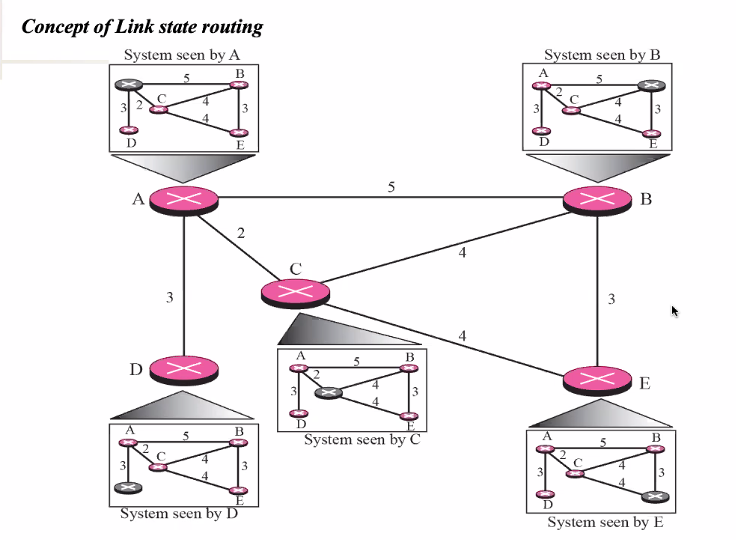
Link state routing
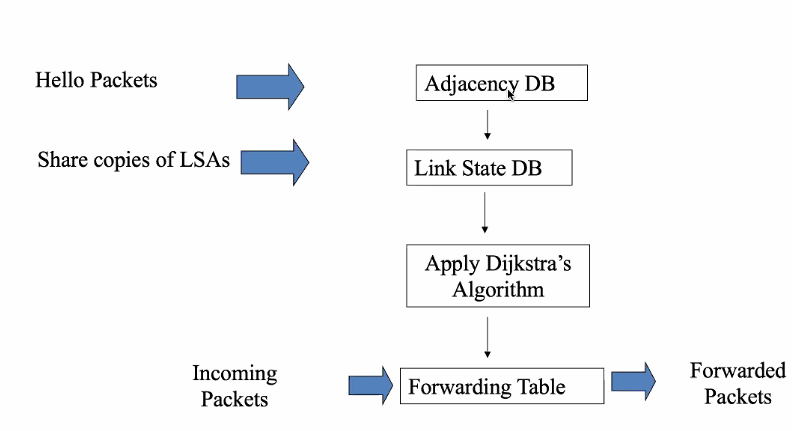
Each router in the network knows the link state so that they can plan the appropriate path
- Distance vector: Router knows only cost to each destination
- Link state: Router knows the entire network topologu
- Computes shortest path by itself
- Independent computation of routes
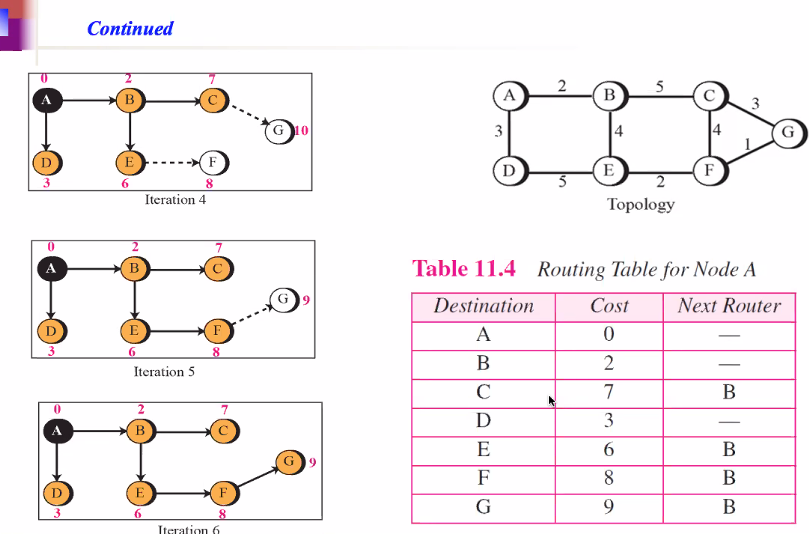
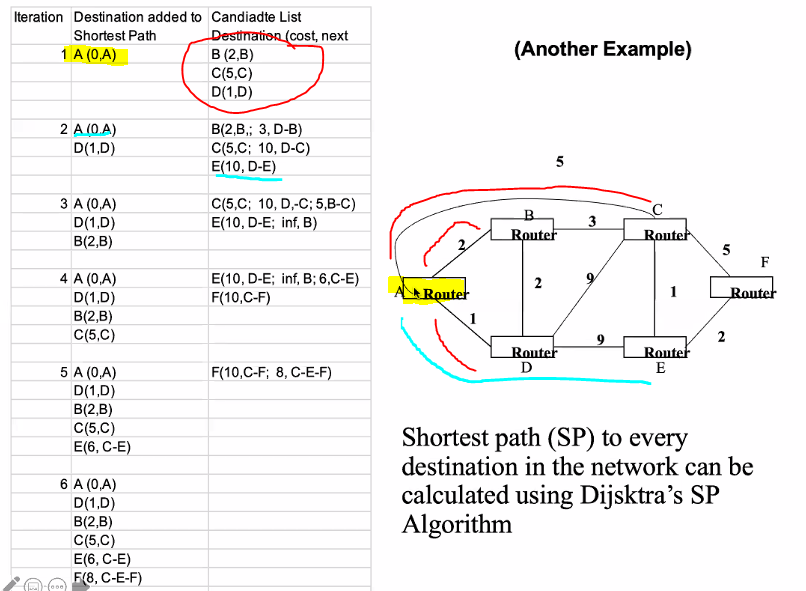
Forming shortest path tree for router A in a graph (Dik Algo)
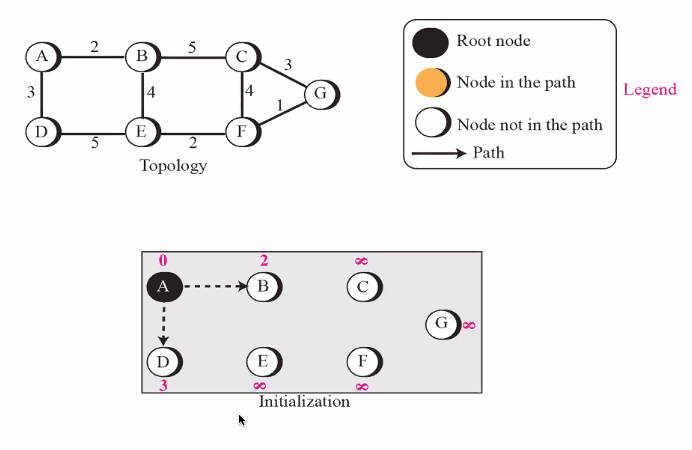
THe cost can be anything depending on the protcol (like latency)
Reading the table:
OSPF (Open shortest path first)
- Every router in an area computes the shortest path
- Two issues
- Determine router local environment
- Neighbour discovery protocol
- neighboring routers
- n links to connected networks
- n cost of the links (metric) - delay, $ cost, transmission time,
- xchange info with the rest of the oruters to maintain identicial database
- Link state protocol
- link-state packets are sent to all routers in the area.
- n they contain list of network links The open shortest path first protocol is an intradomain routing protocol based on link state routing. Its domain is also an Autonomous system
- Determine router local environment
- Neighbour discovery protocol
Key elements:
- Topology dissemination
-
Uses link state routing to compute shortest routes
- Open pub available
- Uses link state algo
- Link State Advertisement dissemination
- Topology map at each node
- route computation using dikjstra algo
- LSA flood throughout the entire AS
- Does not use any transport layer
- Directly over IP (Not UDP OR TCP)
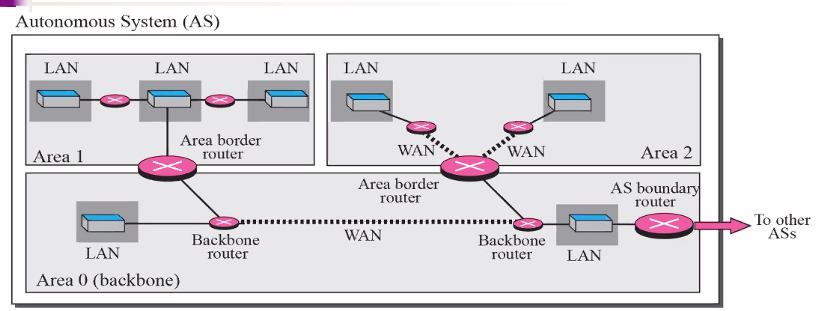
Area in autonomus system
- Within an OSPF area, all router maintain the same topoly database. They have no knowledge of network topolgies outside the area
- There is always one router connected to the outside
- There is two types of router
- Area border router: Lets network knows about the outside
- Backbone router
- AS boundary router: Carry infopmation of the network and send outside
Issues in building the routing table
- Determine router local env
- Neightbour
- Links
- Cost of links
- To exchange infomation with the rest of the router to maintain identical database
- Sent to all router in the area
- List of network links and their associated cost
For every netowrk interfacce a router has, Hello messages are generated:
- router ip address for that interface
- Hello interval
- Subnmetmask
- List of neighbour whose hello the sender has already heard
If there is no hello for 40 sec, the link is considered to be broken
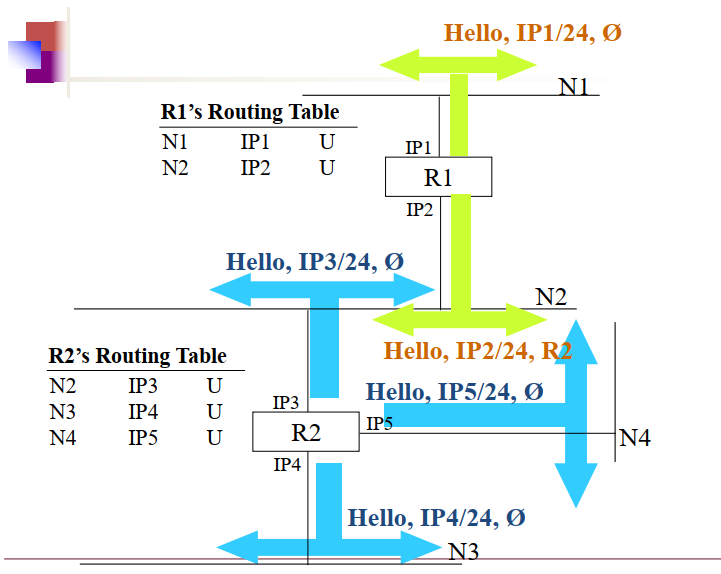
- IP5: Hello I am ip5, i dont know anyone
- IP3: Hello I am IP3, i dont know anyone
- IP4: Hello I am IP4, i dont know anyone
- IP2: Hello I am IP2, I only know where R2 is
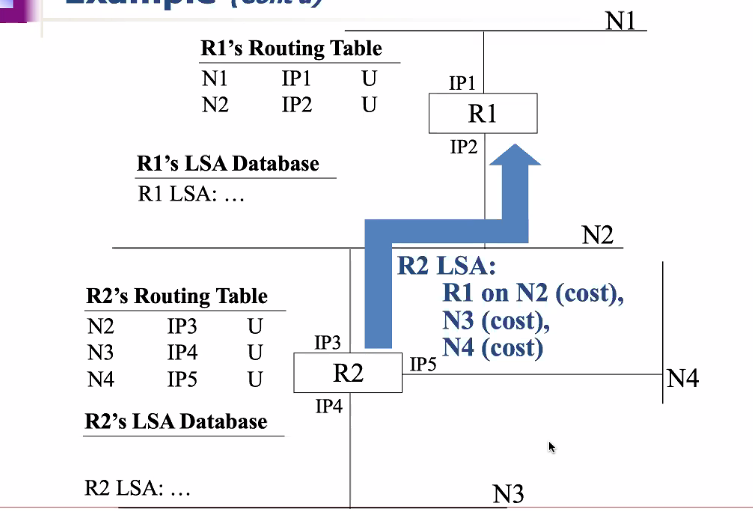
Link state advertisement (LSA): Each entity in an area distributes infomation about its llocal env in these packets
Sent only:
- Router discover neighboiur new
- Link to a neighbour down
- Cost of link change
- Basic refresh backets are sent every 30 mins
Sent using reliable flooding to syncrhonise
Every node will get to know the LSA of other nodes
- Recieving the LSA, the router will update its table
- If suppose new node is joining:
- New router says hello to its neighbours
- The subsequent will sent hello and spread to all its router in its table and continous
- Every router in an area recieves the LSA generated by other routers in an area and builds the database of LSA that describes the topology of the area
- The database of LSA maintained by all routers in an area are identical
- Each router then constructs the shortest path with itself as the root and using the metric as the cost to build its routing table
- U : Direct
- UG: Indirect
Types of Links for OSPF
- Point to point
- Transient
- Stub
- Virtual
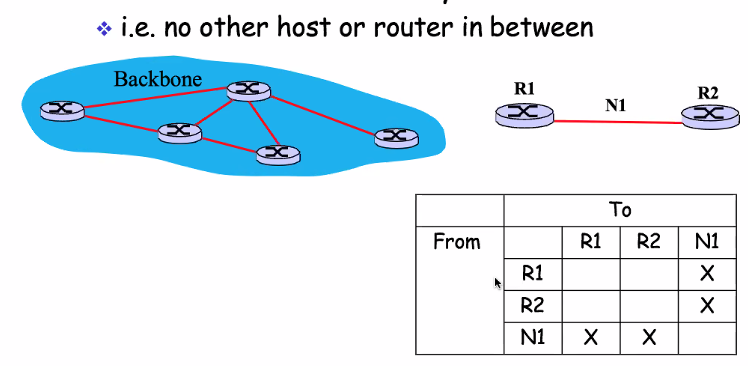
Point to point
- Connect router direct (The two router must be connected to each other)
- Can be backbone
- Can be for any area
Any arisement come to the network or from, it is applicable for both router
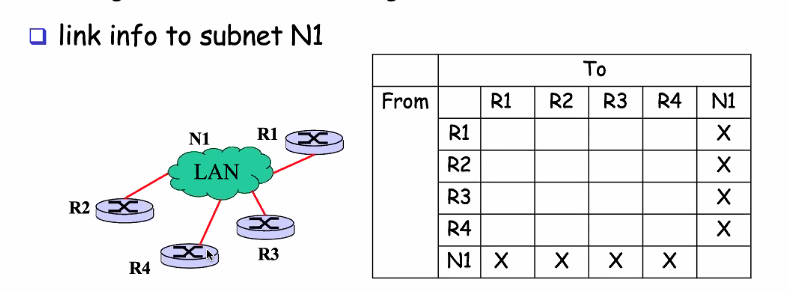
Transient
- Network have multiple router
- Packet enter and leave through any rotuer
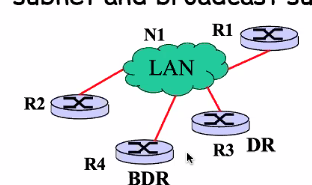
Designated Router (DR)
Our network sending infomation to the router but the subnet cannot speak for itself. For a broadcast domain with N router, its LSA Message complexity could be O(n^2)
- Designated router and backup router are elected to represent the subnet and broadcast subnet info (Using HEllo protocol)
- All advisement/info will be done by designation router
- ANy router that find changes, will communicate to DR
- DR will broadcast to everyone
- Backup will take over if the DR is not operating
- Each router will only have DR and BDR as neighbour
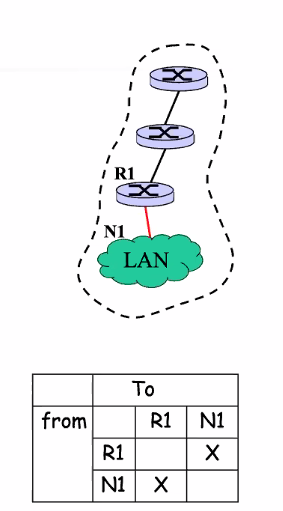
Stub
- Network connected to only one router
- Packets enter and leave throguh the same router
- R1 Becomes the DR for N1
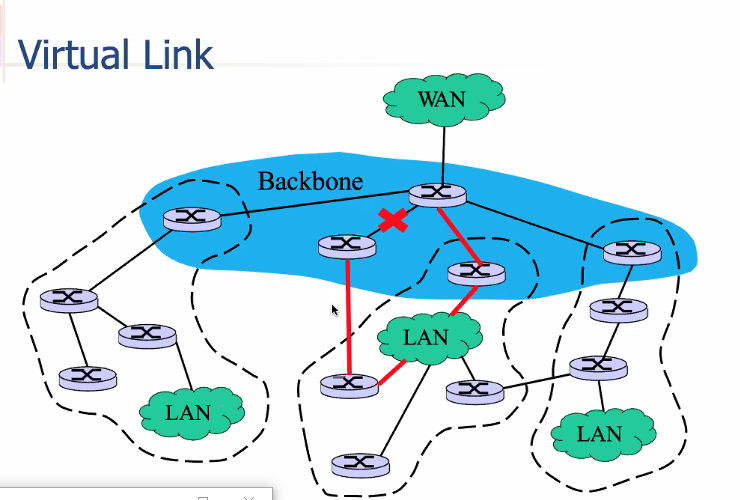
Virtual link
- Possibly that one of the links go down.. admin can configure another link but with a higher cost
OPSF Packets types
- Hello
- Database description
- Link state request
- Link state advertisment: Sending link state to the router
- Router link
- Network link
- Summary link to network
- Summary link to AS boundary router
- Extrernal link
- Link state acknowledgement
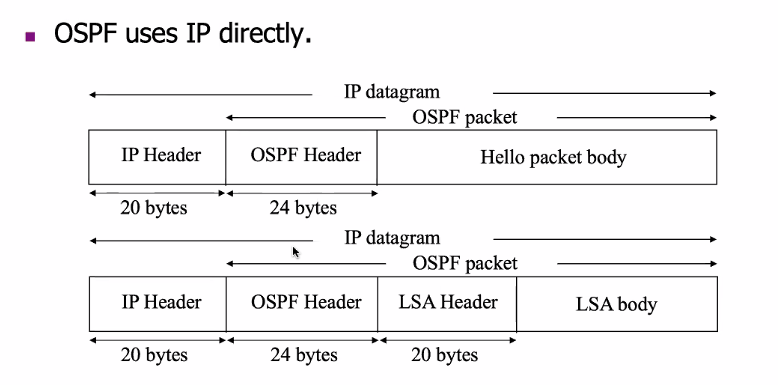
- OSPF uses IP directly
Hello messages and LSA are encapsulated in OSPF packets for transmission
Database synchronisation
- LSA Database initalisation when a new router is added to the segment
- DR send summary of its database of LSA to the new router - database description packets
- New router responds with a list of LSA that it does not have or that are outdated: Link state request packets
- DR forwards the full LSA in the list to the new router: Link state update or advertisement packets
LSA
- Router link: Sent by normal router
- Network Link: DR or BDR
Others:
- Summary link to network: Prov info on router or networks outside the area
- Summary link to AS boundary router: Flooded to all routers by ABR (Area border router)
- External Link: Info about networks outsides the AS
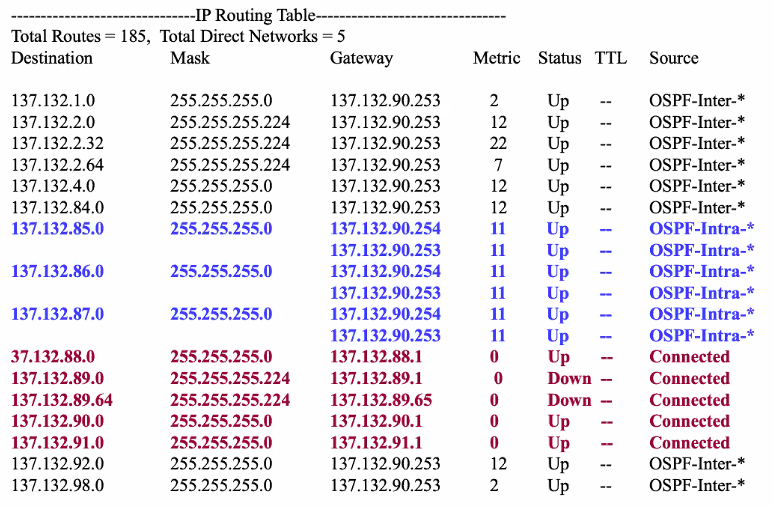
Router infomation maintained at Router
- Router maintains much more infomation than a host system
- Network mask is stored as part of the infomation
- Some sub subnet destination network
- Observe that the network mask is stored as part of the infomation
AD: Defines which protocol has a higher priority for portocol, this is to choose whether to use OSPF or RIP protocl