Experiement
Foruzan TextBook
Link state routing
- different from distance vector routing
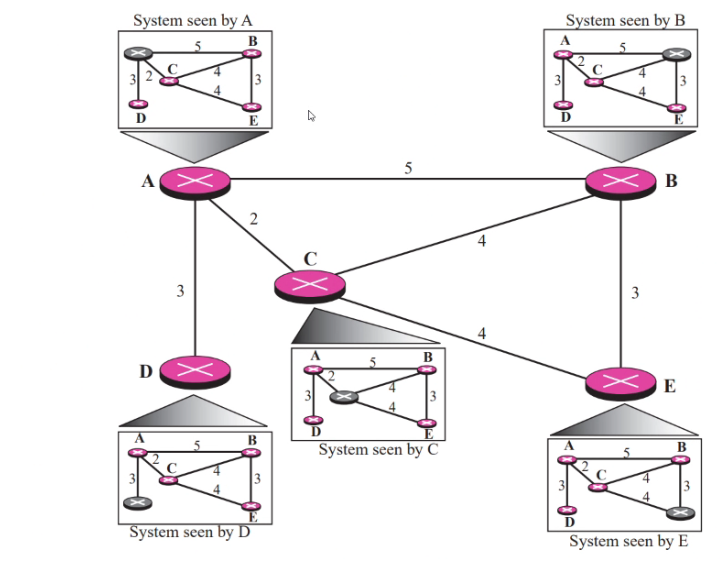
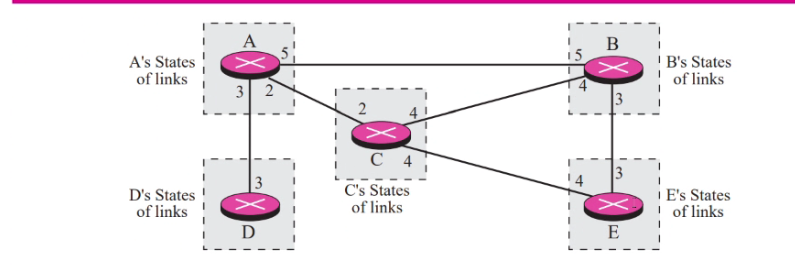
- Each node in the domain has the entire topo of the domain: the list of nodes and links, how they are connected including the type, cost and condition.
-
Uses dijsksta algo
- Any changes the topolgy must be updated in each nodes
- Link state knowledge: Each node knows the state of each node
Build routing
Link state routing:
- Creation of the states of links by each node: LSP
- Dissemination of LSP to every other router called flooding in an efficient reliable way
- Formation of a shortest path tree for each node
- Calculation of a router table based on the shortest path tree.
Creation of Link state packet (LSP)
LSP can carry a large amount of infoamtion.
- Assume it carries a min amount of data:
- Node identity: Need for topo
- The list of links: Need for topo
- Sequence number: Flooding and differentiate new LSP from old
- Age: Prevent old LSP Generated on:
- Change in top
- Periodic: Ensure that old info is removed
Flooding
After a node prepare LSP, it must flood the network
- The creating node send copy of LSP out of each interface
- The node that recieves lsp compare it with the copy it might have, it keeps the newer one whilst discarding the old one and send a copy in its interface to other nodes
Dikstra: Greedy algo that picks the shortest path each time
Routing table: each router stores the number of hops needed to destiantion and the name of the enxt router it have to hop to
OSPF
The Open shortest Path first protocol: AN intradomain routing protocol based on link state routing, It is autonoummous
Areas:
- All networks inside the area must be connected
- Areas inside must flood the area with routing info
- Special router:
- Area border router: Summaries the info about the area and send to other area
- Backbone: All of the areas inside the autonomous systerm mus be connect to this
- Not all router is connected to each other
Backbone router can also be area border router
There can be a virtual link between router to ensure the connectivity between backbone and primary area (In case the abckbone link drops)
Metric
The OSPF protocol allows adminstrator to assign a cost call metrix to each route.
Metric:
- Minimum delay
- Max throughtput
Router can have multiple routing tables depending on the metric
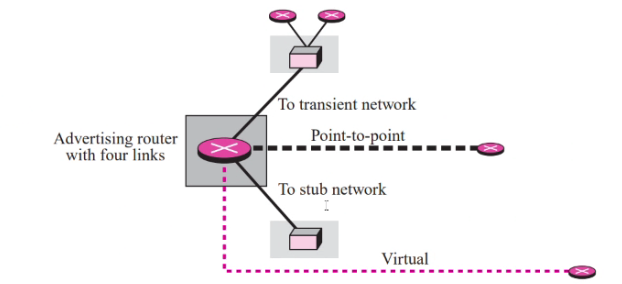
Types of links
- Point to point: Router to router
- Transient: Network with several router attached
- Stub: Network that is connected to only one router
- Virtual: A another path that goes through other routers
Look at the lecture slide
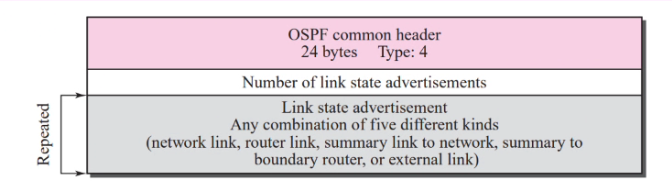
OSPF Packets
- Uses 5 differnt types:
- Hello
- Database descriptions
- Link state request
- Link state update (This have 5 subtypes)
- Link state ack
Important header parts:
- Version: Ver OSPF protocol
- Type: Type of the packet (there are 5)
- Message length: Lenght of total msg including header
- Source IP
- Area identification: Location where the routing take place
- Authentication type: 16 bit, define teh authentication protocol
- 0: None
- 1: Password
- AUthentcation: Actual field of authentca
- If the type is 0, this field is all 0
- If type is 1, password
Link state update packet
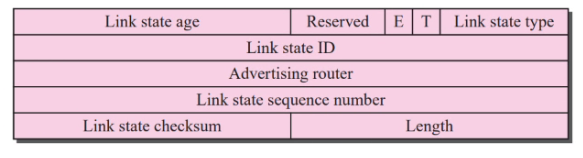
Field:
- Link state age: Since the msg was generated, starting is 0 and increase bsaed on transit time (Added by router)
Header for LSA
- E flag: 1 means stub area
- T flag: 1 means router can handle multiple service
- Link state type:
- Network
- Summary to network
- Summary link to AS boundary router
- External link
- Link state ID: (Base on type)
- 1: Ip address of router
- 2: Ip address of designated router
- 3: Address of network
- 4: Ip address of As boundary router
- 5: Address of external network
- Advertising router: IP address of router advertising the message
- Link state sequence num: Seq num assigned to each link state update mewssage
Router Link LSA
Defines the links of the true router. True router use advertisment to announce info about all of its links and what is at the other side of its links
Fields of router Link:
- Link ID: Depends of type of links
- Link data: Give additional info about link
- Link type: Four diff types of links
- TOS (Types of services): Define num of types of services announced for each link
- Metric for TOS 0: The field defines the type of services
- Metric: Defines the metric for corresponding TOS
Network link LSA
Definies the links of a network. A desinated router on behalf of the transient network sends it to other
- Network mask: Defines the network mask
- Attached router: Deifnes IP address of all attached routers
Summary link to network LSA
Use by area border router to announce the existence of other netowkr outside the area
- Netowrk add deducde form the network mask and source ip
Summary Link to AS Boundary router LSA
For network outside autonoumous system, provide the area with the infomation of the route by flooding.
External Link LSA
Provides infomation about which network are avail outside the autnoumous system.
- Seperate announcement are made for each network outside of the AS
Other packets
-
Hello message: Create relationship in the neighbour hood and to test the reachability
- Database descp: Send when its first time neighbour hears
- Outline: Title of each line in database
- Link state request packet: Router need info about specific route ro routes
- Link state ack: Force every router to ack the packet
Encapsulated
OSPF are encapsulated in IP datagram, DO not need transport layer protocol