Forusans DNS
Name space
A name space that maps each address to an uniqye name can be organised flat or hierarchical.
Flat Name
In a flat name space, a name is assigned to an address. A name in this space is a sequence of characters without structure. The names may or may not have a common that is cannot be used in large systerm such as the internet because it must be centrally controlled to avoid ambiguitive and duplication.
Hierarchical Name space
In a hierarchicaly name space, each name is made of several parts.
1) Nature of the organisation 2) Name of organisation 3) Define departments in the organisation etc.
- Manager does not need to worry that the prefix chosen for a host is taken
Label
- Each node in a name tree has a label:
- A string with max 63 chara
- ROot label is annull string
- DNS requires children of a node have a different label whcih guaranteese the uniquesness of the domain names
Domain
Fully qualified domain name
- Label terminated by null string
- a domain name that contains the full name of the host
- Contain all labels from most specific to the most general
- Label ends with dot (.)
Partially qualified domain name
- Label not terminated by null string
- Starts from node buyt does not reach a root
- Used when the name to be resolved belongs to the same site as the client
- Resolver can supply the missing part called suffix to create FQDN.
Domain is the subtree of domain name space. The name of the domain is the name of the node at the top of the subtree.
DNS server serves as a hierarchy of name server to divide the whole space into many domains based on the first level.
Zone
- What server is responsible for is called a zone
- Contigupous part of the entire tree
- If server doesnt divide their zone, the domain and zone is the same thing
- Server keeps every info about every node in its domain
- If server creates subdomain, domain and zone are different
- The server only need to care about the top level nodes
- Original server might keep some sort of references of these lower level servers but most details are kept by the lower level servers
Root server
- Server whose zone consist of the whole tree
- Does not store info about domains but keep referecnmes of other servers and delegates it authority to other server
Primary
- Stores a file a about zone for which it has authority
- Responsible of maintaining, creating and editing zone
Secondary
- Transfer the info about a zone from another server
- Store info in local disk
- Neither creates or updates zonefile
Pri and secondary are both authroitative for the zones they serve - Create redundancy for data
A server can be a primary server for one zone and a secondary for another zone at the same time.
DNS in the internet
Generic domain
- Define generic host accourding to their behavior
COuntry domains
- Use two character country abbreviation
- Second labels can be organisational and more specific
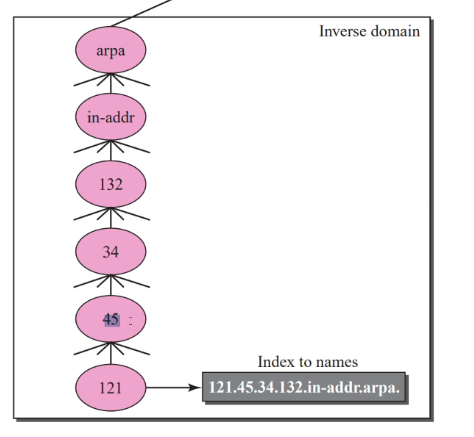
Inverse domain
- Map address to name
- Server ask resolver to send query to the DNS server to map an address to a name to determine if the client is on authorisation list
- Pointer query: The inverse domain is added to the domain name space with the first level node called arpa
- Second level: A single node name in-addr which store the ipaddress in reverse order
- Second level: A single node name in-addr which store the ipaddress in reverse order
Look up will be 121.45…
Registra
- Handle new domains added to DNS
- ICAAN
- Verifies the domain is unique then enters it into the DNS database
Resolution
Mapping a name to address or vice versa
Resolver
- DNS client that maps the address to name or the other way round
- Access closest DNS server with mapping request
- Has info: Resolves
- No have info: Refers to others
- Interpret the response to see if it real resolution or error
- Delievers to the process that request
Mapping name to address
- Gives domain name to server and ask from corresponding address
- Generic:
chal.atc.fhda.edu - Cannot resolve: Refers to other server
- Country:
ch.fhada.cu.ca.us
- Generic:
Mapping address to name
- Client sent ip address to server to map (PTR)
- DNS use inverse domain
- IP address is reverse with arpa and ipaddr appended
- Resolver:
- Invert
- Send with in-addr.arpa appended
Recursive resolution
- Resolver expects server to supply final answer
- Server not authority: ask other server and wait
- Server authority: Returns response
iterative
- Same recursive but if cannot reply then it returns the ipaddress of the server that it thinks can reply
- Client responsible for repeating the query till it gets the server
- Iterative because the client repeatedly send the same query to different servers until it gets answers
Caching
- Stores info into cache memory
- Marks the response as unauthoritative if its from its cache
- Speeds resolution but can be probamatic
- Uses TTL to check if its current
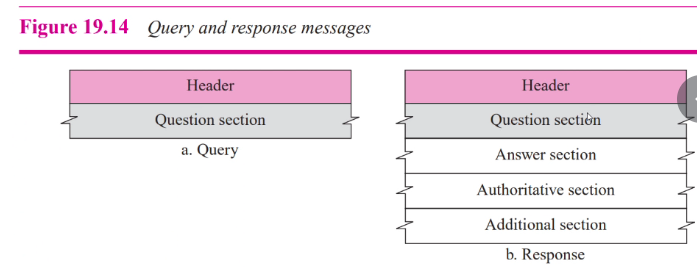
DNS Messages
- Query and response
- Same format
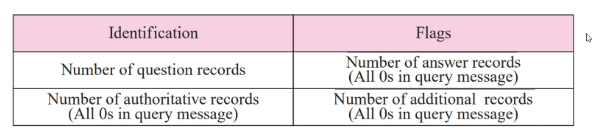
Header
- Set to 0 for querys for some fields
- 12 bytes
-
Indetification: 16 bit use by client to match response with query. Use a different id number each time it send query.
-
Flags: 16 bit consisting of subfields
(4 bytes)
- Num question record: Num of queries in the question section
- Answer: Num of answer records in the answer section of the response message, value is 0 in query
- Num of autho: Num of authroative records in response
- Num of additional : Additional section of resposne message, value is 0 in query



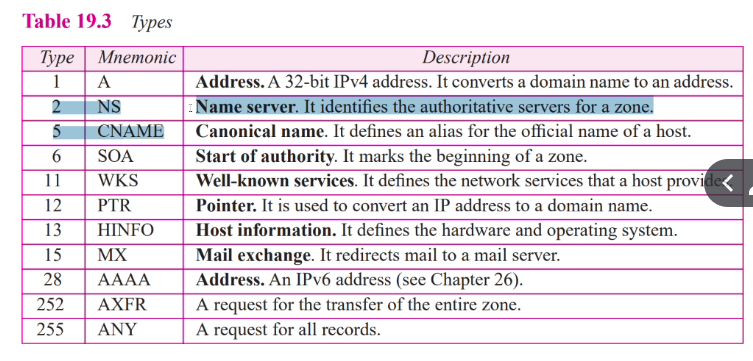
Types of records
- Question: Question section
- Resouce: answer, authroitative, additional
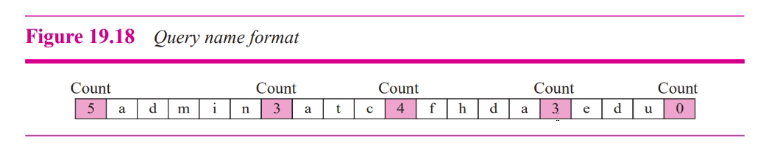
Question records
- Get info from server
- COntains domain name in query name
- COunt field: States the number of character
Types of query:
Query class:
- Define the specific protocol using DNS
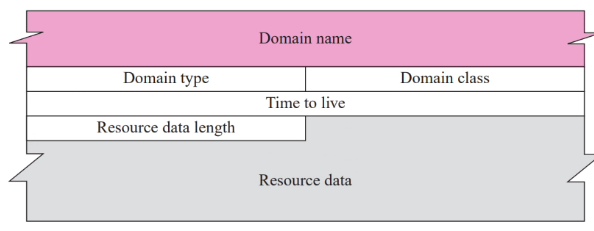
Resource records
- Each domain name is associated with record called resource record
-
Return from server to client
- Domain name: A pointer offset to the question record
- Domain type: Same as query type field in question record
- Domain class: Same as question records
- TTL: 32 bits that determine when it is valid, 0 record means rr is used only in single transaction and is not chace
- Resoucedata: Contain the answer to query or domain name of authrotitative server such as
- A number (ipv4 or ipv6)
- Domain name
- OFfset pointer: Domain names replaced by this
- Character string