IoT Market and Challenges
What is a thing
- Mini computer system
- Sensors
- Actuators
What is Internet of things?
- Computing in Cyber Domain
- Limited interaction with physical environment
- Modern computational devices are cuber physical domains (IOT/CPS)
- Sensors and actuators
- Analogous to humans interacting with physical world
- Internet addressable
- Perform computaton
- Collect data
- Network connectiveity
- Control envrioment
- Enables remote operation and control
Various name, one concept
- M2M
- Internet of everything
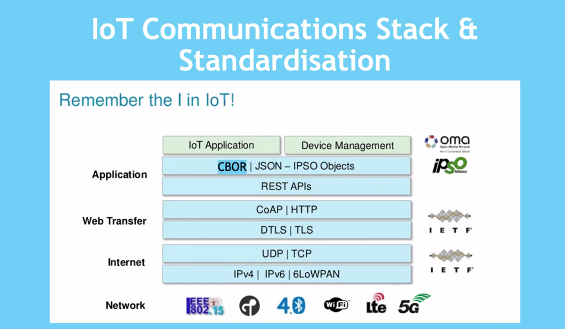
IOT Protocols and Standards and Application
The impact if IOT
- Billions of devices
- Many application fomains
- Different Business approaces
Challenges:
- Security
- High price
- Interfration with operational tech
- Lack of internal support
TOP IOT Tech
- Security
- Analysitcs
- Device management
- Low power short range IOT
- Lower power 5G
- IOT Processes
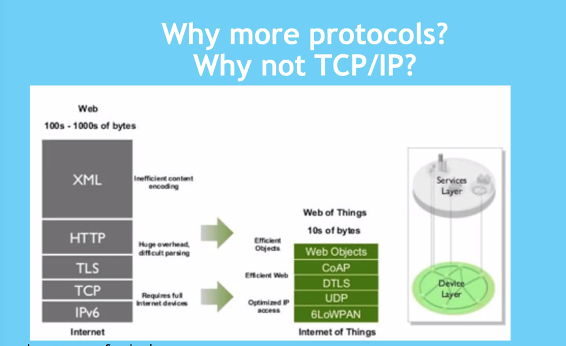
Why don’t use the original protocols
Why more protocols?
Why Not TCP/IP
The existing technology is good but the issue lies
- data usage
- Optimised IP access
such examples:
- XML : Inefficient content encoding
- HTTP: Huge overload , difficult parsing
- TLS/TCP/IPV6: Requires full internet devices
- UDP: No security layer thus relies on DTLS
- REST API: Lies on top of HTTP
- JSON: Not sufficient enough (Text based), this results in CBOR which includes binary data
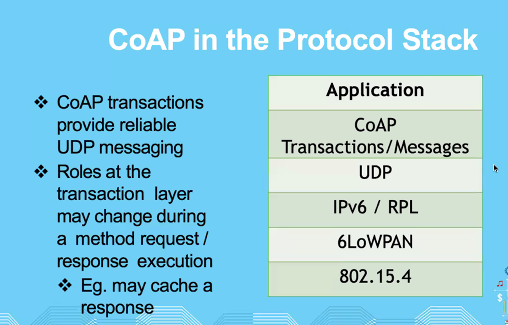
Co-AP , MQTT
CoAP
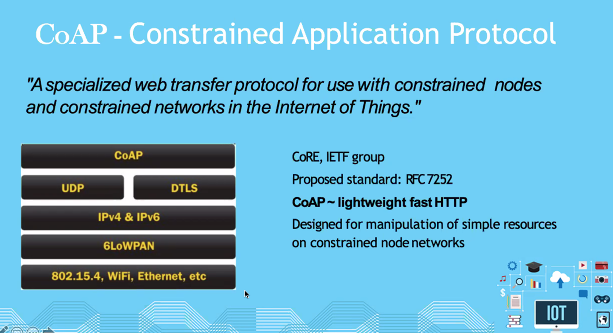
- Provides bluetooth
- 6lowPan: Adopting layer between bluetooth and upper layer
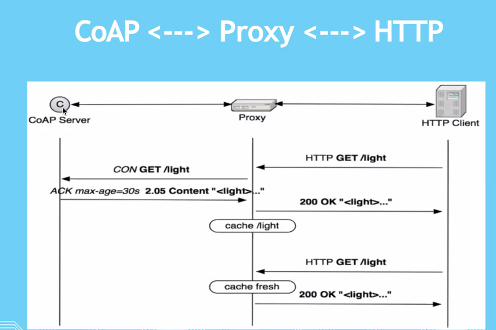
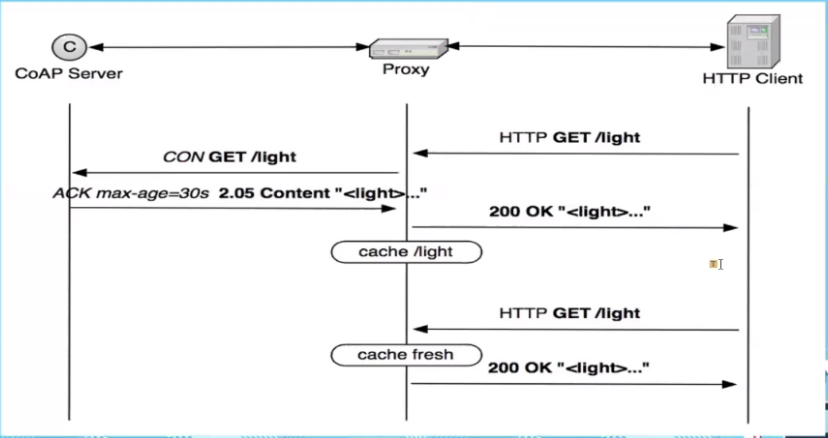
IOT devices will use CoAp to communicate to the proxy which will in term communcate to the server using HTTP. The reason why we do not use the IOT device to connect direct to the server using CoAP is also due to the cost of maintaining a network for such a small device
There can be many multihop protocols before reaching the proxy.. but most IOT is single hop.
Provides a restful environement.
- End to end is restful
- There can be a proxy
- Proxy can convert the COAP to http
- CoAP server is a light device
- HTTP Client gets the light infomation
- Proxy converts the outgoing CoAP to http, and incoming http to CoAp
- Can cache the value for 30 sec
- Reply returned is the from the cache, this is to prevent the requerying
Proxy can be edge router.. (IOT Gateway)
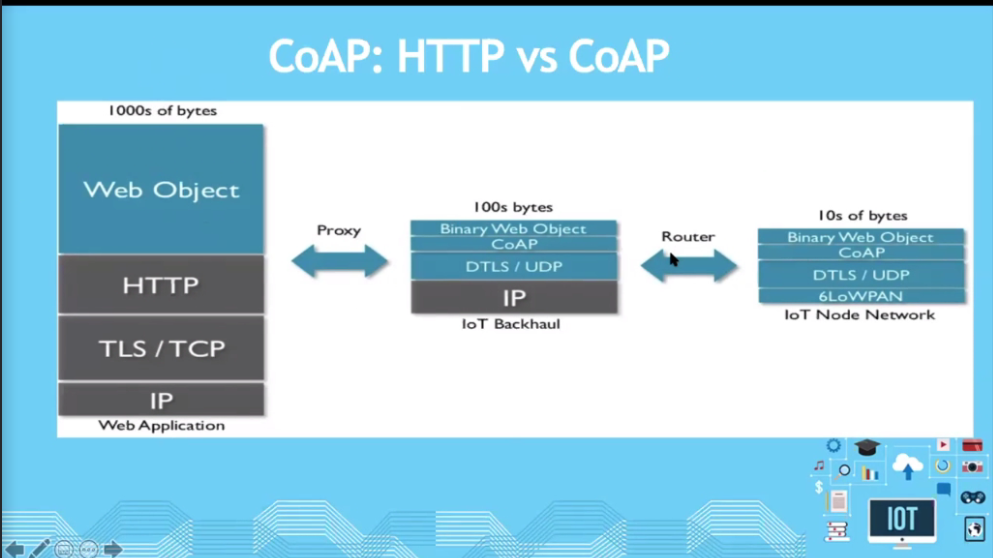
HTTP vs COAP
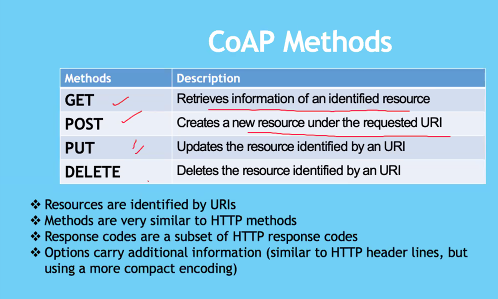
Functionalities of CoAp:
- Addressable URI
- Low Header overhead and parsing complexity
- GET/PUT/POST/DELETE
- Content type support
- Built in discovery
- Designed to be extensible
- Allows rest architecture
- Simple proxy and caching
- UDP binding (May use IPsec or DTLS)
It is better to have a public ip addressable so that the outside server can connect (that is why its ipv6)
6LowPan: Only for ipv6
Expectation is that every IOT device will have a public address..
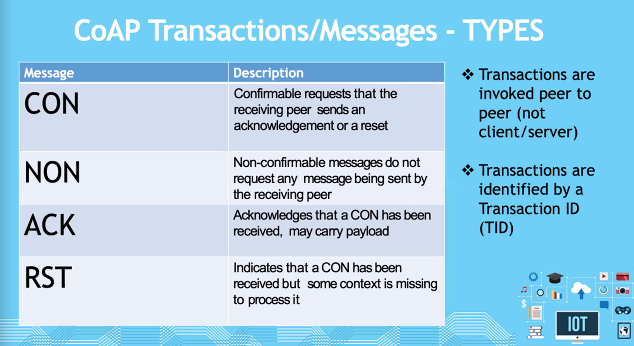
Types
Transaction here are considered peer to peer. Transaction are identified by a ID (TID)
Methods
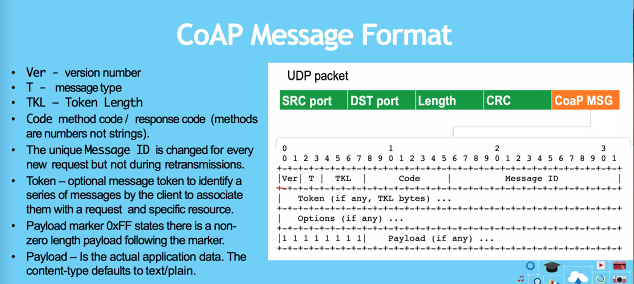
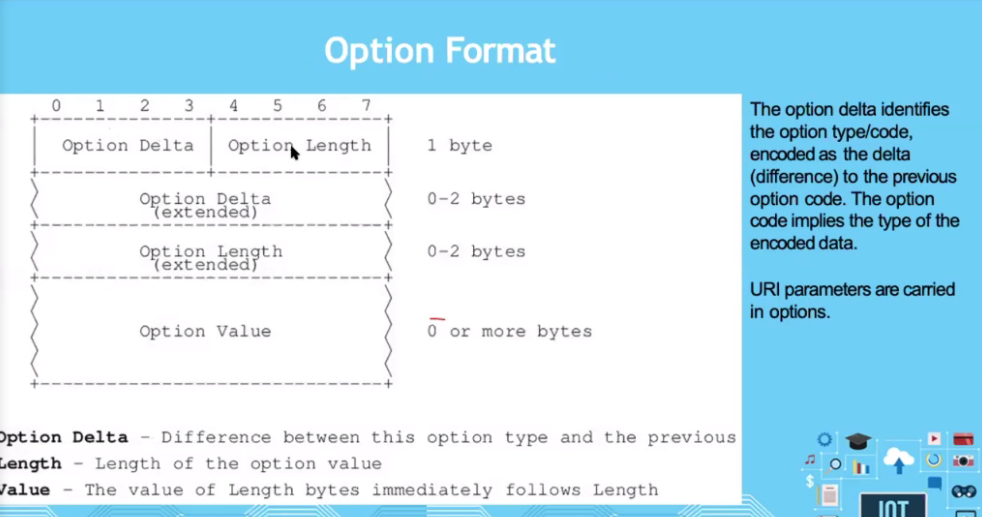
Message format
If theres a loss, what happens to the data?
If its a Confirmable request, there is a way to apply reliability
Examples
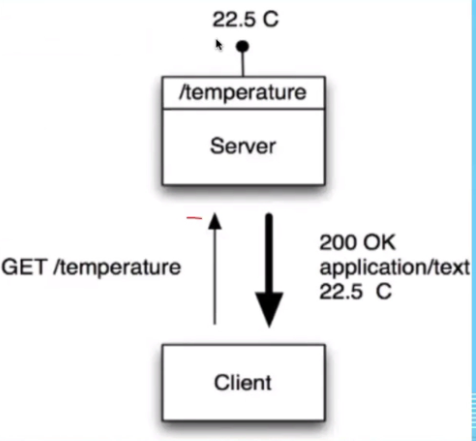
Client servers:
- URI path:
/Temperature
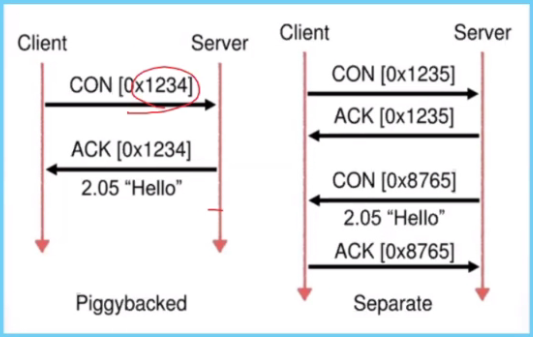
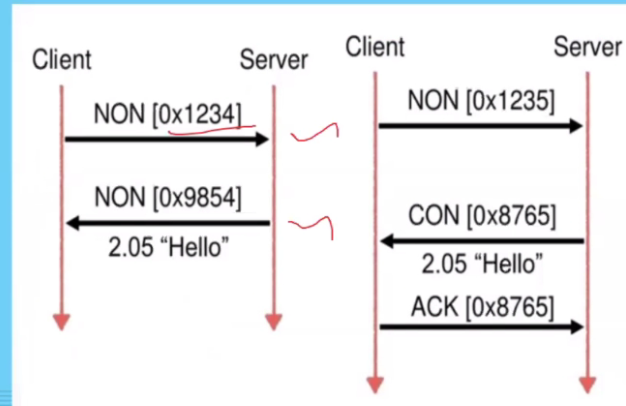
Confirmable:
- Response ID and Send ID is the same. Data is piggy backed wiht the response (ACK)
- If data is not ready, the data can be sent later..but the ID is different. In the seperate sending, the client sends the ACK
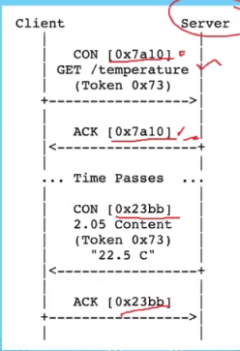
Using token:
- Data is not ready, so a token is sent.
- When the data is ready, the server will send a CON message (Which have different ID) but includes the same Token ID that was prev sent
Non-confirmable
- It is independent
- It is possible for the client to ask for a NON but the server sends a CON in reply.. (This depends on our application)
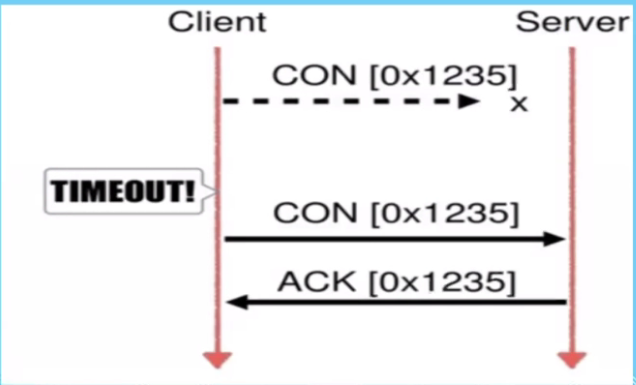
Is there a time out?
Yes, it is the time between the CON and ACK .. see RST
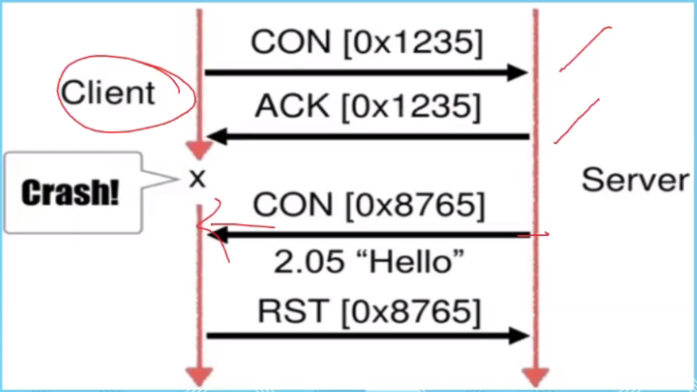
Reset:
- Data receives at the client, but the client does not know when it had made the request
- It sends RST to reset
*Packet Loss
- Use the CON and ACK to determined which packet has been lost
- If one side recieves another CON, means the packet was lost
Reliability
- message reliability is handled at application layer (Different application requires different waiting time)
- Congestion control (retransmit increase exponentially up to 247s): Might be improved
- This features can be disabled if we need more speed
If you disable congestion control: We need to handle it at application layer.
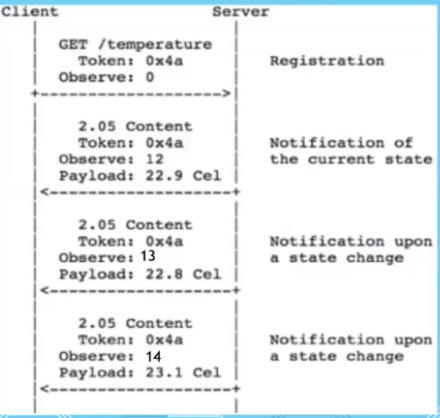
Observing resources
- Protcol extension
- Client intereseted in a resource over period of time
- Observer pattern
- Server to client (constrained devices acts as a server)
- State what you want to observe,
observe = 0 - Server will register
- Server will continue send data over a period of time
- Observe number will be random generated at first but will be increasing order afterwards
- Token sent will be the same throughout
Block transfer
- Extension added to CoAP Spec
- Transfers large resource representations
- Maybe get /light gives a very large amount of data
- Split the data into segments
- Sends them using the M to state the number of blocks that are following
- This continues until m = 0
Note that for each send, the client must ack back
This is a proposal now that just accepted so not all vendors has it
Caching
- Freshness Model: Focus on Max age, proxy uses this data to see if can resent the data
- Validation model: Check using Etag option
- Proxy would cache the data and when the HTTP client calls again, it can use the cache provided that the Max age has not timed out
- Code 2.05 means HTTP
- MID: Message ID
- Payload: Data
- Token: (See token in examples)
Deals with packet loss using token as an identifier
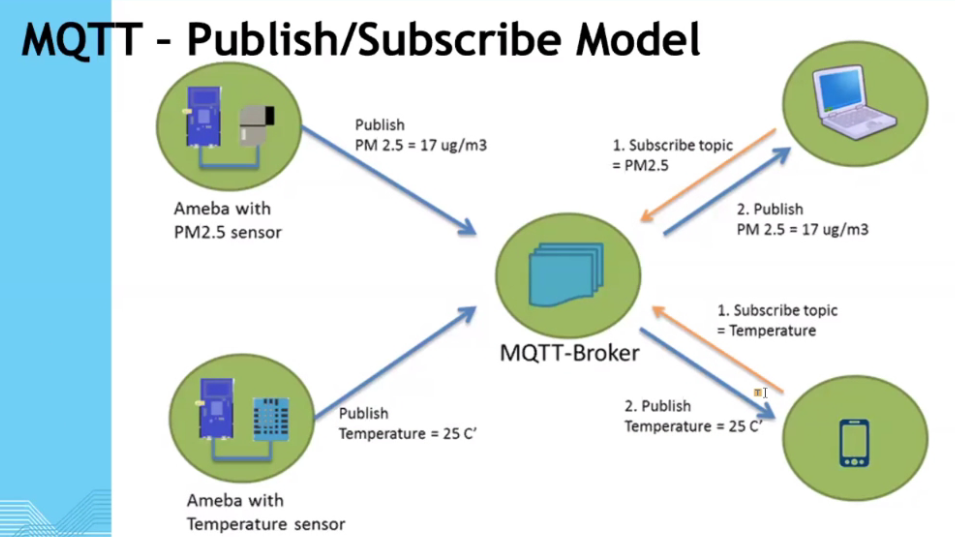
MQTT
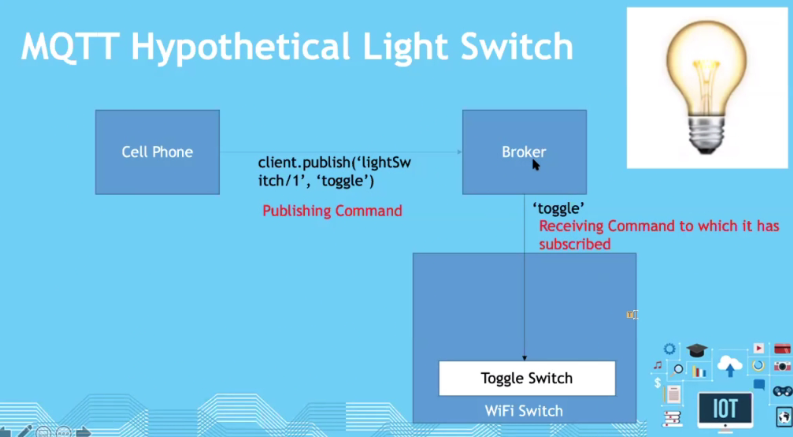
Example:
- Publishing can be data or command
- Subscribing to this data means you will get this command
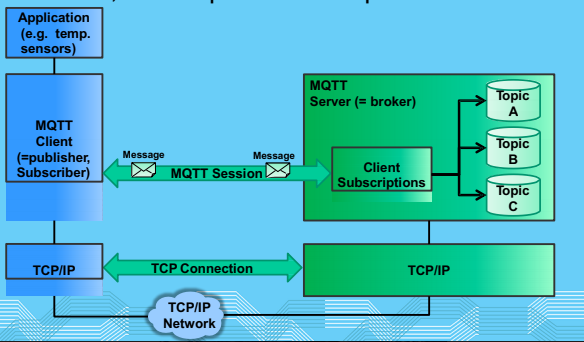
MQTT Model
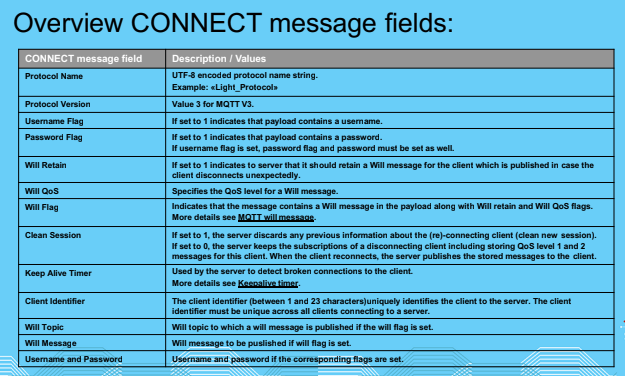
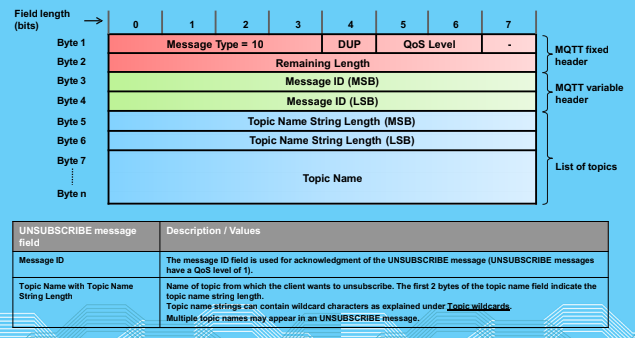
The core elements of MQTT are client, servers (brokers) , session , subsciption and topics
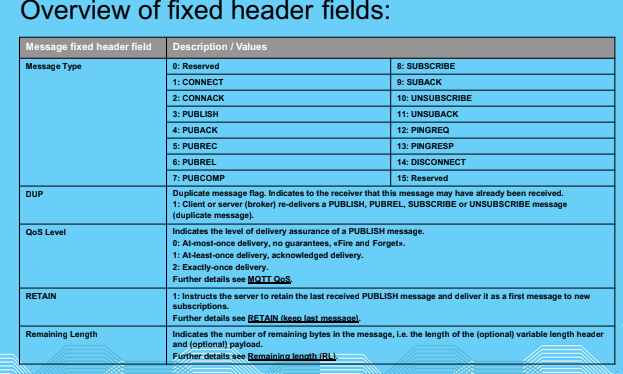
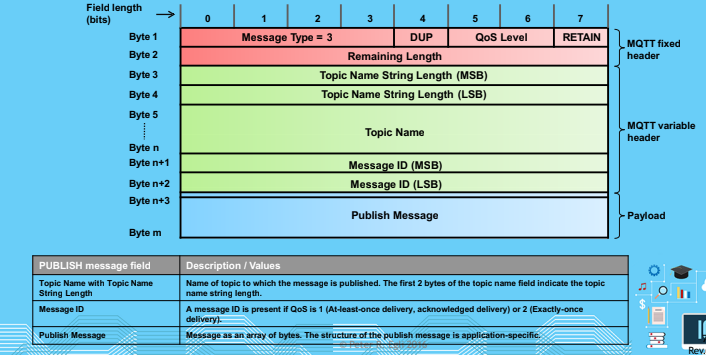
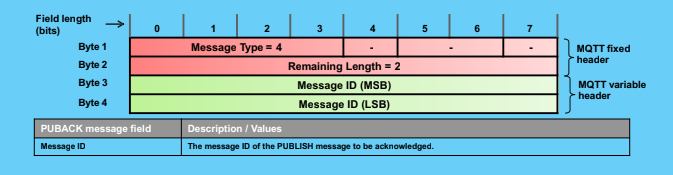
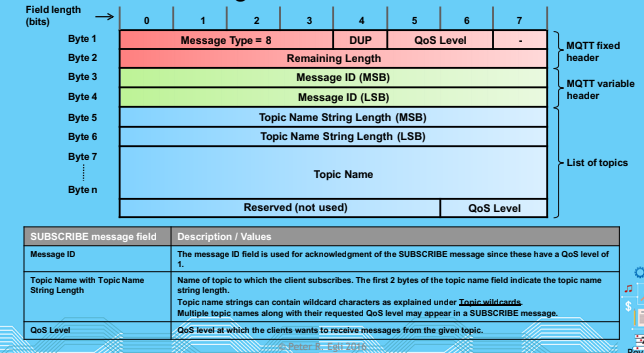
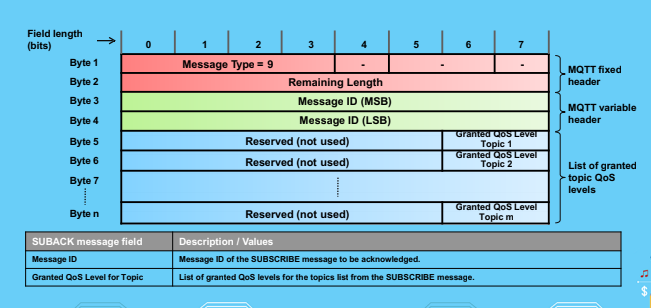
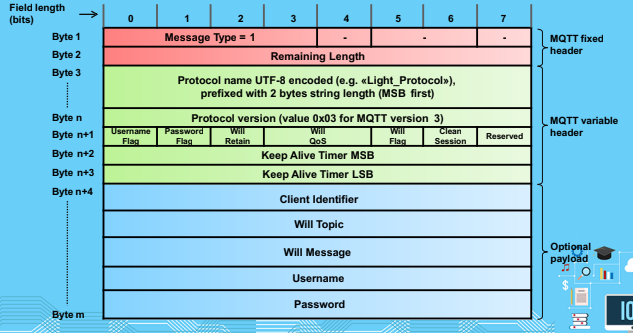
Message format
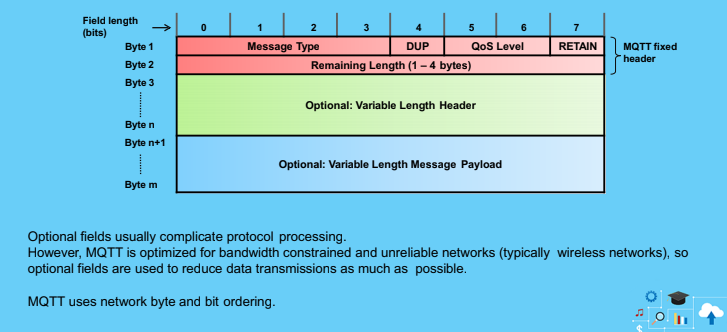
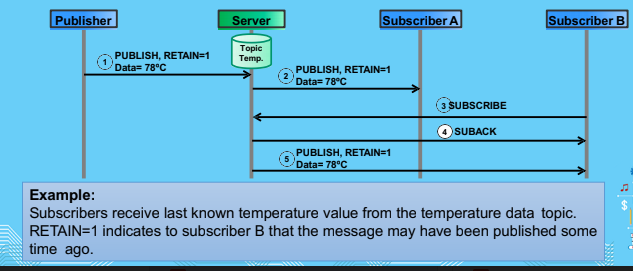
Retain
- Retains the message for the next client that subscribes
- The new client would recieve the previous message
- RETAIN=1 in a PUBLISH message instructs the server to keep the message for this topic. When a new client subscribes to the topic, the server sends the retained message.
Connect
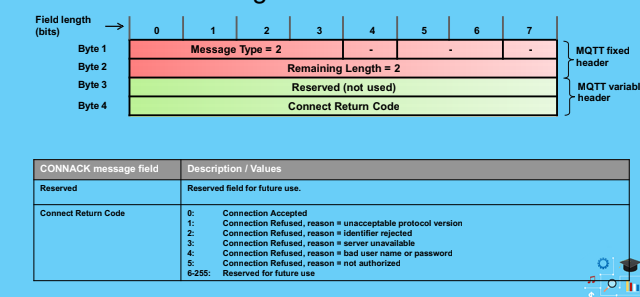
Connack
Publish
PubAck
Subscribe
SubAck
Unsubscribe
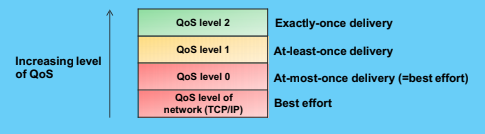
MQTT QoS
- Provides typical delivery quality of services levels of message oriented middleware
- Even thou TCP/IP provides guaranteed data delivery,data loss can still occur if a TCP connection breaks down and messages are lost in transit
- MQTT adds 3 QoS levels on top of TCP