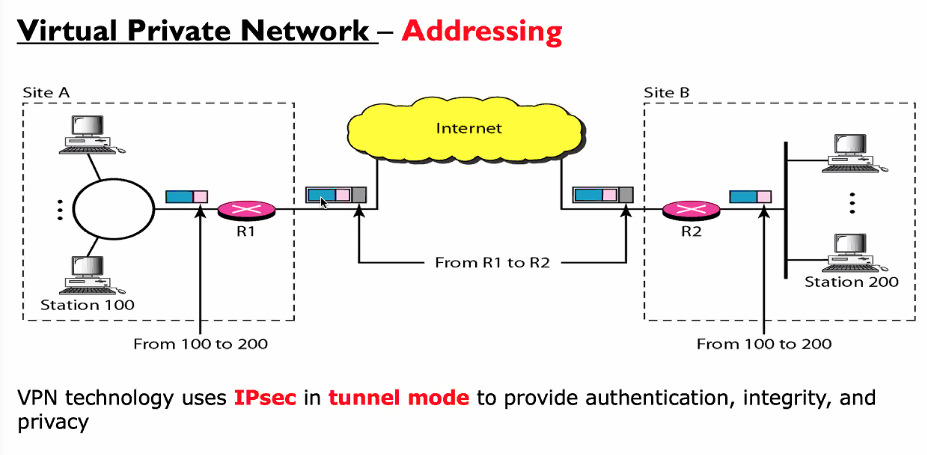
IPsec in use – VPN (Virtual Private Networks)
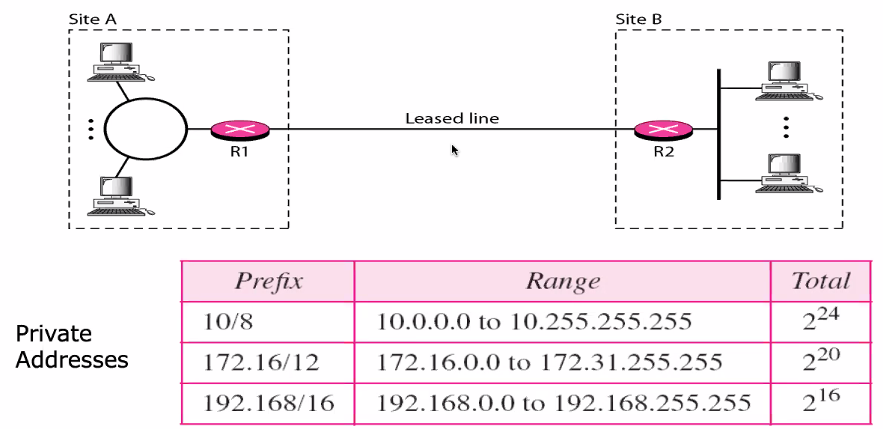
Private internet: Internet of private LAN and private WANs
- The packet from R1 to R2 is encrypted
- R2 decrypts the packets and forward accordingly
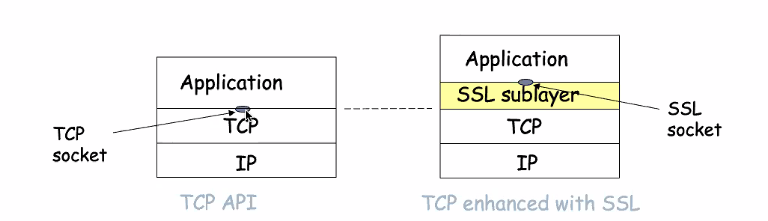
SSL (Secure sockets Layer)
- Transport layer security to any TCP based APP using ssl service
- Use between web browsers, servers for ecommerce
- Secuirty services:
- Server authentication
- Data encryption
- Client authentication
SSL was init developed as an application btu then it provides an api that is similiar to transport layer, thus it is debated as a transport layer protocol
Phases:
- Handshake
- Key deriviation
- Data derivation
- Handshake
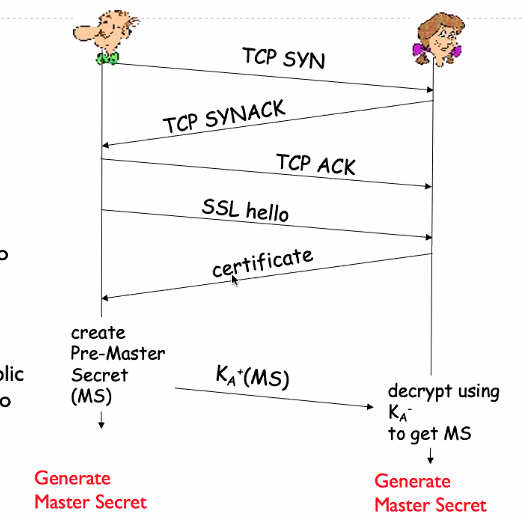
- Bob establishes TCP connection to ALice
- Authenticates alice via CA signed certificate
- Creates and encrypts (Using ALice public key) Sends premaster secret key to Alice
- Key derivation
- Uses master secret to generate 4 keys
- 2 keys for encruption on both side
- 2 keys for authentication on both side
- Symmetric key encryption but uses different keys on both side
Why 4 keys? One for each direction, this is enhance security
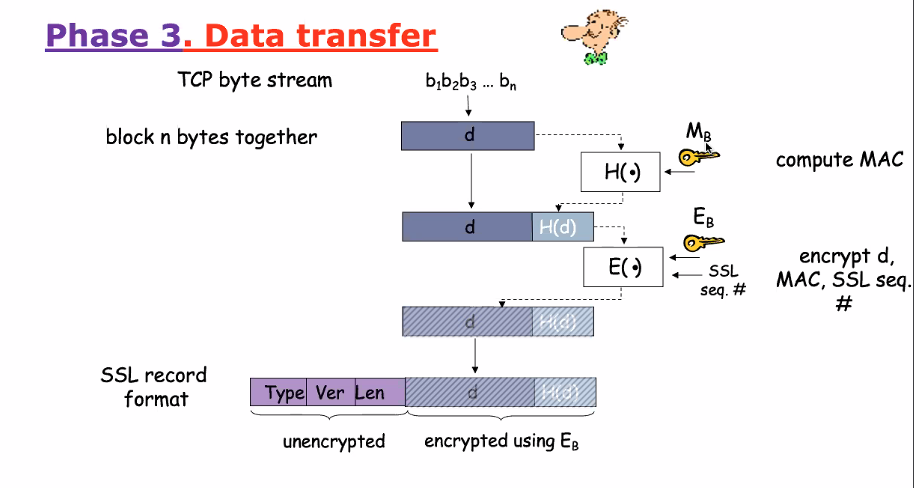
- Data transfer
SSL Handshake:
- Client send cryptography and hash algorithms it supports to server in client Hello message
- Server selects a symmetric key algo, public key algo and MAC algo. Sends choices to client with a certificate and server nonce
- Client verifies certificate, extracts server’s public key and generates pre-master key (PreMS). Encrypts the preMS with server public key. Sends encrypted preMS to server
- Both client and server use the same key derivation fucntion to generate MS and the 4 keys from the MS
- Client sends MAC of all handshake messages
- Server sends MAC of all handshake messages
Connection close:
- An SSL record with type filed set to close is send. Then tcp fin is send
Secure email and pretty good privacy (PGP)
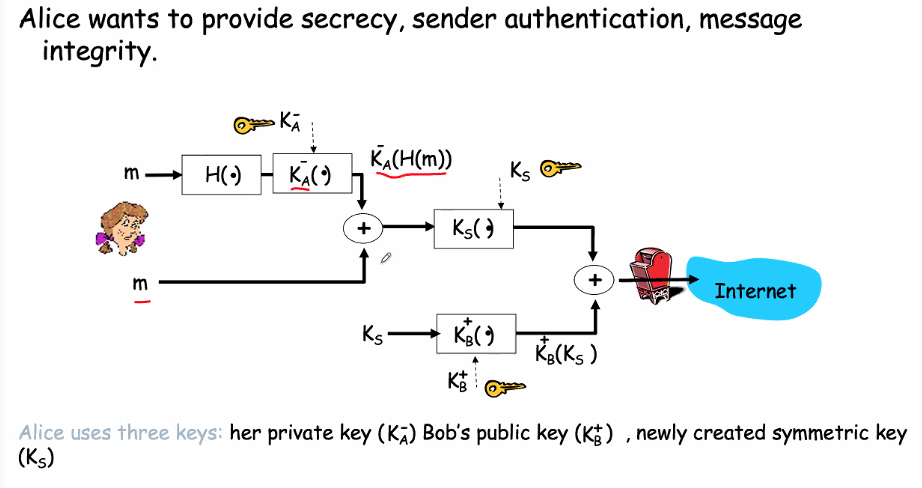
Authenticated encryption
- Use hash , symmetric key and pkc