Experiement
Command link: Click me
Korusans
- Router is a layer 3 switch
DHCP
Note how many times the srever sends a broadcast
NAT
- A table in the router
- MAPS the IP address from outside to the client
See Different networks in FORSUANS
VLAN
Drawback with hierechally:
- Lack of traffic isolation: Broadcast traffic must traverse its own instituitional network. This also might be a security flaw since the packet have to go through the entire networks to reach the top hierachy
- Inefficient use of switches: A single switch will not be able to provide traffic isolation. If assign a switch to a small group of people e.g 10, we have to waste a 96 port switch
- Managing users: Can move within groups easier.
Switch just have to supports VLAN.
- Host within VLAN communicate with each other as if its connected through a switch
- In a port base vlan, the host are divided to groups
- when moving to another group, network manager just need to reconfigure the vlan software so that the port that person is connected to will be associated with the other VLAN
- Table of port to VLAN is maintain within the switch
- Switch hardware only delievers frame to the same vlan
New difficulty:
- how does traffic from one vlan to another
- Configure a router with the VLAN connected to the router and just configure that port too belong to both groups
The datagram would go first go to VLAN to reach router before being forwarded by the router to the other VLAN
- Configure a router with the VLAN connected to the router and just configure that port too belong to both groups
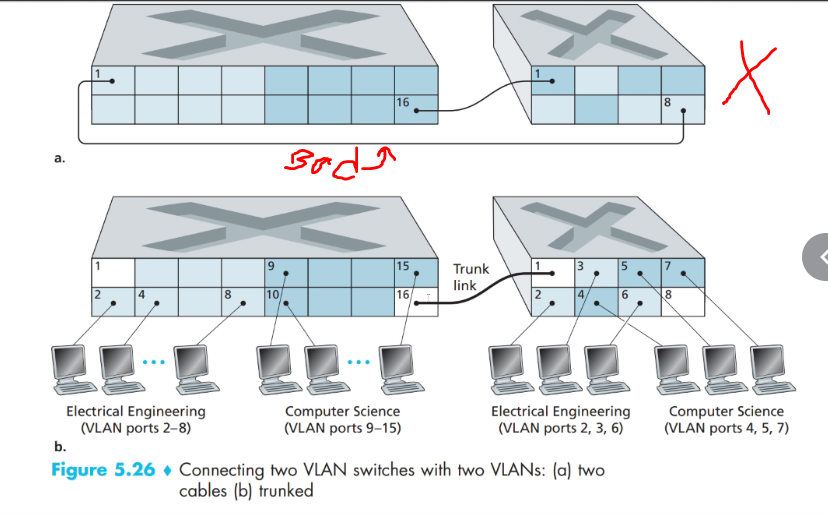
Another scalable approach is to interconnect vlan switches with VLAN trunking.
- A special port on each switch is configure as a trunk port to interconnect to the VLAN switches
- Trunk port belongs to all vlans
- Frames Sents to any vlan will be fowarded to the other VLAN through the trunk link.
how do we know which vlan is the packet suppose to be
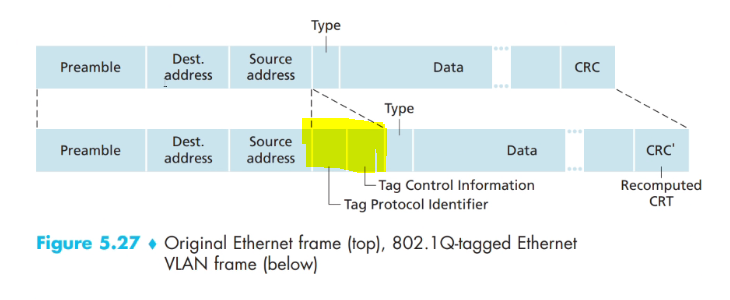
- Extended ethernet frame format contains a 4 bit vlan tag in the header that carries the identify of the vlan to which the vlan belongs
Connecting two routers from two differnet location:
Use trunking to connect two different router from differnet location
TPID field (VLAN TAG)
- Tag protocol id
- Tag control info
FORUSANS
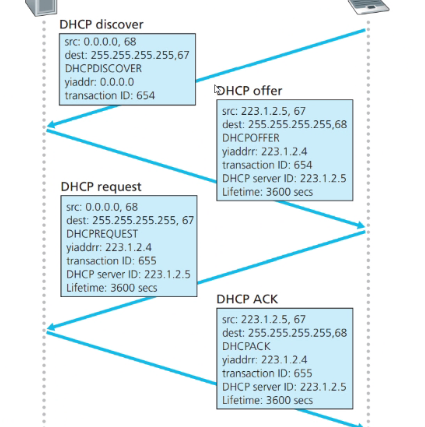
DHCP
Can be same networks or differnet
Same networks
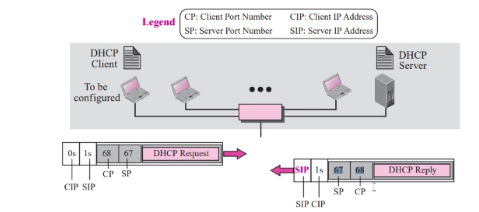
- DHCP issues a passive open command on UDP port 67 and waits for client
- Booted client issues an active open command. Message is encapsulated in UDP user datagram, which in turn encapsulated in IP datagram
- Client use all 0 as source
- All 1 as dest
- Serverr response with either broadcast or unicast message using UDP source port 67 with destination port 68
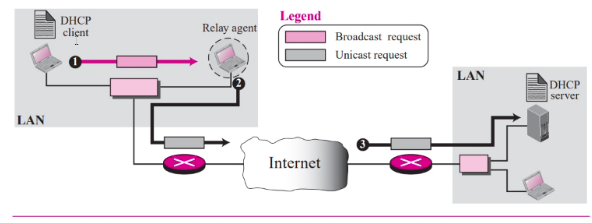
Different networks
- Broadcast to a relay agent which can be a router or host = Relay agents knows the unicast add of a DHCP server and listens for broadcast messageat port 67
- When recieve, it encapsulate the message in unicast datagrams and sends the request to the DHCP server
- The rest is the same
the reason why we use a standard port 68 because of demultiplexing issues
Error control
- Checksum: UDP uses this
- Retransmission policy: Retransmit if the timers runs out
Configuration
DHCP can be devsied to provide static allocation or dynamic address allocation
Static
- DHCP server has a database that statiscally binds physical address to IPaddress.
- Deprecated protocol BOOTP
Dynamic
- DHCP has second database with pool of ipaddress
- DHCP server provides requesting clients with ip addressing with its pool
- Check static
- Not exisst: Select and assign
- add entry
- This is temporary with a lease which is a time out
- can renew the lease
Transistion states
- DHCP client acts as a state machine that performs transmission from one state to another depending on the message it recieves.
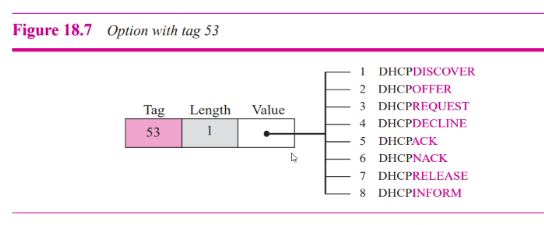
Option:
Init state
DHCPDiscover is broadcast by client
Selecting state
- Server response with DHCPOFFER
- Server locks
- Client recieve offer and choose
- Client sents the DHCPRequest
- If client never recieve anything (DHCPDISCOVER), it will send DHCPDICOVER 4 more time
Request State
- Client remains in requesting state until receiving a DHCPACK message from the server
- After receipt of DHCPACK, the client goes from BOUND state
Renewing state
- Client wait in this state until
- Recieve DHCPACK from server: Renew
- Doesnt receives ack and 87.5 time run out: Go back rebind state
Rebind state
- Client remain in this state until:
- Client recieves DHCPNACK: Init state
- Lease expires: Init state
- Recieve DHCPACK: Bound state and resets the timer
Other issues
Early release
- Client might release the time before it expires
- Client send DHCPRELEASE message to server
- Server release the ip and can assign to another client
Timer
- Timer percentage stage changes:
- Renewal
- Rebinding
- Expiration
- Server can specify the default value