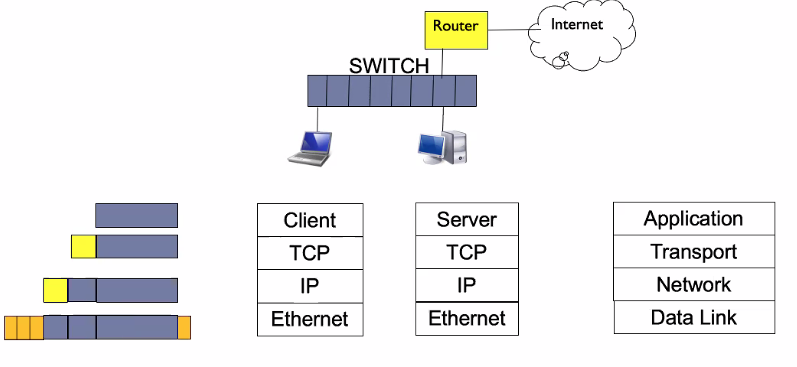
ARP - Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP REQUEST: Broadcast
- ARP REPLY: UNICAST
Motivation:
- Support hop to hop deliever
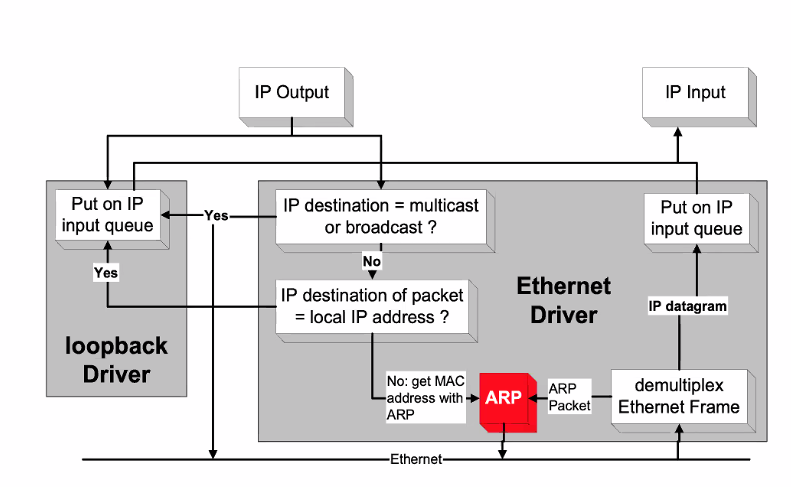
- Ip output send some packet out, it will then check if its multicast or broadcast
- Multicast/Broadcast: Put on ip input queue
- Not: Next step
- IP destination = Local IP?
- Yes: Put on IP queue
- No: Get mac address with ARP
- ARP
- Demux it: Knows it ipv4 or ipv6
- Sents to approporiate layer
- Put on input queue
Multicast must be registered to get the message but broadcast is already automatically sent no matter what
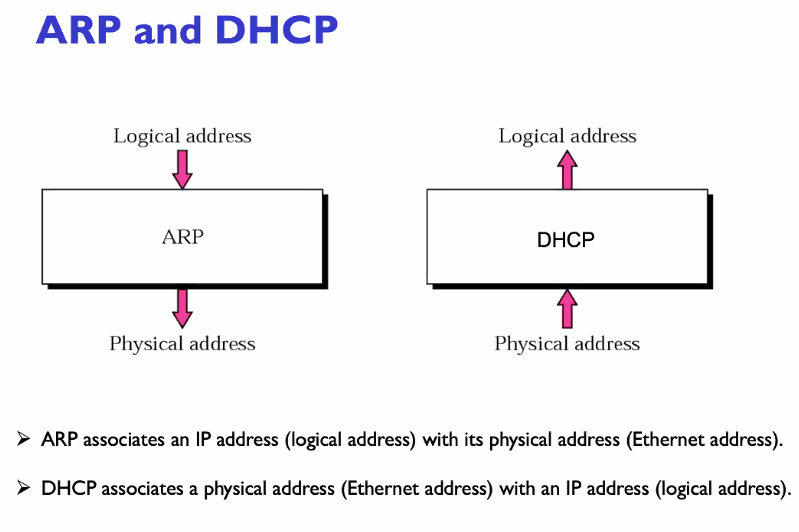
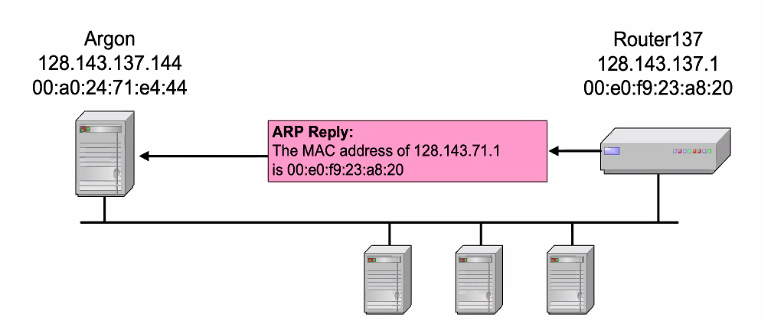
Address Translation with ARP
ARP Request: Broadcast
- Client would broadcast requesting for the MAC address of a node (ARP request)
ARP broadcast is restricted to within a LAN
ARP Reply: Unicast
- Node replies with the hardware MAC address
- Other nodes ignore
- client would store the MAC address in its cache
Arp cache contains address mapping for all host within a single LAN
ARP cache will go two ways
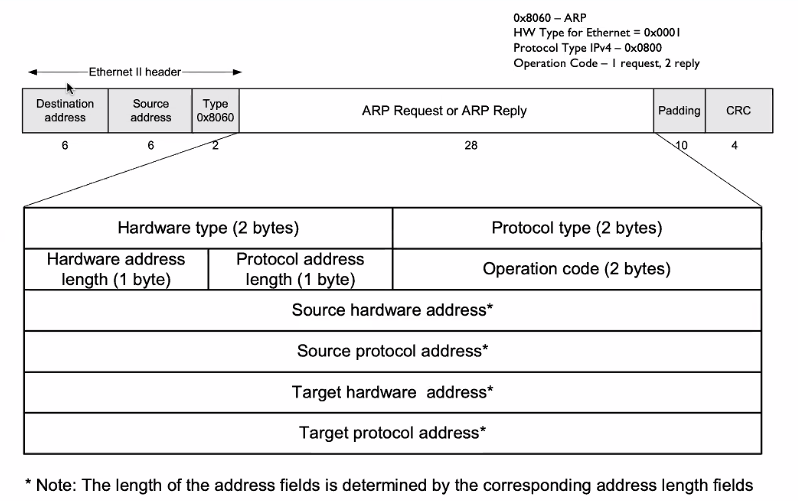
ARP Packet Format
- Hardware type: Mac layer type (Ethernet/Wireless LAN)
- Protocol type: IP layer type
- Operation code: Reply or request
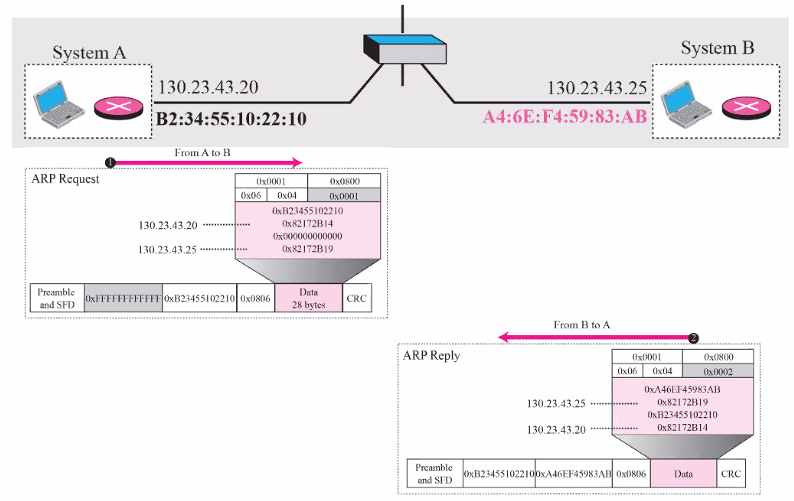
ARP Example
Note that if i dont know the reciever MAC, i would leave as 0
Question: If they broadcast and the destination is not for me, would I update the arp cache?
- Yes, only if I already have a exisiting entry, i will update else i will throw
Question: What is the purpose of having variable length address as Source/Target hardware address/Protocol
- For future expansion
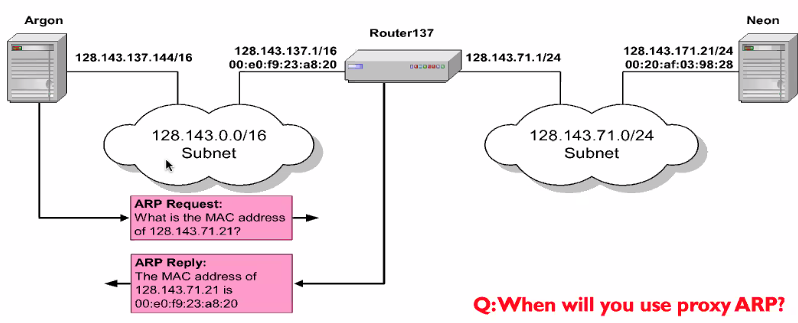
Proxy ARP
Host or router responds to ARP request that arrives from its connected networks for a host that is on another side of its connected networks
- Note how the return mac address is the router’s
Question: When will you use proxy arp?
- When we are moving the packet to another subnet, we can use a router as a proxy arp.
- It is also used as a short cut to connect two different networks without changing it.
Things to know about ARP
- What happens if an ARP request is made for a nonexisting host
- Time out
- ARP cache might refreshes and a host periodically sends ARP request for all address listed in ARP cache
- Gratuitous ARP request: A host sends an ARP request for its own IP address
- Check if its own IP address is assigned to somewhere else.. If it is, the other host will reply.
Vulnerabilities of ARP
- ARP does not authenticate request or replies, it can be forged
- ARP is stateless: It can be sent without a ARP request
- All nodes when recieves a IP address that already has an entry, it should update its cache with the infomation of its source field
ARP Poisoning, the arp cache is tainted with bad pairings
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Allows allocation of IP address from a pool
- Static: For router, servers
- Auto: indefinite time
- Dynamic: Specific duration, loans IP addresses for a limited time
It is a UDP base application
- Server waits on port 67
- Communicates on port 68
ARP vs DHCP
- DHCP: App Layer
- ARP: Network
DHCP is a application layer as it is design at a later stage at the application part thus it is consider to be in this layer
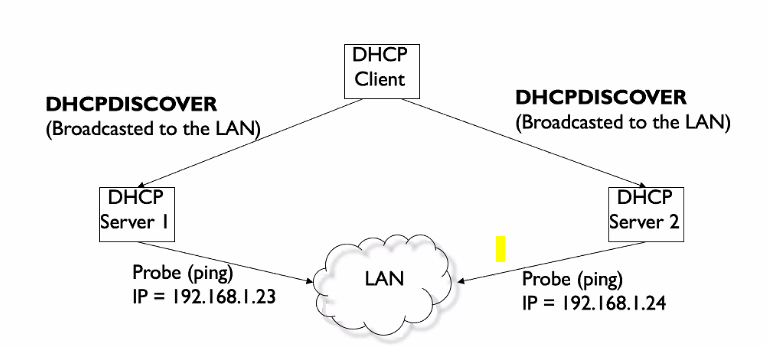
Client - Server Interaction
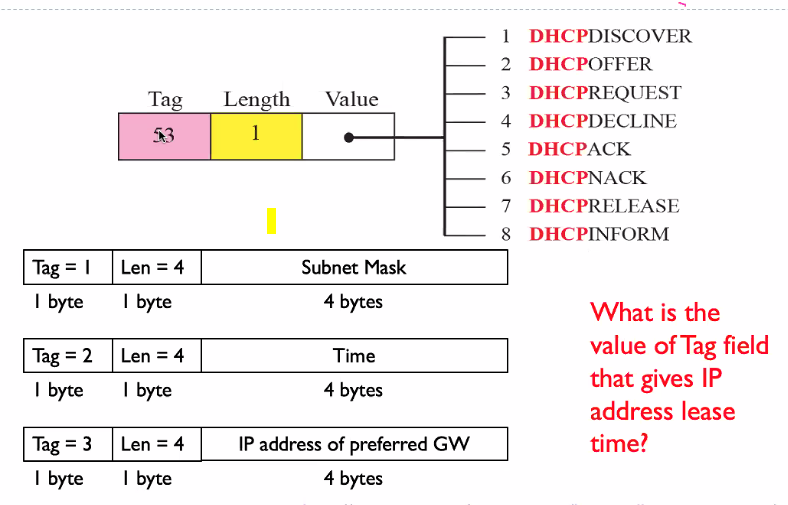
DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCP server will select some ip address to give to the client
Question: What is the use of the ping probe
- To check if the IP address is being used by other nodes
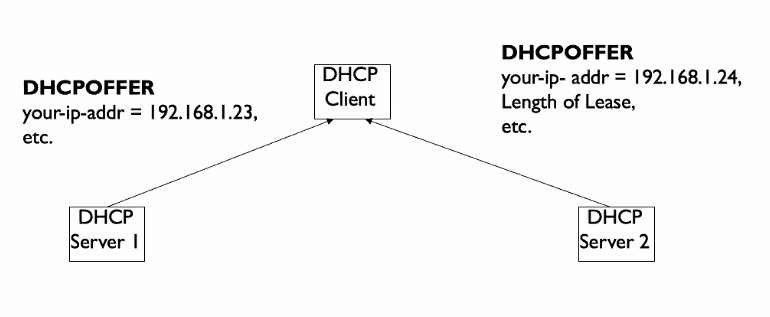
DHCPOFFER
- Broadcast: Nodes cannot participate if it does not have its IP layer configured (ipaddresa)
- Ip address
- How long use the client can use the address
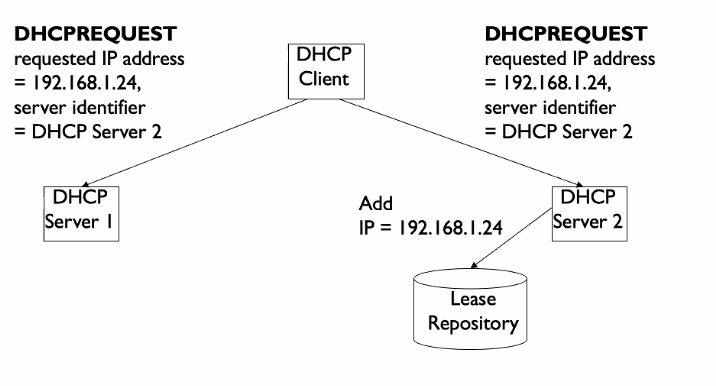
DHCPREQUEST
Question: Why is the request a broadcast?
- To let the other DHCP servers know that the IP address is taken
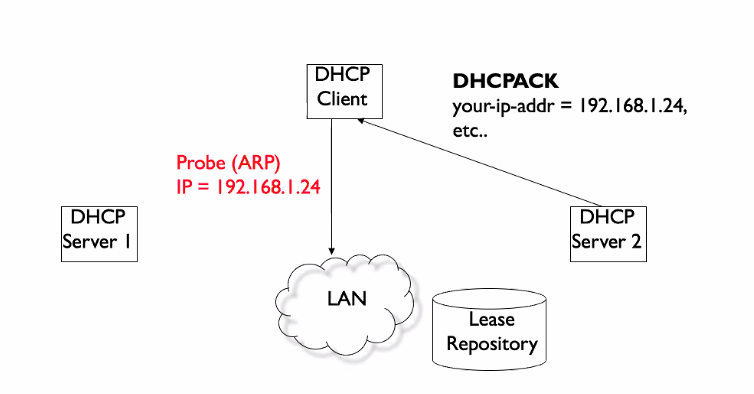
DHCPACK
- Send 3 arp request to the same IP address
- This is to check if the IP address is being used
- Gratituous ARP
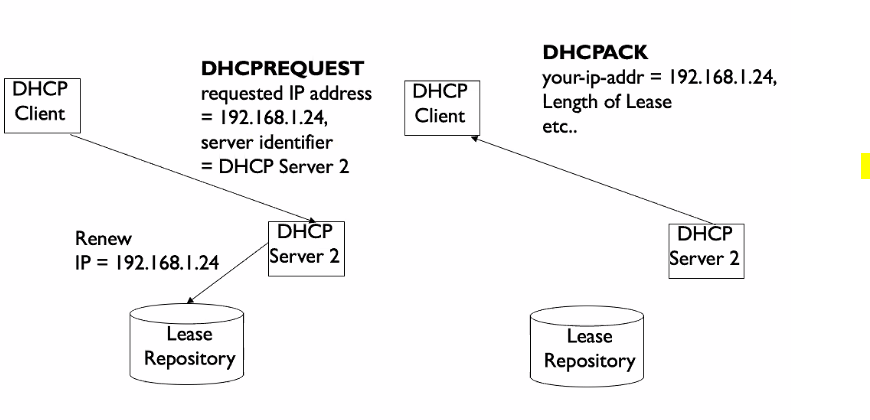
DHCP renew before lease
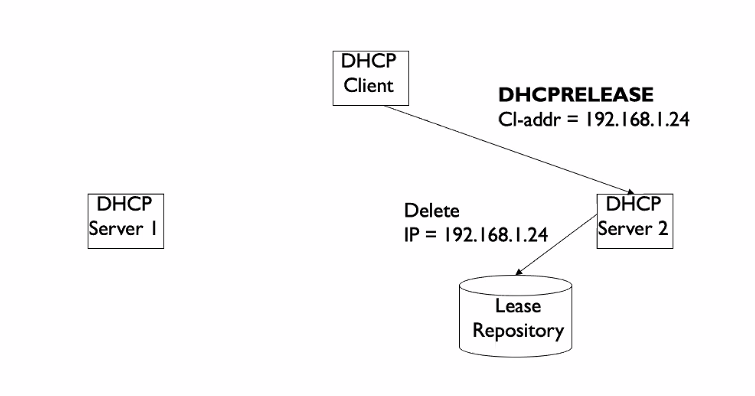
DHCP release
- When we shut down our laptop, not needing the ipaddress anymore
Typical TCP/IP info
- Subnet
- Netmask
- IP address
- Router
- Domain
- DNS#1
- DNS#2
- IPaddress
- Default gateway
- DNS server
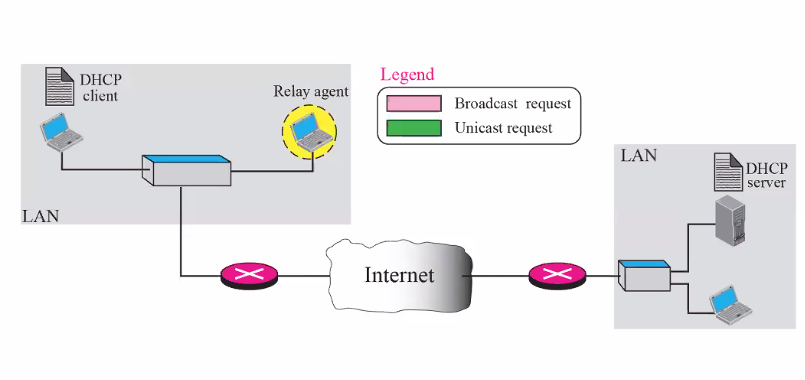
DHCP Discover and DCP request are broadcasted only on LAN/subnet. Does this mean we need one DHCP server for every IP subnet?
- No, we use relay
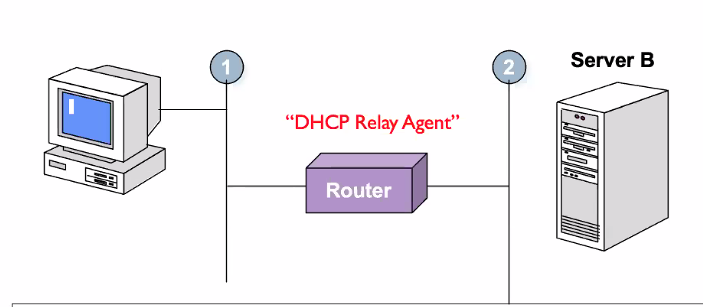
DHCP through Relay agent
- Any dhcp comes, it will be relayed to the other
- Router here acts as the relay
- Router run both client and server program, listen on port 67 and intercepts any dhcp discover messages and forwards (unicast) the request to one or more DHCP servers.
- Change router incoming IP address to its own in the router-address field
- increments hop count to 1
- DHCP server recognises this request is coming from router and not client
- Sends unicast reply to router
- router replies to client
Non-router
A relay agent can also be other nodes other than a router
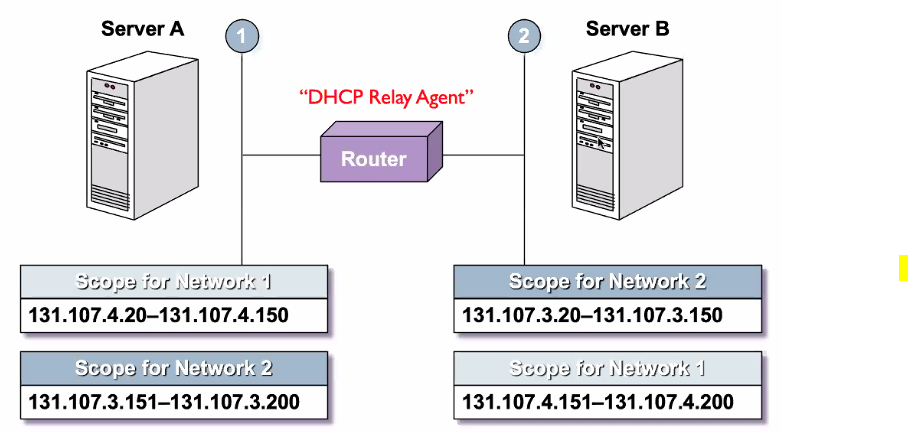
Implementing multiple DHCP servers
- Serves a specific network range
- this is for redundancy if there multiple
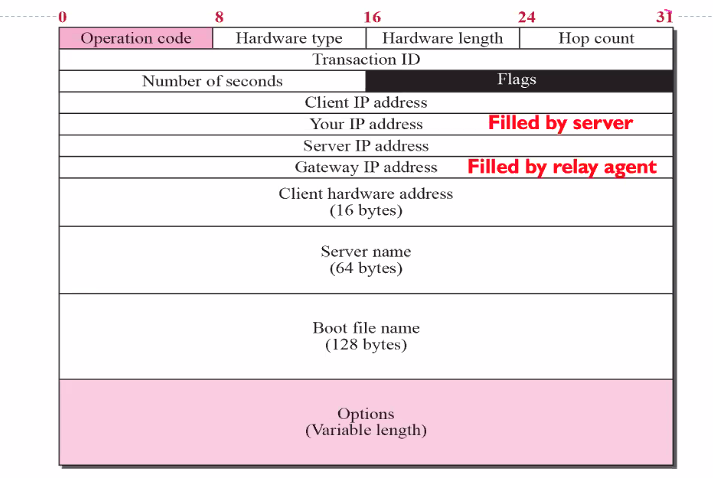
DHCP Packet format
- Hop count: Start from 0
- flags: Indicating broadcast
- Seconds: Number seconds since the client start to boot
- Gateway Ip address: for relay agent to put its ip address
- Field OP: Specifies if its request or reply
-
Htype and Hlen: Type of network hardware (ie ethernet)
- The client fill in much infomation and leave the rest with 0
Question: Why are there fields for client IP and your IP, when is it used?
- Client IP: When client renew its own ipaddress
- Server IP address: renewing, gateway might know the ipaddress
- Your IP: Filled by the server
Flag
- Unicast or broadcast: When the client cannot accept unicast (When it is not configured yet), it can ask the server to broadcast reply by setting this bit to 1
- The remaining bit is 0
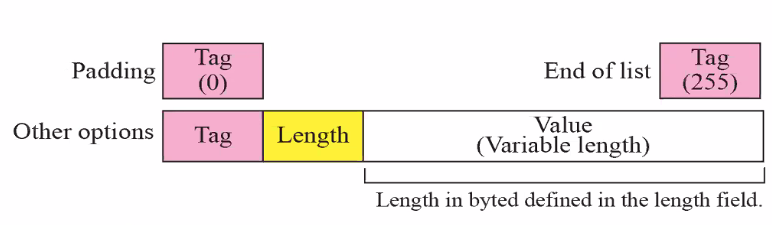
Option format
- Most used in reply message
-
Additional infomation sent to the client
- we can send things like subnet mask, default gateway etc..
- Tag = 0 : Use for padding purpose
- Tag = 255 : Indicates end of option list
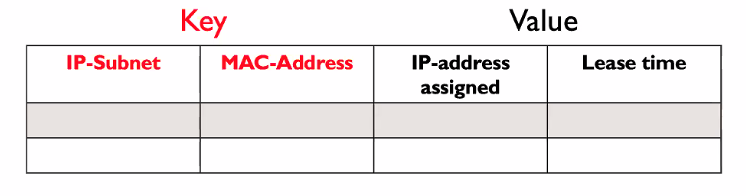
DHCP - server design
- Stores a key value pair for each client
- Key use to identify a client
-
Default key = (IP subnet number, hardware - address)
- Address conflict avoidance
- Servers choose the least recently used address
- Server should perform conflict detection using ICMP echo request (ping)
- Client shld probe before accepting the ip address
- Time value
- Time represents in seconds
- Time express in relation to clients clock
- Client lease expiration time = time when client sent DHCPREQUEST + Least duration in DHCPAck
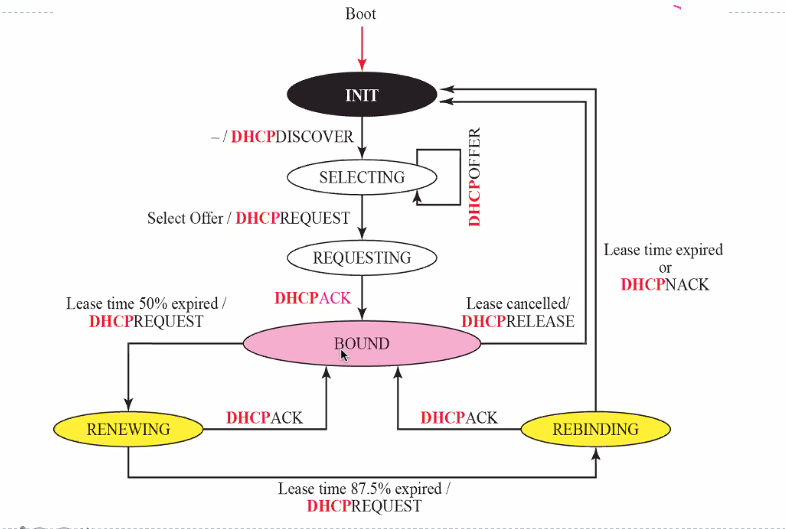
DHCP - Client Design (Transition diagram)
Timer Values:
- Renewal timer: PREREQUEST
- Rebinding timer: PREREQUEST
- Expiration timer
Why use DHCP? WHy not use MAC since its unique
- IP is hierieical
- Routing table would be huge
- MAC is manufacturer dependent, hence no grouping for routing
What is DHCP FORCERENEW? (sent by server)
- RFC 3203
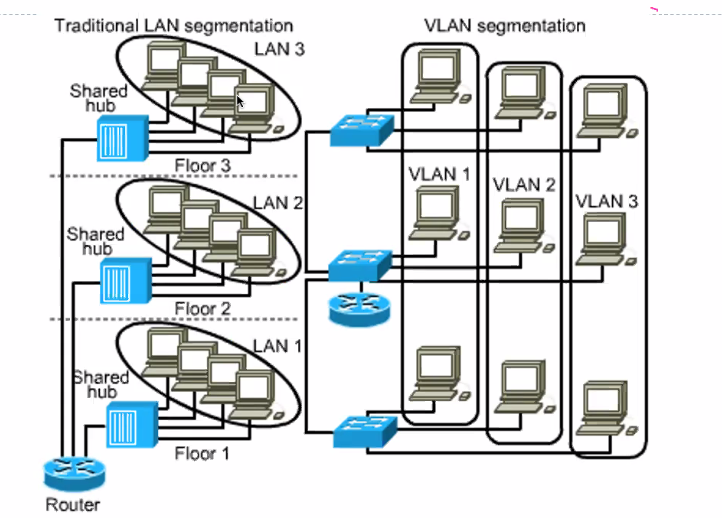
VLAN
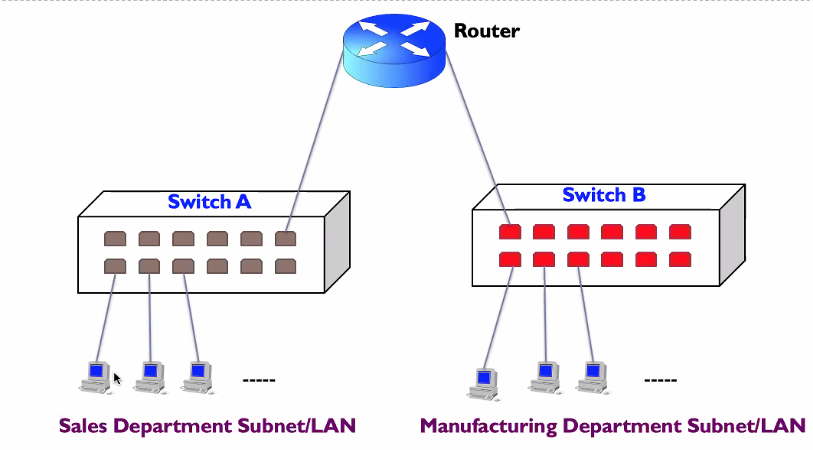
Motivation
- Two departments want to connect to each other, so we use a router
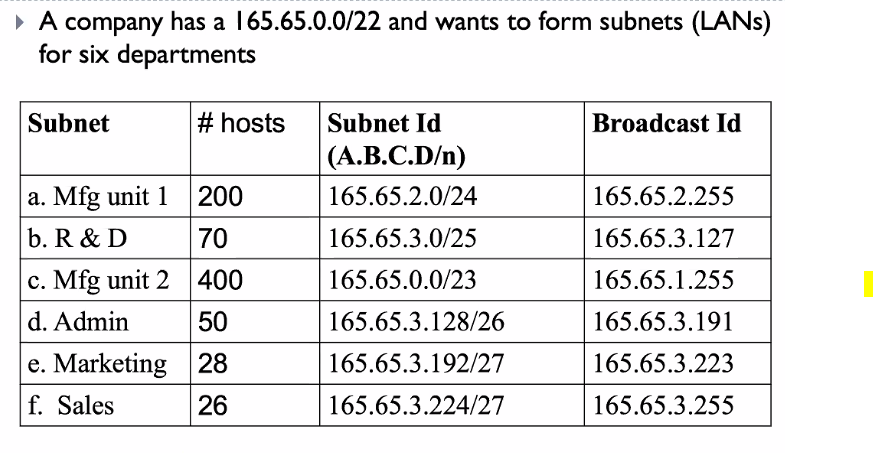
- We have this table
What would happen if the company want to increase the number of host?
If lets say we increase, we need to make more ipaddress for the new hosts. If (IPADDRESS blocks) wont be continous and very hard to manage
This archietecture is also very static, thus when someone wants to change to another subnet (change office location), it is very hard to change to the other subnet
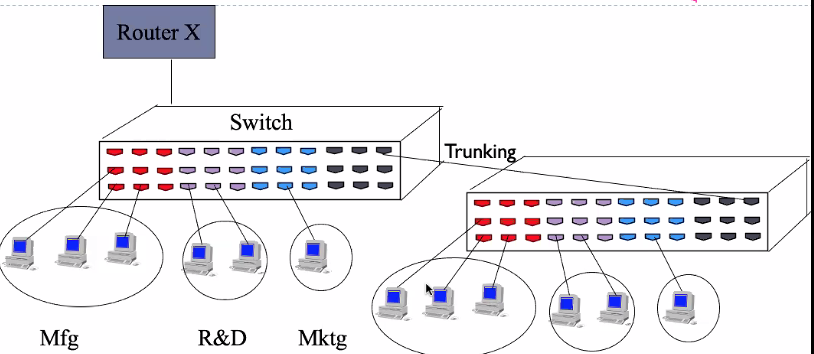
Example
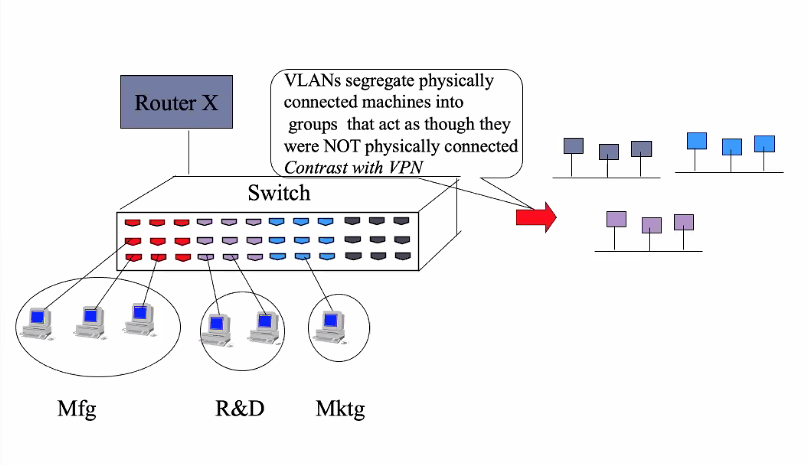
- Segment without physically being in the same network (Which is required by subnet)
- Facilitate easy administration
- Better security and improve performance
- Move anywhere easily and still be in the same VLAN
Switch when you can, route when you must
Vlan - In single switch
Lan VS VLAN
LAN/SUBNET:
- Lan is a broadcast domain under single switch
- Group based on switch/hub (physically)
- Traffic between LAN is routed using a router
VLAN:
- Broadcast domain created by one or more switches
- Group based on logical function, department or application
- 20 percent to 40 percent of work force moves every year
- Traffic can be routed between VLAN with a router
Communicating across networks still needs a router
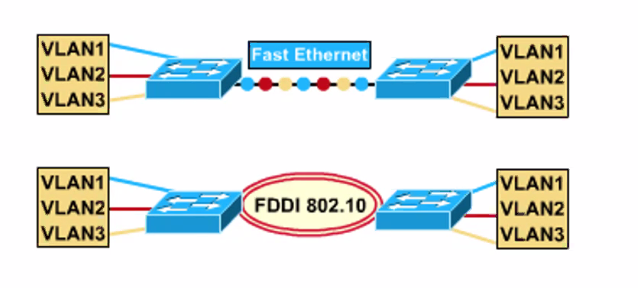
- Trunking is used for VLAN communication between switches
VLAN table and switching
- VLAN id
- Switch interface/port
Switchs maintain a bridging table or VLAN table for each VLAN.
Vlan across backbone
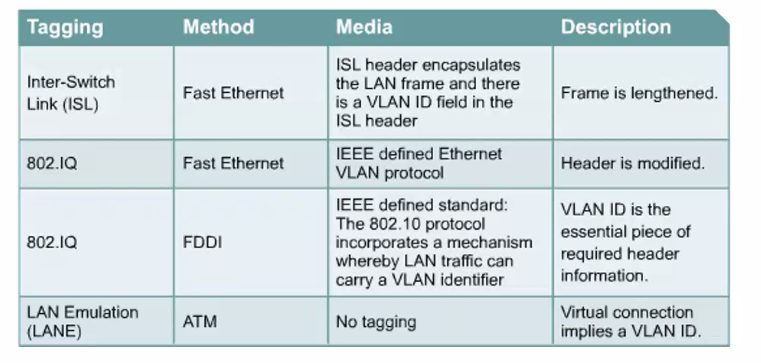
- Frame filtering: Examines particular infomaation about each frame (MAC address or layer 3 protocol type)
- Frame Tagging: Places a unique identifier in the header of each frame as it is being forwarded throughout the network backbone
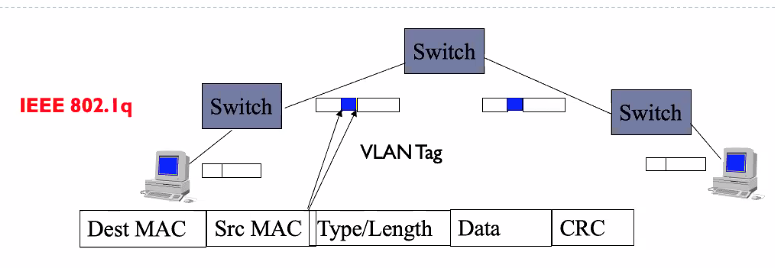
Frame Tagging
- First switch (Ingress) adds tag containing VLAN id to all incoming packets
- Intermediate switches do not recompute the VLAN id
- Last switch (Egress switch) removes tags from all outgoing packet
Vlan is only handled by the switches
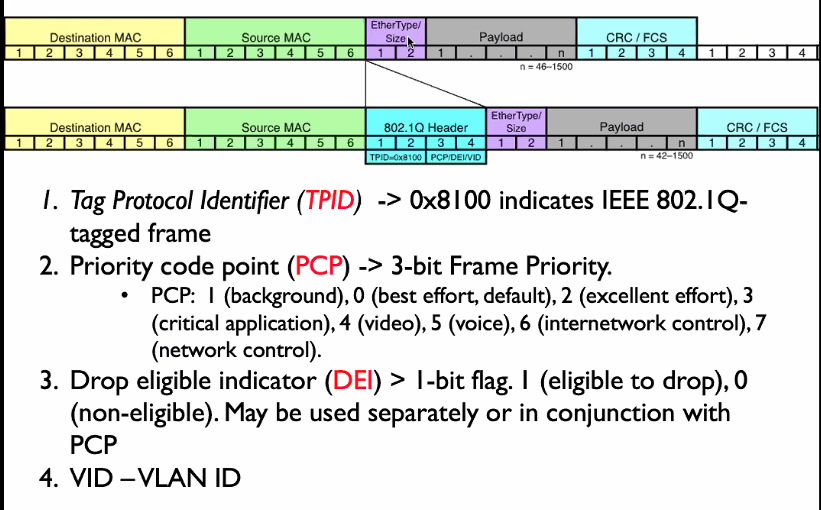
802.1q
- Ethertype: Tells what the payload is about and what type.. it is useful for decapsulating the packet.
- CRC: Error checking
PCP is the quality of service and tells the switches the priority of this frame. Drop indicater can be use in conjestion with the pcp to decide on the treatment of the frames. VID identify the VLAN
Sometimes there might be double tags.
VLAN Routing
Switches do not bridge traffic between different VLAN as this violates the integrity of the VLAN braodcast domain.
- Traffic must be routed between VLAN
- Routers can be use to route emails to other clients on other vlan
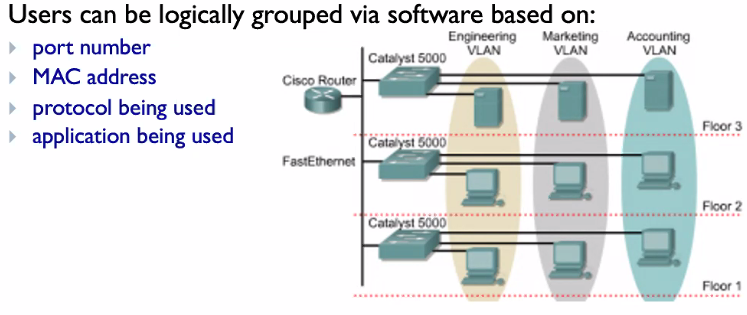
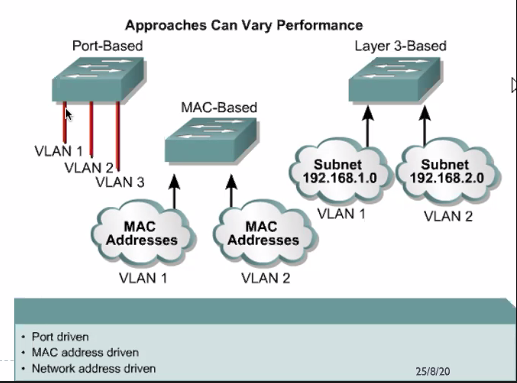
VLAN implementation
Methods in implementing Vlan:
- Static: Port centric or port based
- Dyn: Mac address based or Layer 3 protocol based
They will classify the different address based on different things. Ie Similiar mac address will be connected to VLAN 1
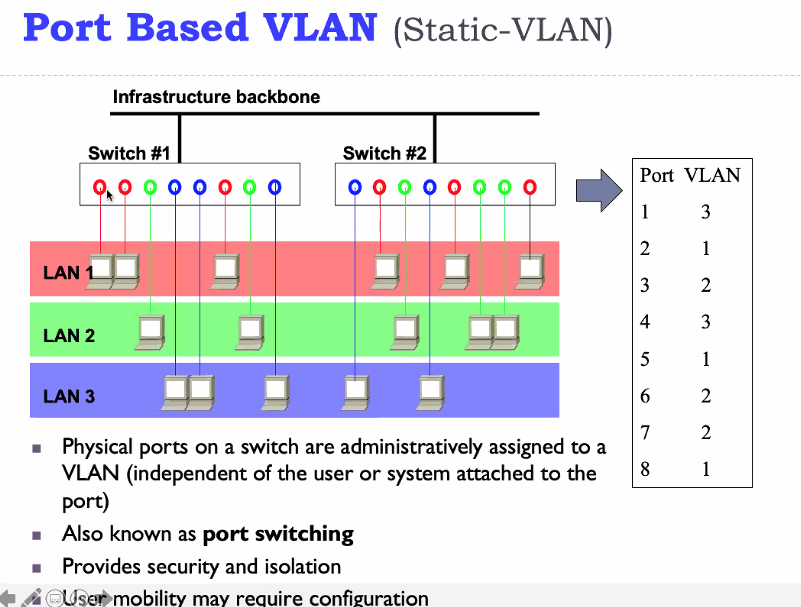
Port Centric VLAN (Static)
Disadvantages:
- Need to label the switches
The default VLAN for every port in the switch is the management VLAN. The management is always VLAN 1 and may not be deleted. All ports on the switch may be reassigned to alternate VLANS
Benefits:
- easy configure
- Easy moniter
Probelm:
- User movement in the network shld be controlled
With a router, we can connect two pc with differnet subnets
Configuring using CLI

A trunk is a point-to-point link between two switches or between switches and routers. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple (all) VLANs found in a switch to another switch.
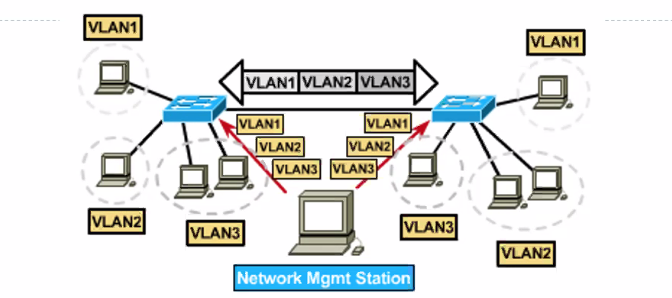
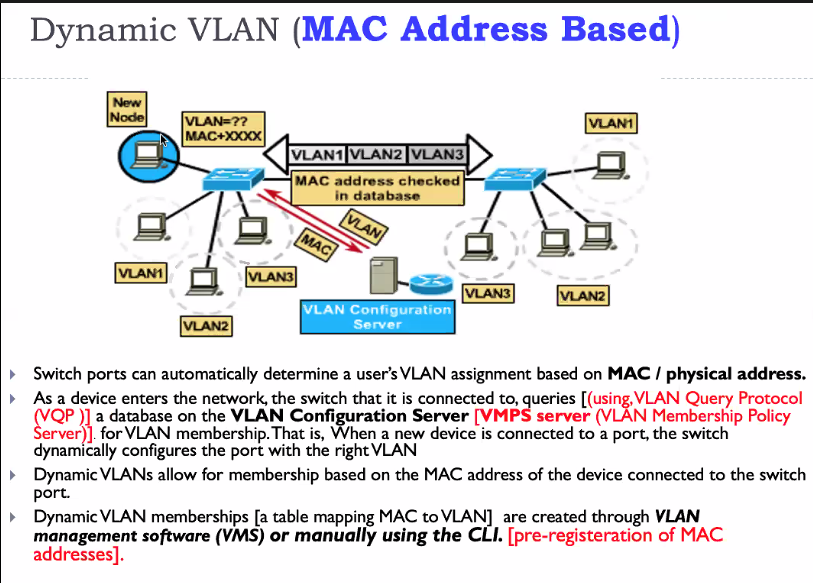
Dynamic VLAN
MAC address Based
- Switch port auto determins a user vlan assignmenent based on MAC address
- LAN defined by list of MAC address
- Centralised database
- Every switch will have the database
- Provides full user movement
- Client and servers always on the same VLAN
- Requires computers to be preregister
Problems: Too many address needs to be managed
We can manage the database by using CLI or some datamanagement software that comes with it
- Connect to a port
- Send some Packet to the switch
- Switch sees the packet and will know the MAC address. queries the configuration server
- Server returns the VLAN ID
- Switch will store the mapping of the VLAN ID
This mapping stays until the device is disconnected
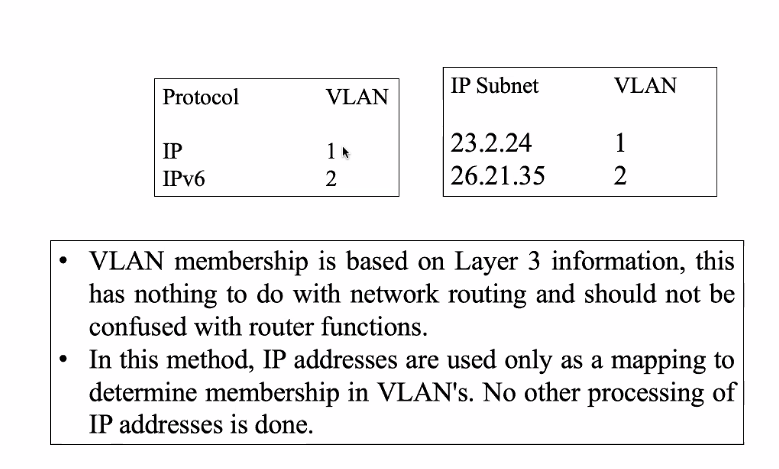
Layer-3 Based Dynamic Vlan
- Vlan membership implied by MAC layer protocol type field and subnet field
- IP address only used in as mapping to determine the membership
- VLAN config is learn by switches
- Stations do not belong to VLAN, packets do
- Multiprotocol station are put intp multiple VLAN
Manage VLAN network wide
- VLAN trunking protocol: Layer 2, maintains VLAN configuration consistency by managing the addition, deletion and renaming of VLANs. This protocol helps synchronise the database
- A VTP domain: (also called a VLAN management domain) is made up of one or more network devices that share the same VTP domain name and that are interconnected with trunks.
- Switches can be VTP server or client or VTP transparent mode
- VTP server mode: can modify the database
- If its a client, it can only read but not change
- VTP transparent switches do not participate in VTP but do forward VTP advertisment recieved through their trunk ports
Question: Is VTP server same as VMPS (VLAN Membership server?
- VMPS server can be implemented anywhere, it is just a database software that stores the mapping of the MAC address to the VLAN
- VTP on the other hand, is use to synhronise the data
Does it work with same vlan but differnet subnet but with router?
- Check in the lab
Questions to ponder:
- What is the highest VLAN number : 2^12 = 4090 (12 bits in ethernet frame)
- What is the max vlan per VTP domain
- What is VxLan?
- What is SDN (Software defined networking)
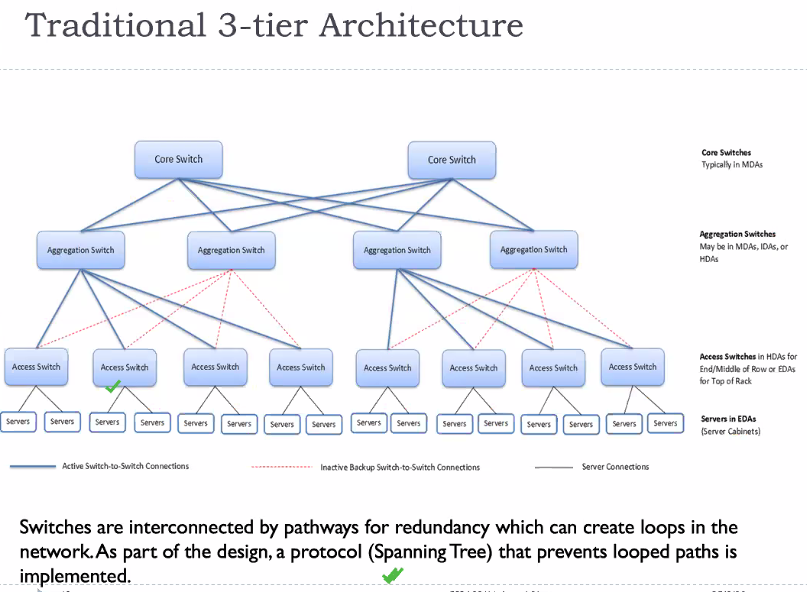
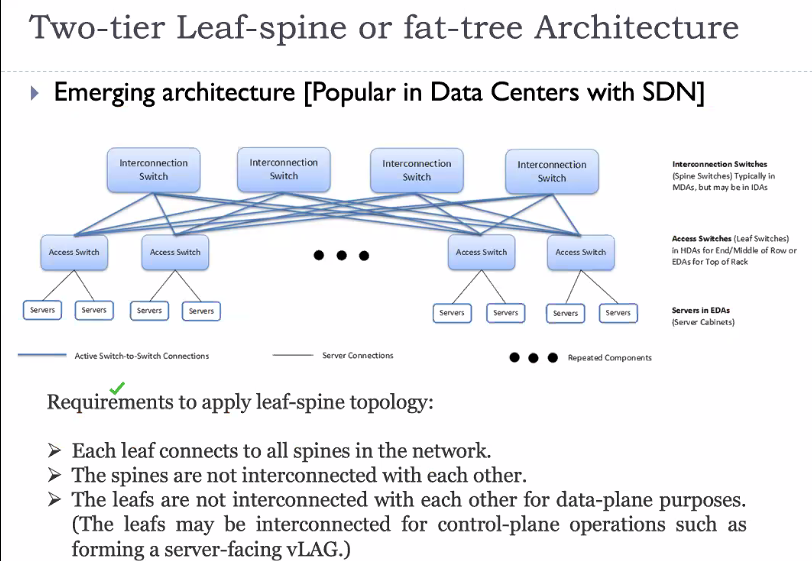
- What is leaf spine architecture? Compare 3 tier architecture vs leaf spine architecture
4090 switches are not really enough for large cloud datacenter database. There are millions and miliions of VM and many of these VM belongs to diffrent companies that want to be in different VLAN.
Architecture:
Most common architecture:
- The spine acts as a backbone
- Normally the leaf switches do not transfer data between each other only sometimes
- The transfer is mostly through the backbone