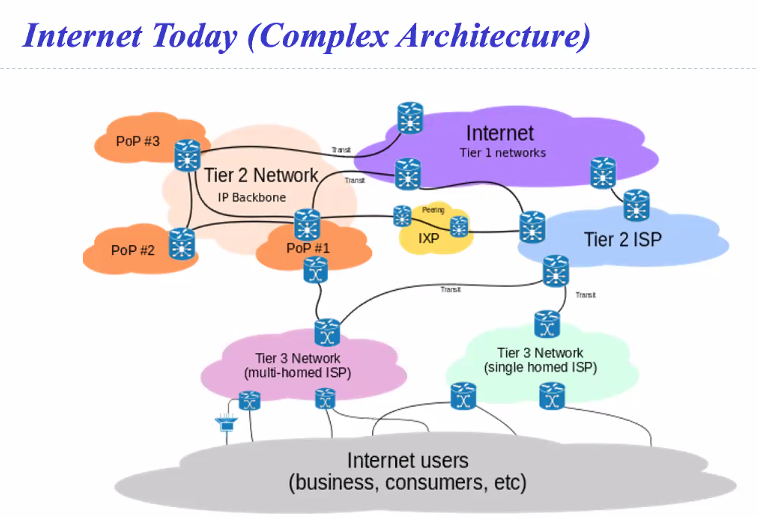
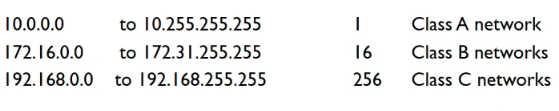Internet Today
- IXP : Internet exchange provider
- PoP: Point of presence
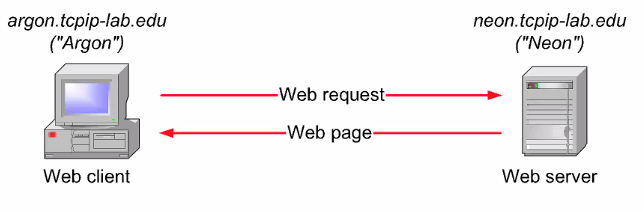
A simple TCP/IP Example
The web client wants to access this web server through the web url.
HTTP Client/server communication
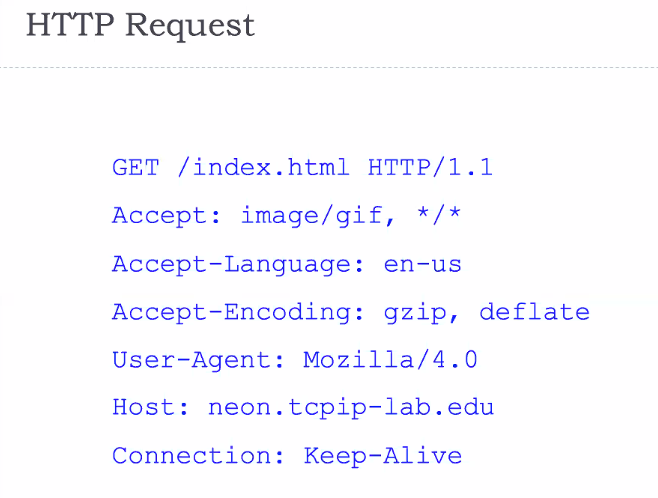
Http request:
The web server will send a response with 200 OK
To send the http, it needs to establish a tcp connection.
Does the TCP work with hostnames?
- Recall TCP Header, there is no place for hostname.. only for ipaddress and port number
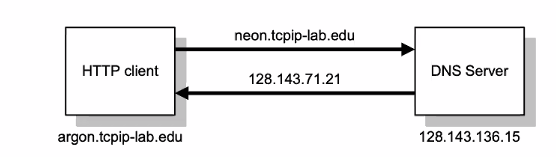
The url is translated into a 32 bit ip address using a database lookup to a DNS Server.
However, there is no mechanism for port number querying, but some port number are default. (e.g http = 80)
Invoking the IP protocol
- Send the datagram to the ip address
- Dtagram have the connection infomation
- port
- http
- IP address
Sending the ip datagram to an ip router
- Sometiems the clients are in different subnets
- It will only know if it is in the same network or not
- Send the IP datagrame to its default gateway (router)
- This gateway is configured when it is first set up (manually or through dhcp)
Finding the MAC address of the gateway
This is for ethernet
- Translate the ip address to mac address
- ARP protocol
- Does a broadcast
- The intended recipient of the query shld reply their mac address
Recieve at the router
- It wil send up the level until it reaches the application level
-
Ethernet driver knows the content is an IP packet from the header (l2 frame header, ie Ethernet frame type)
- Sends the frame to the server using the mac address
Data has arrived at server
- Payload of the IP datagram is passed to the IP protocol
- The payload of the IP datagrame is a TCP segment
How does the ip module knows that the content is a tcp segment
- header protocol field 1byte
Since the TCP segment is a connection request (SYN), the TCP protocol does not pass data to the http program for this packet. Instead the tcp protocol at neon will response with a syn segment to argon
Conclusion
- The server only receive on packet {TCP-SYN}
- TCP connection takes up more work then the HTTP request
- Simplified
- Transmission error
- One router
- Client knows how to connect to DNS
Internet Address
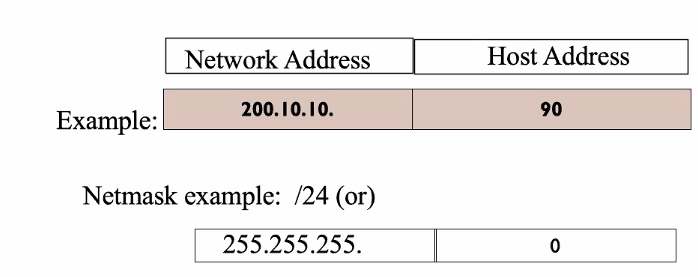
- Each Ipaddress is a pair (Netid, hostid)
How many bits for network and host
- Based on network mask
Special address
- First and last: Reserved and not assign
- First: Netowrk indentification
- last: Broadcast address
- Netowkr part all zeros: the host on this netowrks
- Host past all ones: Direct broadcast address
The boradcast have limited else the whole internet would be flooded
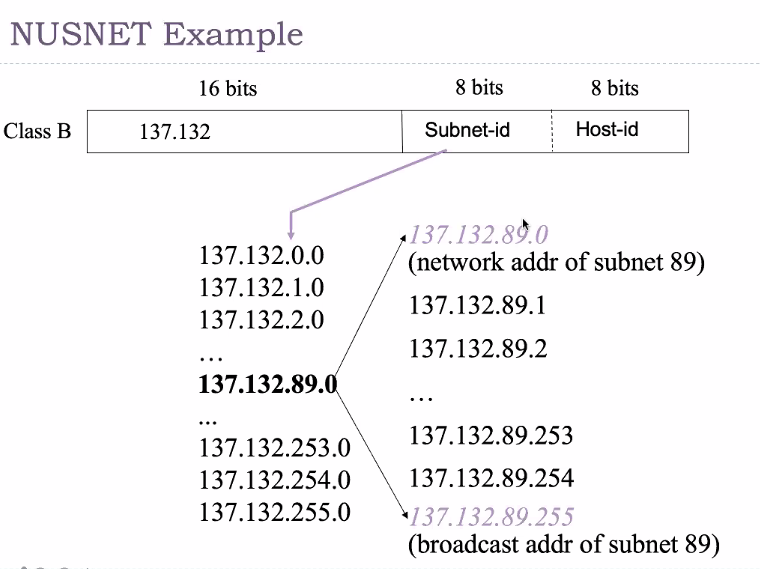
Ip subnet addressing
- Organisation owning laarge address blocks have too many host on a single networks
- Thus we might divide
Reason:
- Less congestion
- Secure
The number of available assignment in this subnet is 256-2 = 254
Within each subnet, the first and last of the block cannot be used as well.
We are using switch networks thus there is no need to worry about seperate collision domains
Supernetting
- Class C is too small for many organisation and companies
- CIDR also allows
- merging small networks like CLass C networks into a larger network with single prefix
Problem with small address block
- There might be alot of small address, routing table will explode
Thus we use supernetting such that the routing table can group the entire subnet as one
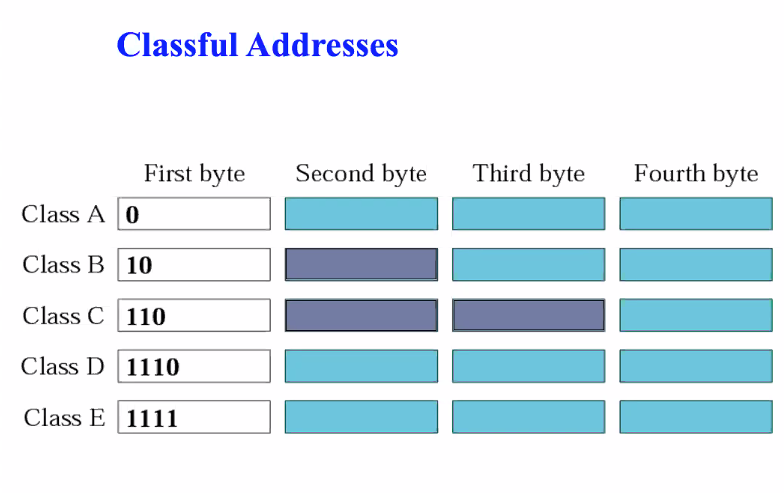
Classless addressing
- Classful address deals with a few fix class of predic lengths
Sol:
- classless addressing deals with any prefix length of any size
- Each subnet can potentially have variable length subnet mask
- Another approach is through the use of NAT and private IP address
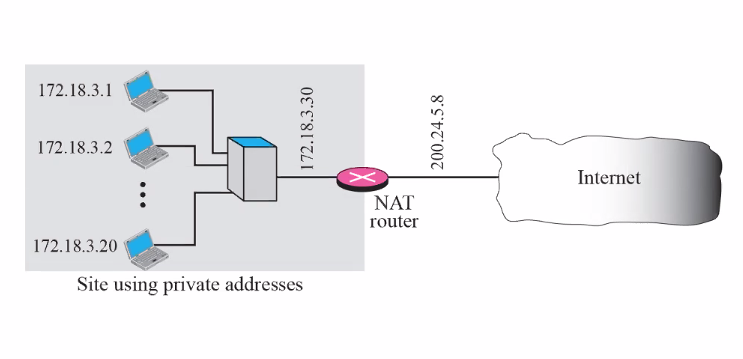
Private IP address
- Not gloabbaly routable
- Available freely
- Use: For private use within homes etc
Ip address networking
- The first and last network address in the block are not to be use
Private IP address
- Not routed global
- Does not have to be unique among other private ip but need to be unqique among its own
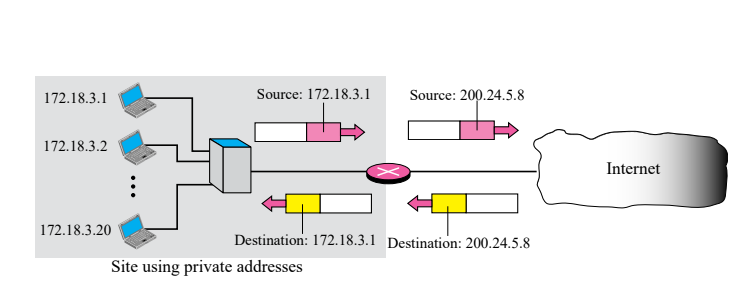
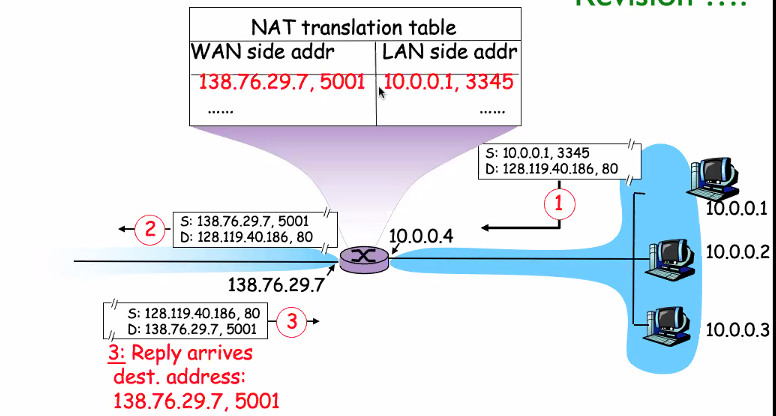
NAT
To route the private ip address to the internet. The router will swap the source of the outgoing packet and swap the destination of the incoming packet.
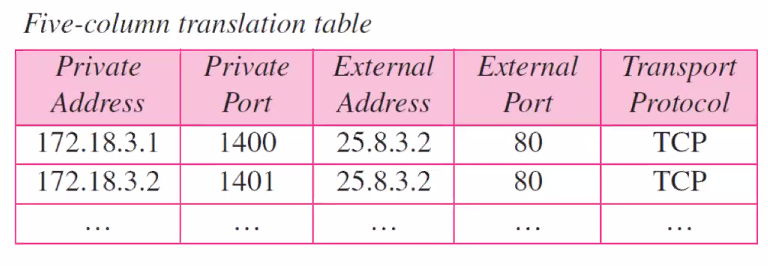
LAN manages the simple table, the table shows the WAN side address and LAN side address.