Overview
Authentication: The process of assuring that the communicating entity or the origin of a piece of info is the one that it claims to be
Types:
- Entity authentication
- For connection oriented communication
- Communicating entity is an entity involved in communication
- Mechanism: Password, challenge, response and biometrics
- Data origin authentication
- For connectionless communcation
- Communicating entity is the origin of a piece of info
- data origin authneticity implies data integrity
- Mechanisms: MAC or digital signature
Threats
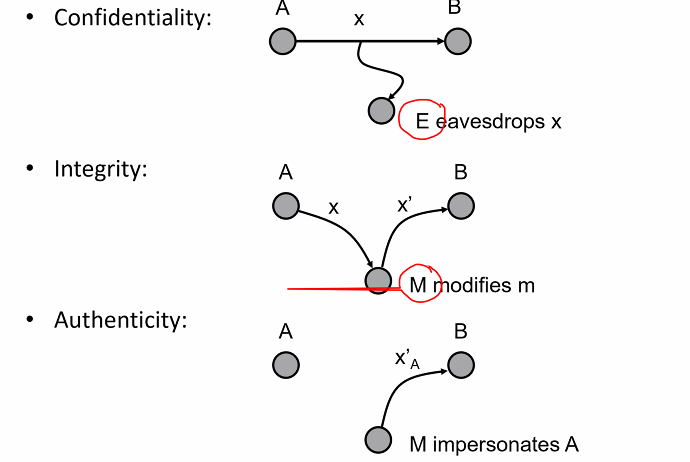
Authenticity and integrity
- Authentic: The claimed entity/origin is assured by supporting evidence
- Authenticity: The condition of being authentic
- Authenticity and integrity: Are they related? Yes
Data origin authenticity implies data integrity
- Authenticity is a stronger requriement than integrity
But the reverse is not true: Data integrity does not imply data origin authenticity
- Some documents use the term integrity to mean authenticity
- Some claim that authenticity does not necessarity give integrity
- Pay attention to the context and the application involved
Examples
Over different communication channels:
- Alice get call
- Claim to be from police
-
“Police” ask for info regarding brother
- Alice log into luminNUS
- Wonder if laptop is actually interacting with the real lumiNUS
-
Why is lumiNUS server convinced that the user logged in is ALICE
- ALice tries to connect to WIFI using phone at NUH
- The was item “NUS” listed in wifi list
- Was that WIFI access point real?
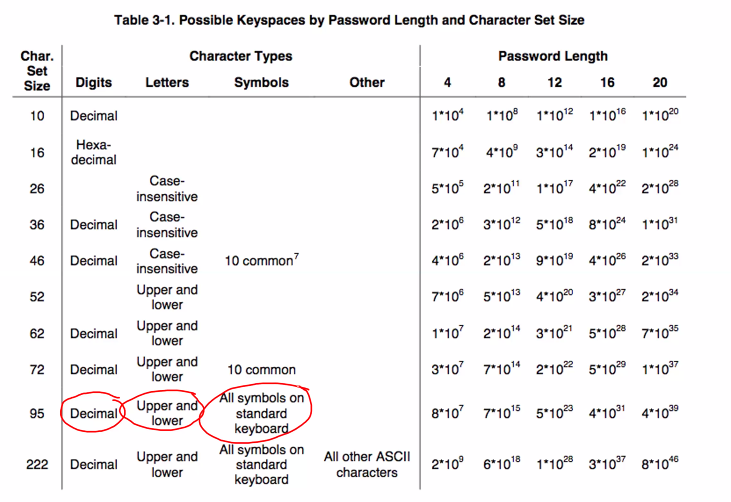
Password (Weak authentication)
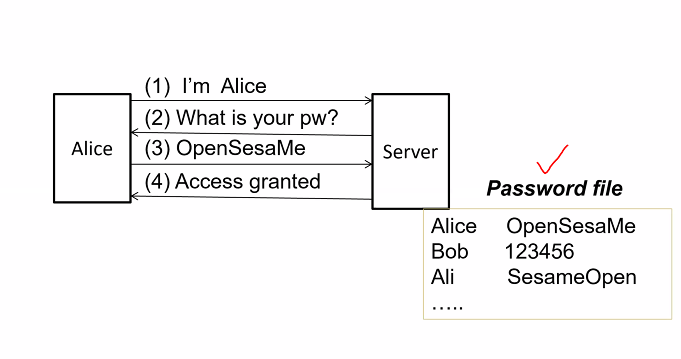
Stage 1: Bootstrapping
- Server and user establish common password
-
Server keeps track of a file recording the identity and corresponding password
- The password is to be established during bootstrapping
- This can be done
- Server choose password
- Default password
Question: Describe some bootstrapping mechanism that you have encountered
Stage 2: Authentication
- Server authenticates an entity
- If entity gives the correct password corresponding to the claim identity, the entity is deemed authentic
The identity does not need to be kept secret:
- It could be: User name in computer system, bank accound no, customer id
The password is a secret:
- Only user and server knows
Question: Anaylyse a password system where no identity is involved
- Same password
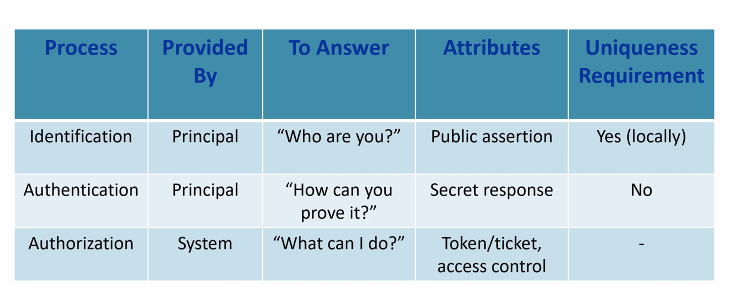
Identification, Authentication, Authorisation
Password system is classified as weak authentication system
- Weak authentication: Something subjected to simple replay attack, infomation can be sniffed from communication channel and can be used to impersonate the user
- Strong authenticaton:
- Info sniffed during process cant be used to impersonate the user
- PKI
Understand the difference between sniff and spoof
Possible attacks:
- Attacking bootstrapping
- Search password:
- Guess
- Dictionary
- Exhastive
- Steal:
- Eavesdropping: Sniff the network , use key logger
- Phishing
- Spoofing login screen
- Password caching
- Insder attacks
Intercepting password while bootstrapping
Attacker may intercept the password during bootstrapping
Attacker use default password
There are IOT devices which still has the default password
Question:
- What are the implication of shipping all access with the same default password
- With same password, attacker can access the device if the common default password
- What are the implication of shipping each access point with its individual password
- Expensive: Database and printing
- Usability will decrease for users when they cannot find the password (Bad product review) Tutorial question
Searching password
The attacker gain social info about user and infer the password
- Mobile phone number, spouse name
Password guessing:
- Online guess: Directly interacts with authentication system
- Offline guessing: An attacker can obtain the password file from authnetication system
Exhastive search and dictionary attacks
- Attacker tries differnet password during login sessions
- Attacker can employ exhastive search: tries all combo
- Restrict the search space to large collection of probable passwords
- Words from dictionary
Dictionary attacks
Hybid attacks: It is possible to carry out exhastive search together with dictionary attack/
Stealing password
Shoulder surfing, sniffing
- Shoulder surfing: Look over the shoulder attack
- Sniffing: Listening/intercepting the communication channel:
- Some system and protocol simply send the password over a public network in clear
- FTP, Telnet, HTTP/
Key-Logger
Captures/records the keystrokes and sends the info back to attacker via covert channel
- By software: Some computer virus are designed as keylogger
- By hardware
Login spoofing
Fake loging screens
Prevention:
- Some system has a secure attention key or secure attention sequence
- When press, system starts the trusted login processing
Phising
- Same as login spoofing
- User is tricked to voluntarily send password to attacker over network
- Phising attacks ask for password under some false pretense
Spear phishing
- Phisihing can be targetted to a particular small group of users
- Such attacks is known as spear phishing which is targetted
- Social engineering attack
Prevent phishing:
- User education
- Phishing repository site
Password caching
- Shared workstation, password can be stolen
- Prevention: Clear browser cache
Insider attack
- Malicious system admin who steals password file
- System admin account is comporomised, leading to lost of password file
Preventive measures
- Random
- Automated password generator
- High entrophy but difficult to remember
- Limited login attemps
- Add delay in login session
- Add security questions
- Lock account after few failed attempts
- Password checker:
- Check for weak password
- Password metering: Indicate weak, avg, strong password
- Password ageing
- regularly change password
- Password usage policy
- Rule set by org to ensure that users use strong password
- e.g password has to be 10 chara long
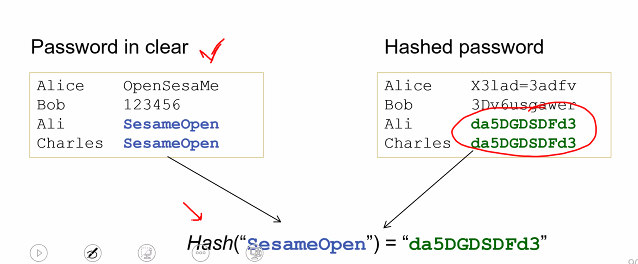
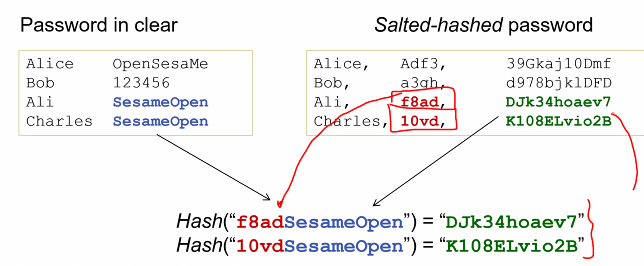
Hash password
- Passwords should be hased and stored in password files
- During authentication, the password entered by entitty is hased and compared with the value stored in the password file
-
Desired tthat the same password will be hased into two diff values for two diff userid
- salt
Security questions
- Fall back authentication or self services password reset
- Enhancing usability: A user can still login even if password is lost
- Reducing cost: Reduces operating cost of help desk
- (BAD) Weakening security: Attackers have another mean to pbtain access
- Common secret questioN?
- Pet name etc
Choosing:
- Memorable
- Consistant: should not change over time
- Nearly universal: Question apply to a wide audience of people
- Safe: Answers should not be something easily guessed or researched
ATM attacks
To get authenticated, user has to present a card and the PIN. The card contains a magnetic stripe which stores the user account id. Essentially, the magnetic stripe simplidies the input of accound id into ATM system: Instead of keying in
- The pin: password
- Data: Encoded into magnetic stripe using well known standards, attacker can cipy the card by reading the info from the card and write on spoofed card
ATM skimmer
- Reveals the victim account id (Username and password)
- Consist of
- Card reader attached on top of existing ATM reader
- Camera overlooking the keypad or spoofed key pad
- Some means to record and transmit the infomation back to the attacker
Attacker can 1) Spoof victim ATM card 2) Obtain the pin
Preventive measures
- Instll anty skimmer device
- Shield the keypad
- User awareness
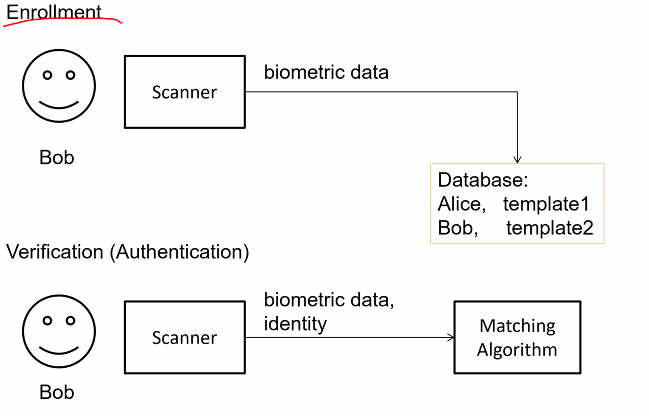
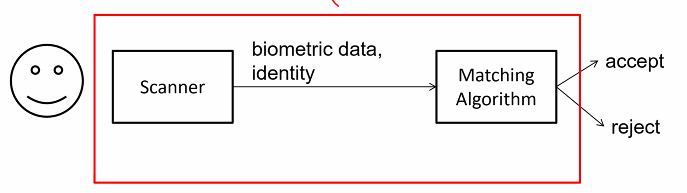
Biometrics
- Uses unique physical characteristics of a person for authentication
- Enrollment: reference template of an user biometric data is constructed and stored
- Verfification: Biometric sample data of person in question is captured and compared with template using matching algo
- Algo decides if to reject or accepts
Diagram:
Differences
| Password | Biometrics |
|---|---|
| Can be changed (revoked) | Can’t |
| need to remember | Dont have to |
| Zero non matched rate | probability of error |
| User can pass the password to another person | not possible |
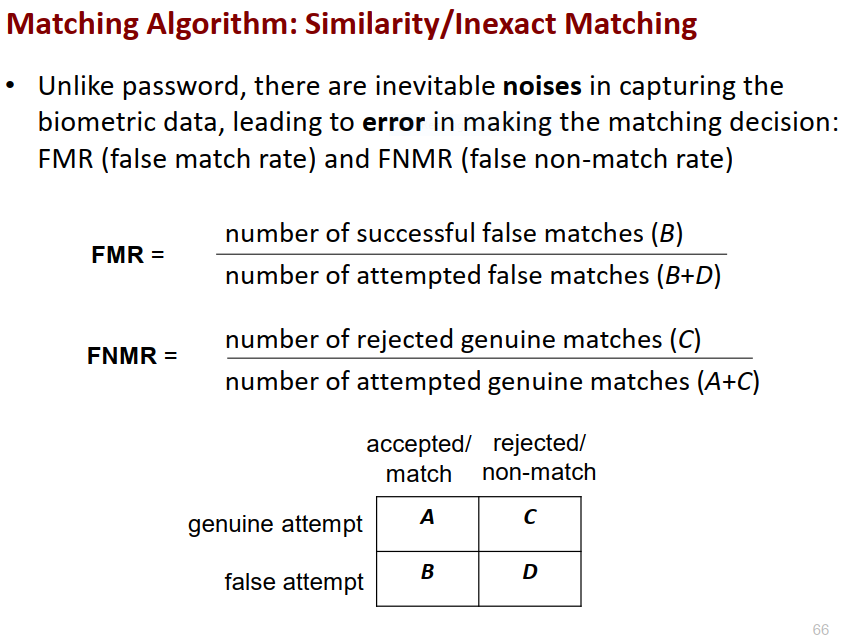
Matching algo: Similiarity
- there might be noises in capturing data
- leads to error making matchinf decision
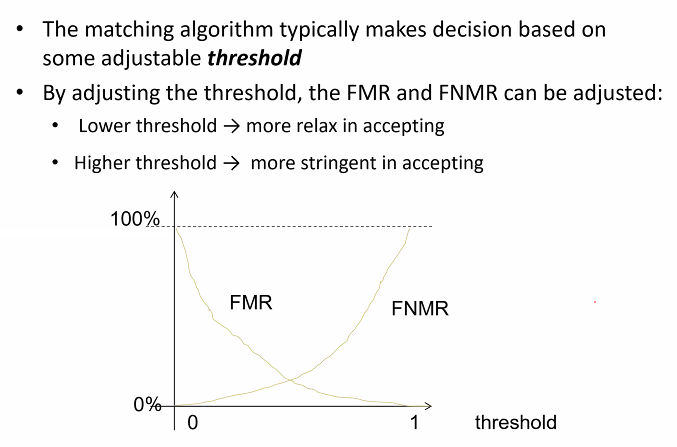
Threshold value selection
- make decison based on adjustable threshold
- Lower: More relax in accepting
- Higher: More stringent
Other erros
- Equal error rate (EER): When FNMR = FNR -Failure to enroll rate (FER): Some user biometric data cannot be captured during enrollment
- Failer to capture rate(FTC): Users biometric data cannot be captured during Authentication
Multifactor authentication (2FA)
- Require at least 2 different authentication factors
- Common factors:
- What you know: Password, pin
- What you have: Smart card, atm, mobile phone, OTP,
- Who you are: biometrics
- Possible factors:
- Where u are
- What u do
- It is called 2 factor authentication if 2 factors are employed
- MAS expects all banks in sg to provide 2fa for ebanking
What you have
OTP Token
- A hardware that generates one time password
- Each token and the server shared some secret
- Types:
- Time base: Based on the shared secret and current time interval, a password k is generated
- Sequence based: An even triggers the change the password (Like user pressing the button)
Password + OTP Token:
Registration:
- The server issues a OTP token to the uer which contains a secret key that the server knows
- User set a password
Authentication:
- User press the token which computes and display OTP
- User sends username and password and OTP to server
- Since the server has the secret key, the server can also compute the OTP
- Server verifies that both otp and password are correct
Password + Mobile phone (SMS)
Registration:
- User gives the server his mobile phone number and password
Authentitcation:
- User sends password and username to server
- Server verifies that the password is correct, server sends OTP to the user via sms
- User receives the SMS and enters the OTP
- Server verifies that the OTP is correct
Examples:
- Singpass, internet banking
SMS OTP is not secure
Security threats:
- Interception of cellular network channel
- SMS messages are stored as plaintext by the short message service center
- Malware and trojan on smartphones
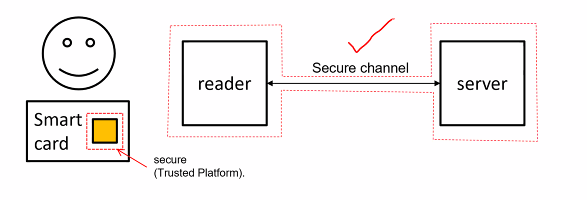
Smart card and Finger print (door access system)
Registration:
- THe server issues a smartcard to the user (which contains a secret key k)
- The user enrolls his fingerprint
Authentication:
- User insert smartcard to the reader.
- The reader obtains the user identity and verifies whether the smart card is authentic. If so, continue
- User presents fingerprint to the reader
- The reader performs matching to verify that it is authentic, if yes open door
Security requirements:
- Very often info on user identity, the secret k, and fingerprint template are not stored in the reader
- The reader has a secure communication channel to a server that stores these info
In this case we also assume that the reader and server are secure. (Attackers are unable to access them)
Notes:
- A smart card has this security feature: Even if an attacker has a physical access to card, it is extremly difficult if not impossible to extract a secret stored in a card
- What are the actual two factors
- What is the role of the secret
- It is possible to eliminate the need of the server e.g By storing the fingerprint in the card and storing a small secret key in the reader
How to achievement