Internet of things
Thing + Computer intelligence + connection to internet
Architecture
- Embedded system (Things)
- Node devices (THings) collect data through sensors
- Data is sent to the internet through the gateway
- Data analytics takes place in cloud or data center
These things may not have connection to the internet, thus it needs to connect to a computer system (Gateway) whcih are considered as edge (of internet)
Understanding IOT Data
Important:
- Power management
- security
- Data conversion
Data:
- Too big
- Too fast: Data streaming and often processed in real-time
- Too diverse: Different types of data types (Image data, heart rate data)
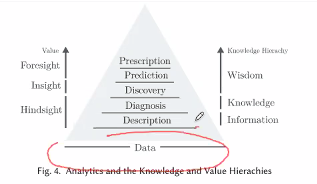
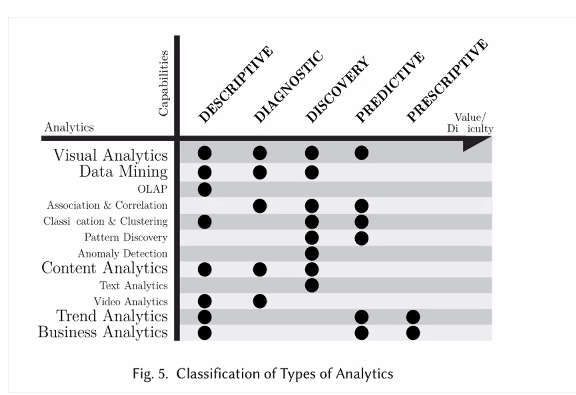
Ways to understand data:
- Descriptive: “What happen”, summarises/presents the raw IoT data
- Diagnostics: Look and understand the process that is causing the data (ML)
- Discovery: Find patterns that we did not notice earlier, explain those patterns (Event)
Marketing found that epoeple in the eastern part of singapore prefer a particular brand of shampoo compared to those of the west. (Pattern)
- Predictive: Use data and answer the question of what is going happen next
- Prescriptive: Find a solution to the predictive analysis
Unlike the 3 prev tech, these are foresight techniques as we try to guess what to do in the future
Machine learning
- Present the machine with alot of data
- Machine learns on its own to recognise patterns in the data
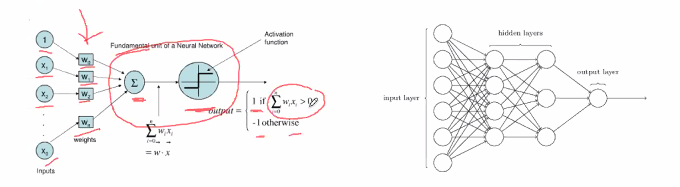
Neural Networks
- Dense networks
- “Neurons” are computational unit called nodes
- Neurons fires a 1 if the sum exceeds a treshold through an activation function (Step function)
Learning laws: To give labels to figure out the meaning of the weights
Deep learning
Problems with neural
- Adjust the parameters according to a learning law based on data given
- Need large number of parameters to learn highly complex tasks
- Curse of dimensionality
- The number of parameters increases, the number of training data required grows exponentially
- Neural network “Overfits” - it memroises the data it is presented instead of learning from it. Good results for data that is use for training but bad for any other data
What about deep?
- Simplify the data
- Extract features
- Make data invariant
- Shift invariance
- Scale invariance
To remove unneccessary data
Note that deep learning is part of neural
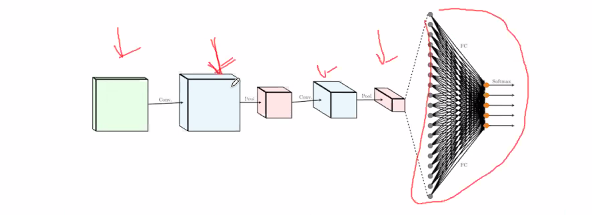
Convolutional neural networks
- Kernal layer: Small window scan over image
- Pooling layer: Summarise previous convolution layer to ease learning
- Dropout layer: randomly drop info frm prev layer to prevent overfitting of training data
- Dense layer: Classify based on simpify data
Kernal
Take many filters and scan over the image to produce activation maps
Apply fucntion to introduce non-linearity
In a neural networks, linear results are very bad (ax+b), thus we insert function to make it not linear
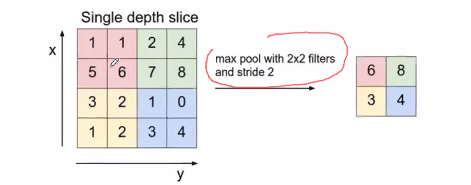
Pooling
-
Pick the max number within the window
- Reduce the data produce
- Remove the unnecessary data to remove noise
The distance the pooling window moves is called a stride
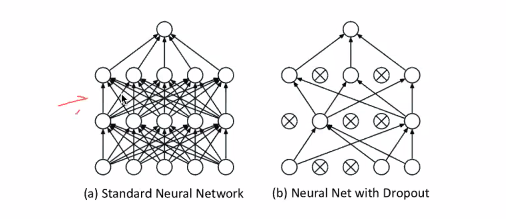
Dropout
- Prevent CNN from memorising the data
- Choose some to deactivate = Remove weights = require less data to train
- Nodes might be reinserted again
Dense layer
- Look at the summarised maps
-
Make a classifcation
- Each layer we will get a more abstract view of what is in the image. This help us simplify the image such that we can learn the data without many parameters
We can see a more abstract version of the image, the abstract view is the thing that enables it to recognise the image without too many data
How deep learning is used in IoT
- Sensor gather data
- Deep learning and analytics can be put on this data
- Try to predict the future base on the data